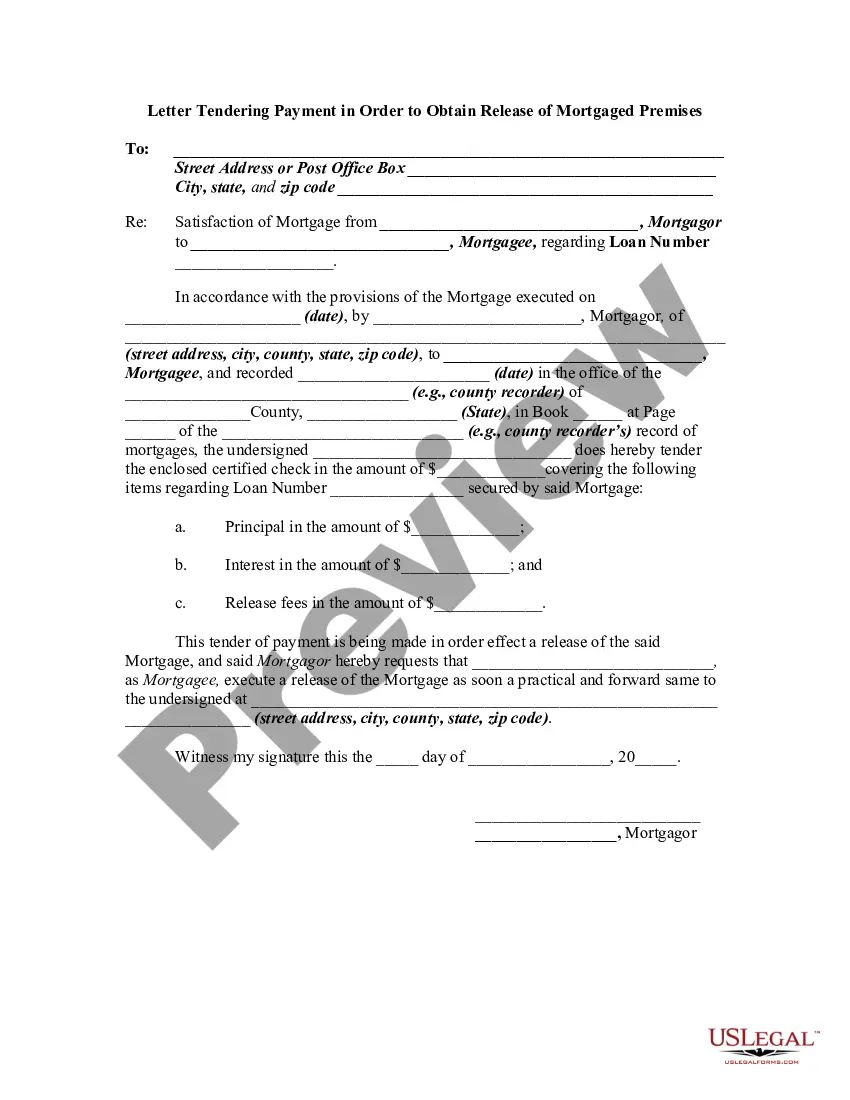
This form provides boilerplate contract clauses that designate the rights of parties to appoint an Indemnitor Representative and outlines such representative's powers and obligations under the contract.
Louisiana Indemnity Provisions - Parties to the Indemnity
Description
How to fill out Indemnity Provisions - Parties To The Indemnity?
Discovering the right legal papers template can be quite a have a problem. Needless to say, there are plenty of layouts accessible on the Internet, but how do you find the legal develop you require? Make use of the US Legal Forms site. The services provides 1000s of layouts, such as the Louisiana Indemnity Provisions - Parties to the Indemnity, that you can use for organization and personal requirements. Each of the kinds are checked by specialists and fulfill federal and state needs.
When you are previously listed, log in in your accounts and then click the Down load switch to find the Louisiana Indemnity Provisions - Parties to the Indemnity. Utilize your accounts to check from the legal kinds you may have bought formerly. Proceed to the My Forms tab of your accounts and have an additional copy of the papers you require.
