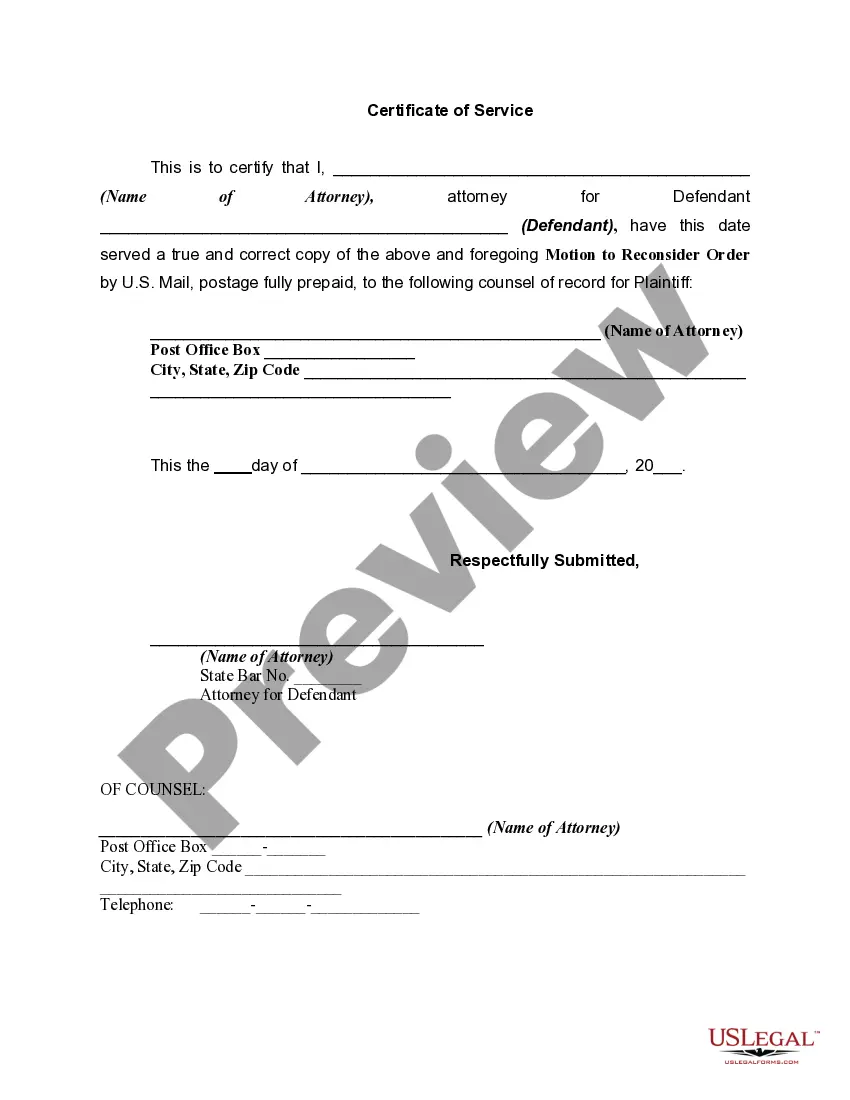
US Legal Forms - one of several largest libraries of lawful varieties in America - delivers an array of lawful file templates you can acquire or print out. While using site, you can get thousands of varieties for enterprise and personal functions, categorized by types, says, or search phrases.You can get the newest models of varieties such as the Louisiana Motion of Defendant Requesting Court to Reconsider an Order and Notice of Motion to Plaintiff in seconds.
If you already have a subscription, log in and acquire Louisiana Motion of Defendant Requesting Court to Reconsider an Order and Notice of Motion to Plaintiff through the US Legal Forms library. The Down load button will show up on every type you view. You gain access to all earlier acquired varieties in the My Forms tab of the bank account.
In order to use US Legal Forms initially, listed below are straightforward directions to obtain started off:
- Be sure to have chosen the best type for your personal metropolis/county. Select the Review button to check the form`s articles. See the type explanation to ensure that you have chosen the correct type.
- In case the type doesn`t satisfy your needs, take advantage of the Look for industry near the top of the screen to obtain the the one that does.
- Should you be satisfied with the form, verify your choice by simply clicking the Buy now button. Then, pick the rates prepare you want and give your credentials to sign up for the bank account.
- Process the purchase. Use your charge card or PayPal bank account to finish the purchase.
- Choose the format and acquire the form on your product.
- Make changes. Fill out, edit and print out and indication the acquired Louisiana Motion of Defendant Requesting Court to Reconsider an Order and Notice of Motion to Plaintiff.
Every single format you added to your money does not have an expiration particular date and it is your own property for a long time. So, if you wish to acquire or print out one more backup, just visit the My Forms section and click on in the type you will need.
Obtain access to the Louisiana Motion of Defendant Requesting Court to Reconsider an Order and Notice of Motion to Plaintiff with US Legal Forms, by far the most substantial library of lawful file templates. Use thousands of professional and condition-specific templates that satisfy your company or personal requires and needs.