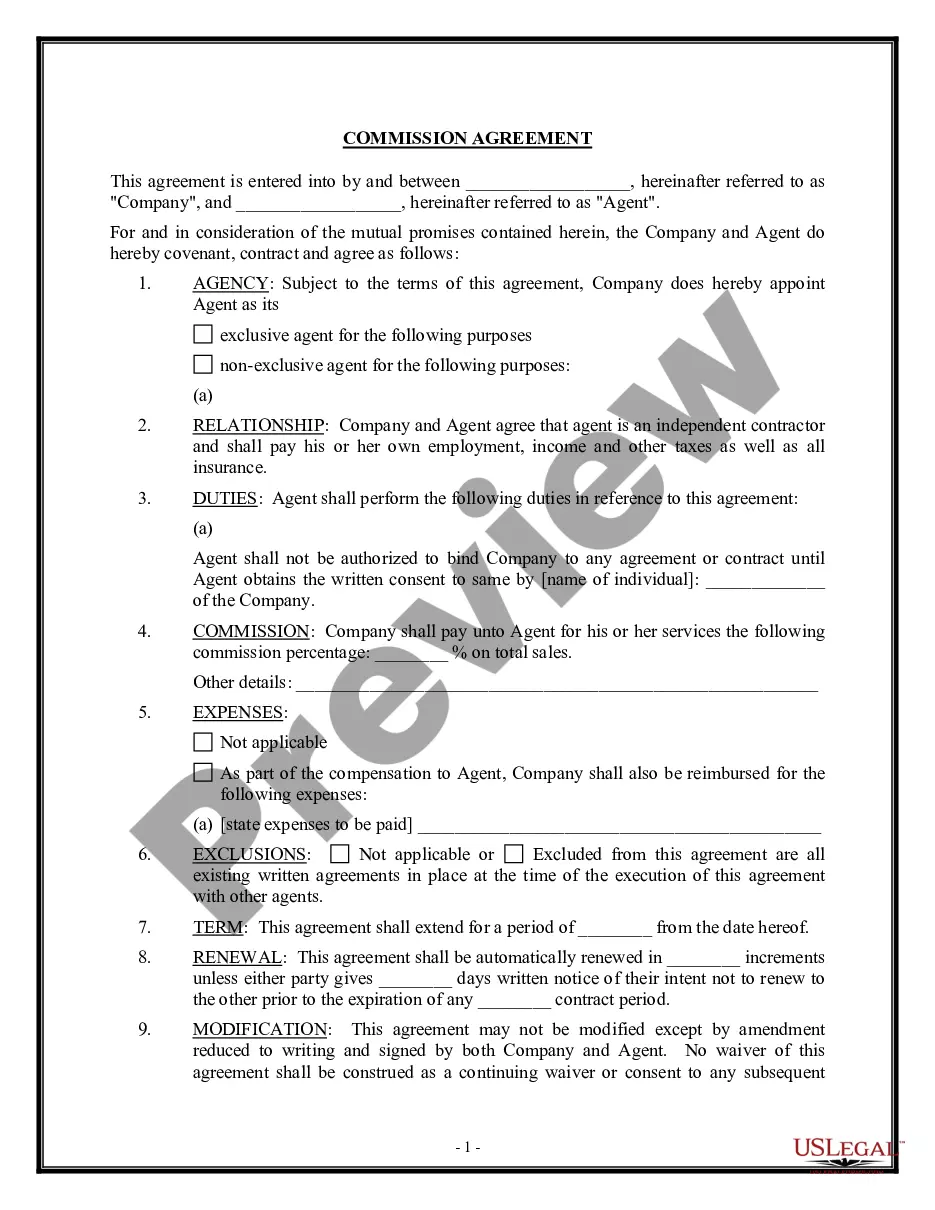
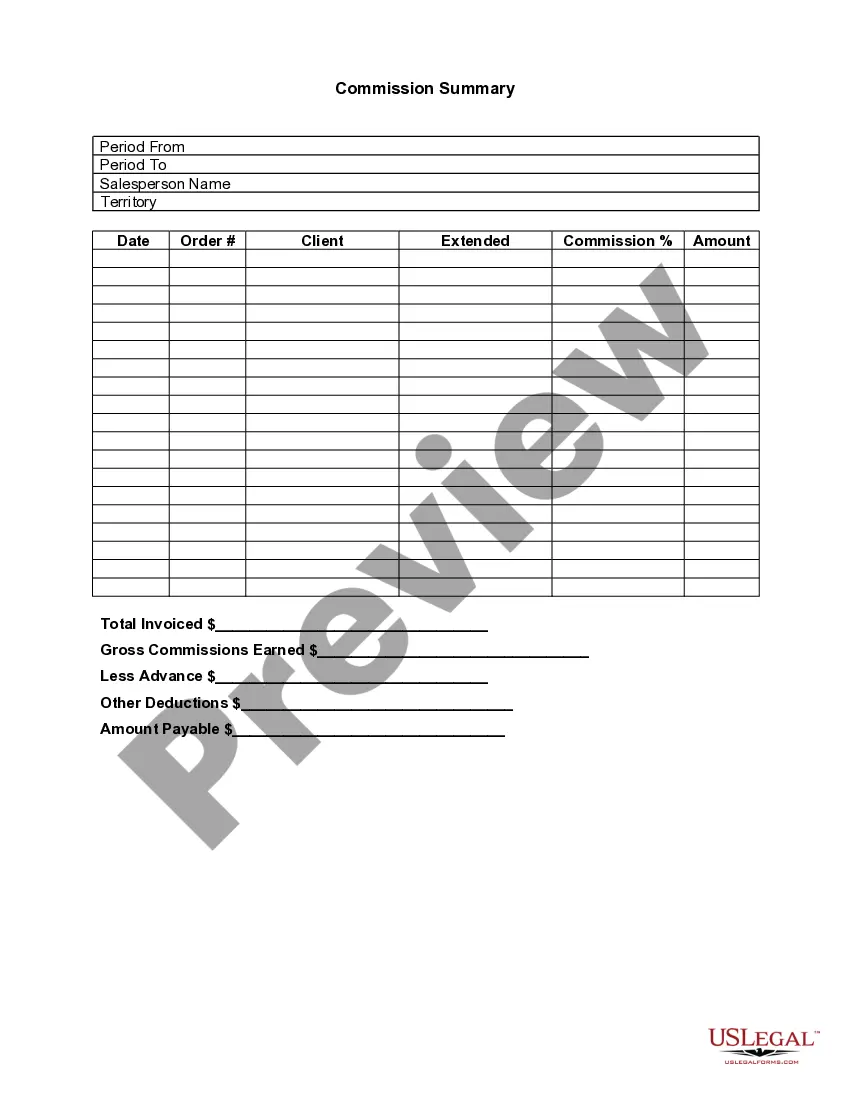
Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy
Description
How to fill out Sales Commission Policy?
You have the capability to spend time online searching for the legal document template that meets the federal and state regulations you require.
US Legal Forms provides a vast array of legal documents that are reviewed by professionals.
You can easily download or print the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy from our platform.
If available, use the Preview button to review the document template as well. If you wish to get another version of the document, use the Search section to find the template that meets your needs and preferences.
- If you possess a US Legal Forms account, you may Log In and then click the Acquire button.
- Afterward, you can complete, modify, print, or sign the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy.
- Each legal document template you acquire is yours permanently.
- To obtain another copy of any purchased form, visit the My documents section and click the appropriate button.
- If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the simple guidelines below.
- First, ensure that you have selected the correct document template for the state/city of your choice.
- Review the form details to confirm you have chosen the correct document.
Form popularity
FAQ
The sales tax rule in Massachusetts mandates that most retail sales are subject to a sales tax of 6.25%. This rule is critical for compliance under the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy. Sellers must collect this tax from buyers at the point of sale, and failure to do so can result in penalties. Keeping accurate records and understanding exemptions will aid in proper tax management.
To establish a sales commission plan, start by defining clear objectives based on performance metrics. Outline the structure, including commission rates and the payment schedule, ensuring it aligns with the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy. Regularly communicating the plan to your sales team will foster transparency and motivation. Additionally, consider using platforms like uslegalforms to draft comprehensive agreements.
Yes, commissions are often considered wages in Massachusetts. Under the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy, commissions earned by employees are treated as part of their overall compensation. This classification affects both the employer's responsibilities and the employee's rights, particularly regarding payment schedules and termination conditions. It's vital for businesses to understand these regulations to avoid potential disputes.