When you are a fresh end user of US Legal Forms, listed below are easy directions so that you can follow:
- Initially, make sure you have selected the right develop for your town/area. You can examine the form making use of the Review switch and read the form outline to ensure it will be the right one for you.
- If the develop is not going to fulfill your requirements, take advantage of the Seach area to obtain the proper develop.
- Once you are certain that the form is acceptable, click the Get now switch to find the develop.
- Opt for the rates plan you want and type in the required information. Create your accounts and pay money for the order utilizing your PayPal accounts or charge card.
- Opt for the file format and acquire the legal papers template in your gadget.
- Complete, change and print and indication the attained Louisiana Indemnity Provisions - Parties to the Indemnity.
US Legal Forms is definitely the greatest library of legal kinds where you can discover a variety of papers layouts. Make use of the company to acquire skillfully-manufactured files that follow express needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
For example, in the case of home insurance, the homeowner pays insurance premiums to the insurance company in exchange for the assurance that the homeowner will be indemnified if the house sustains damage from fire, natural disasters, or other perils specified in the insurance agreement. Indemnity: What It Means in Insurance and the Law - Investopedia investopedia.com ? terms ? indemnity investopedia.com ? terms ? indemnity
Indemnifications, or ?hold harmless? provisions, shift risks or potential costs from one party to another. One party to the contract promises to defend and pay costs and expenses of the other if specific circumstances arise (often a claim or dispute with a third party to the contract). Indemnification Clause Sample | Bloomberg Law bloomberglaw.com ? brief ? indemnification-... bloomberglaw.com ? brief ? indemnification-...
How to Write an Indemnity Agreement Consider the Indemnity Laws in Your Area. ... Draft the Indemnification Clause. ... Outline the Indemnification Period and Scope of Coverage. ... State the Indemnification Exceptions. ... Specify How the Indemnitee Notifies the Indemnitor About Claims. ... Write the Settlement and Consent Clause. How to Write an Indemnity Agreement (Step-by-Step Guide) - OnBoard onboardmeetings.com ? blog ? indemnity-a... onboardmeetings.com ? blog ? indemnity-a...
Each party (the ?Indemnifying Party?) shall indemnify, defend and hold harmless the other party (the ?Indemnified Party?), its affiliates, and its respective officers, directors, employees, agents, and representatives from and against any and all claims, damages, losses, liabilities, judgments, settlements, costs and ... The Indemnification Clause in Commercial Contracts - Ironclad ironcladapp.com ? journal ? indemnification-clause ironcladapp.com ? journal ? indemnification-clause
Example 1: A service provider asking their customer to indemnify them to protect against misuse of their work product. Example 2: A rental car company, as the rightful owner of the car, having their customer indemnify them from any damage caused by the customer during the course of the retnal. Indemnification Clause: Meaning & Samples (2022) - Contracts Counsel contractscounsel.com ? indemnification-clause contractscounsel.com ? indemnification-clause
Letters of indemnity should include the names and addresses of both parties involved, plus the name and affiliation of the third party. Detailed descriptions of the items and intentions are also required, as are the signatures of the parties and the date of the contract's execution. What Is a Letter of Indemnity (LOI)? Definition and Example - Investopedia investopedia.com ? terms ? letterofindemnity investopedia.com ? terms ? letterofindemnity
Letters of indemnity should include the names and addresses of both parties involved, plus the name and affiliation of the third party. Detailed descriptions of the items and intentions are also required, as are the signatures of the parties and the date of the contract's execution. What Is a Letter of Indemnity (LOI)? Definition and Example - Investopedia investopedia.com ? terms ? letterofindemnity investopedia.com ? terms ? letterofindemnity
In a business transaction, a letter of indemnity (LOI) is a contractual document guaranteeing that specific provisions will be met between two parties in the event of a mishap leading to financial loss or damage to goods. An LOI is drafted by third-party institutions such as banks or insurance companies. What is Letter of Indemnity?| Meaning, Sample, Importance & More dripcapital.com ? en-us ? resources ? blog dripcapital.com ? en-us ? resources ? blog