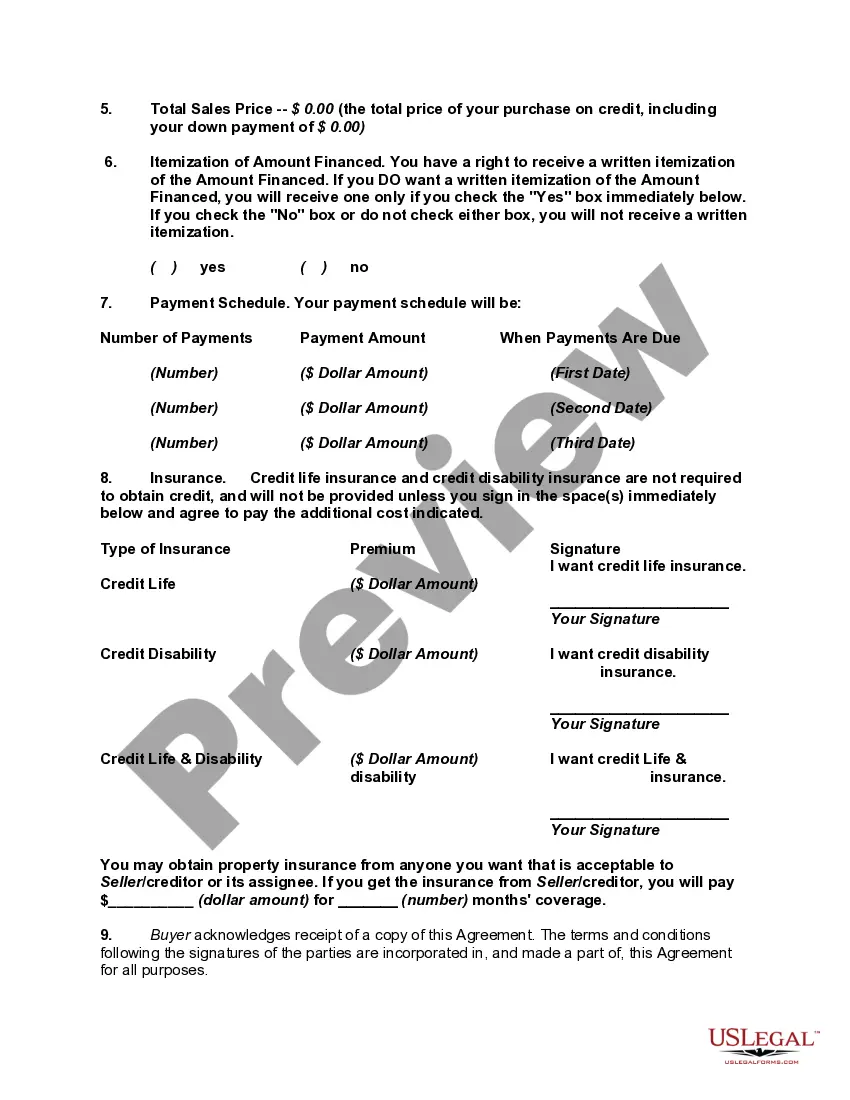
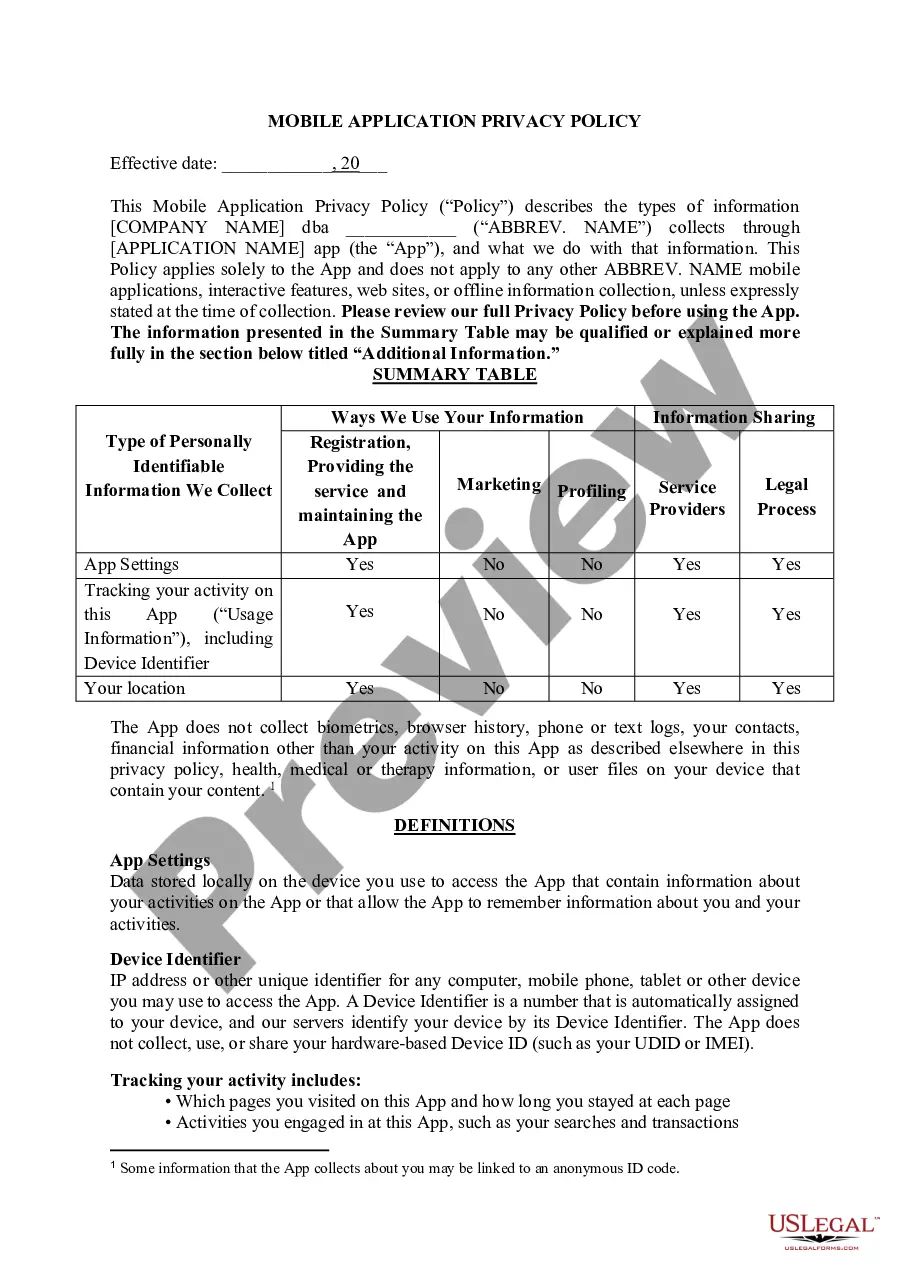
Disclosure of credit terms should have the content and form required under the federal Truth in Lending Act (15 U.S.C.A. §§ 1601 et seq.) and applicable regulations (Regulation Z, 12 C.F.R. § 226), and under state consumer credit laws to the extent that they differ from the federal Act. In connection with specified installment sales and other consumer credit transactions, these enactments require written disclosure and advice as to finance charges, annual percentage rates and other matters relating to credit. Under the federal Act, the disclosures may be set forth in the contract document itself or in a separate statement or statements.
A federal notice regarding preservation of the consumer's claims and defenses is required on all consumer credit contracts by Federal Trade Commission regulation. 16 C.F.R. § 433.2. The notice must appear in 10-point bold type or print and must be worded as set forth in the above form.