In Massachusetts, there is no minimum threshold for sales tax collection. Any business making sales of taxable items must collect and remit sales tax. If you are subject to the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy, it is crucial to factor this tax into sales commissions. Therefore, maintaining accurate records will ensure compliance.
The Massachusetts sales tax rate is currently 6.25%, not 7%. Understanding this tax is essential for businesses operating under the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy. This sales tax applies to most goods and some services sold in the state, requiring careful consideration in transactions. Be sure to stay updated with state regulations to remain compliant.
Yes, commission is often included in wages, but it may depend on specific agreements and state guidelines. In Massachusetts, the treatment of commissions ensures they count towards total earnings, but clarity in contracts can help avoid disputes. It’s essential to refer to the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy for accurate definitions and expectations regarding commissions in wages.
Structuring a sales commission plan involves defining clear objectives, setting commission rates, and establishing performance metrics. Ensure that the plan aligns with the overall business goals while providing incentives for employees to excel. Reviewing the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy can offer insights on the best practices in creating a compliant and motivating sales commission structure.
To calculate commission for sales representatives, first identify the total sales generated by the individual. Then, apply the agreed-upon commission percentage to that sales amount. This method ensures a clear understanding of what a sales representative can earn and aligns with the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy for ensuring transparent earnings.
In Massachusetts, individuals in commission-only positions may qualify for unemployment benefits under certain conditions. To access these benefits, you must demonstrate that your earnings were significantly affected by a lack of available work. It's essential to understand the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy since it outlines how commission structures impact unemployment eligibility. For personalized assistance, consider using USLegalForms to navigate your specific situation and ensure you understand your rights.
The commission system for sales defines the methods and structures through which sales representatives earn their commission. This system may include base salaries, tiered commission rates, or bonuses based on performance. Learning about the Massachusetts Sales Commission Policy can help you understand how these systems work within the state, ensuring that compensation practices remain transparent and lawful. You can utilize resources from uslegalforms to clarify any complex aspects of these systems.