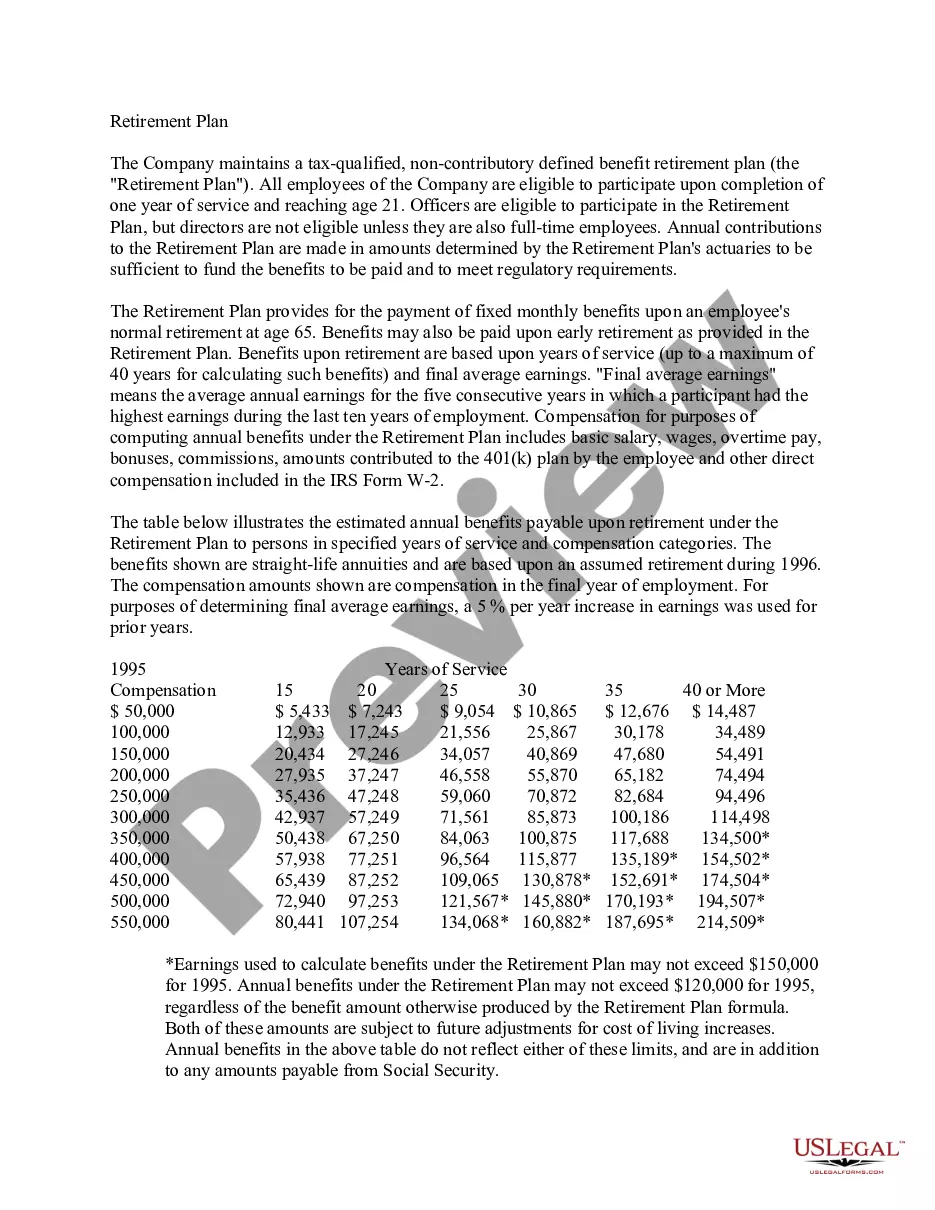
The Massachusetts Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (SERP) is a vital benefit that corporations often offer to their high-ranking executives. This executive benefit plan is specifically designed to provide additional financial security and rewards for key executives, ensuring their loyalty and incentivizing their long-term commitment to the organization. SERPs are customizable programs, offering various features and options to suit the needs of different executives and organizations. These supplemental retirement plans operate alongside the traditional retirement plans, such as the 401(k) or pension plans, and provide supplementary income to key executives during their retirement years. Key executives who qualify for SERPs receive certain benefits, like deferred compensation, additional retirement savings, and various financial incentives. The structure and terms of any SERP vary widely between organizations, as they are tailored to meet specific executive needs and align with the company's objectives. Given the diversity of SERPs, some of the different types that may be found in Massachusetts include: 1. Defined Contribution SERPs: This type of plan allows the executive, and sometimes the company, to make contributions to a separate account on behalf of the executive. The account is invested, and the final benefit amount is determined by the performance of the investments. 2. Defined Benefit SERPs: In a defined benefit SERP, the executive receives a guaranteed benefit amount upon retirement. The benefit is typically based on a combination of factors, such as the executive's years of service and their average annual compensation. 3. Split Dollar SERPs: Split dollar SERPs are designed as cost-sharing arrangements between the executive and the company. The plan provides the executive with a life insurance policy, and the premium payments are split between the executive and the organization. Upon retirement, the plan "splits" the policy proceeds between the executive's beneficiaries and the company. 4. Supplemental Savings SERPs: This form of SERP involves the corporation contributing funds into a non-qualified savings plan on behalf of the executive. These contributions are invested, and the executive receives the accumulated amount upon retirement, providing additional financial security. 5. Cash Balance SERPs: In this type of SERP, the executive has an account that grows annually with a fixed percentage or interest rate. The benefit amount is determined by the account balance at retirement. It is crucial for executives and organizations to review and compare various SERP options to determine the most suitable plan that aligns with the executive's retirement goals and the organization's objectives. Consulting with an experienced financial advisor or retirement planning specialist is highly recommended ensuring the chosen SERP fulfills both the executive's and the organization's long-term needs.
Massachusetts Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan - SERP
Description
How to fill out Massachusetts Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan - SERP?
If you need to complete, obtain, or produce lawful papers templates, use US Legal Forms, the most important assortment of lawful varieties, that can be found on the web. Use the site`s basic and handy search to obtain the documents you need. Numerous templates for enterprise and specific uses are categorized by types and says, or keywords. Use US Legal Forms to obtain the Massachusetts Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan - SERP in a number of click throughs.
If you are previously a US Legal Forms customer, log in to the account and then click the Acquire switch to have the Massachusetts Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan - SERP. Also you can entry varieties you earlier delivered electronically inside the My Forms tab of your respective account.
If you use US Legal Forms the first time, refer to the instructions beneath:
- Step 1. Be sure you have selected the form to the appropriate town/country.
- Step 2. Make use of the Preview choice to look over the form`s information. Do not forget about to see the description.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied using the develop, use the Lookup discipline near the top of the monitor to locate other models of the lawful develop template.
- Step 4. After you have found the form you need, click the Get now switch. Opt for the pricing strategy you like and include your credentials to sign up to have an account.
- Step 5. Process the purchase. You can utilize your bank card or PayPal account to accomplish the purchase.
- Step 6. Find the file format of the lawful develop and obtain it on the device.
- Step 7. Full, change and produce or indication the Massachusetts Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan - SERP.
Each and every lawful papers template you acquire is yours eternally. You possess acces to every develop you delivered electronically within your acccount. Select the My Forms segment and decide on a develop to produce or obtain again.
Contend and obtain, and produce the Massachusetts Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan - SERP with US Legal Forms. There are thousands of professional and status-distinct varieties you can use for your enterprise or specific requires.