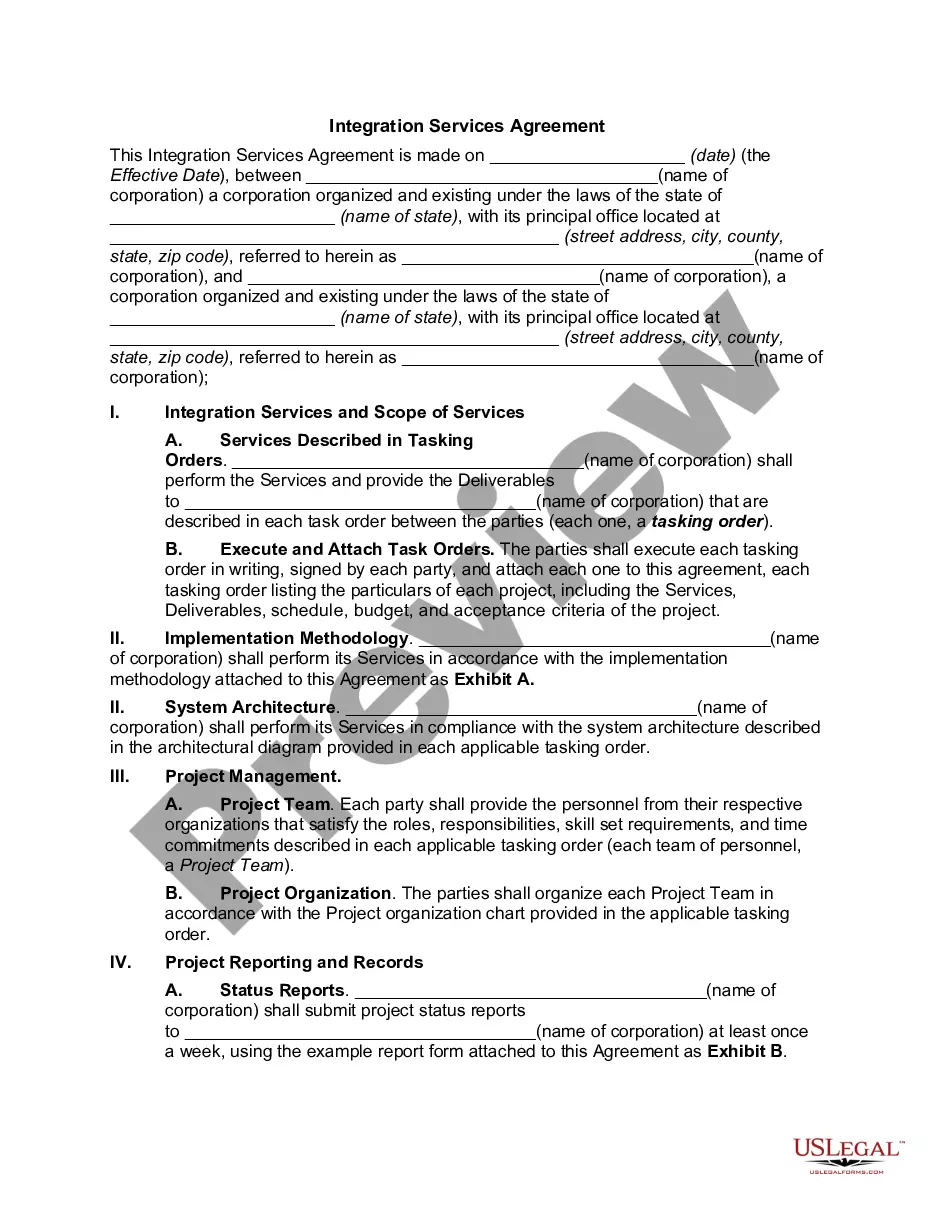
The Governing Law form, the provisions of this assignment relating specifically to title to real property that, due to applicable law, must be governed by the law of the jurisdiction in which the real property is located, shall be governed by the laws of such jurisdiction.
Kentucky Governing Law
Description
How to fill out Governing Law?
If you wish to comprehensive, acquire, or printing legal record web templates, use US Legal Forms, the largest assortment of legal varieties, which can be found on the web. Use the site`s easy and handy look for to obtain the papers you need. Various web templates for company and individual reasons are categorized by categories and suggests, or keywords and phrases. Use US Legal Forms to obtain the Kentucky Governing Law within a couple of mouse clicks.
If you are presently a US Legal Forms customer, log in for your bank account and click on the Obtain switch to obtain the Kentucky Governing Law. You may also entry varieties you previously delivered electronically inside the My Forms tab of your respective bank account.
Should you use US Legal Forms initially, follow the instructions listed below:
- Step 1. Be sure you have selected the shape to the correct metropolis/nation.
- Step 2. Use the Preview solution to check out the form`s content material. Never forget to read the explanation.
- Step 3. If you are not happy using the develop, utilize the Lookup field at the top of the display to find other variations from the legal develop design.
- Step 4. Upon having found the shape you need, click the Acquire now switch. Select the prices prepare you choose and add your qualifications to sign up for an bank account.
- Step 5. Method the purchase. You can utilize your charge card or PayPal bank account to complete the purchase.
- Step 6. Choose the format from the legal develop and acquire it in your gadget.
- Step 7. Complete, edit and printing or indication the Kentucky Governing Law.
Every legal record design you acquire is yours eternally. You have acces to each develop you delivered electronically inside your acccount. Go through the My Forms area and pick a develop to printing or acquire yet again.
Remain competitive and acquire, and printing the Kentucky Governing Law with US Legal Forms. There are thousands of professional and condition-certain varieties you may use for your personal company or individual needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
Section 525.060 - Disorderly conduct in the second degree (1) A person is guilty of disorderly conduct in the second degree when in a public place and with intent to cause public inconvenience, annoyance, or alarm, or wantonly creating a risk thereof, he: (a) Engages in fighting or in violent, tumultuous, or ...
The State Law Library of Kentucky has a long tradition of meeting the legal research and reference needs of Kentucky judges, state legislators, public officials and citizens. The library offers access to electronic legal services and also houses an extensive collection of print materials and historical documents.
The Kentucky Revised Statutes enacted in 1942 were primarily the result of six years of labor by the Statute Committee of 1936 and its editorial staff, whose work focused on eliminating from the accumulation of seventy years of legislation those provisions no longer in force or effect, and restating and compiling the ...
The Kentucky Civil Rights Act (KRS Chapter 344) defines DISCRIMINATION as any direct or indirect act or practice of exclusion, distinction, restriction, segregation, limitation, refusal, denial, or any other act or practice of differentiation or preference in the treatment of a person or persons, or the aiding, ...
A citation to the KRS will be in one of the following formats: KRS § Section. For example: KRS § 417.240. Ky. Rev. Stat. Ann. § Section (Publisher Year) Ky. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 417.240 (Michie 1996)
Under the Kentucky Civil Rights Act and the ADA, you have a disability if you have a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits a major life activity. You are also protected if you have a history of such a disability, or if an employer perceives you as having a disability, even if you don't.
The Kentucky Revised Statutes is a subject-based statutory compilation using a decimal numbering system. The broadest subject grouping in the KRS is called a "title"; titles are made up of smaller subject units called "chapters." Chapters contain sections of the KRS, the individual laws.