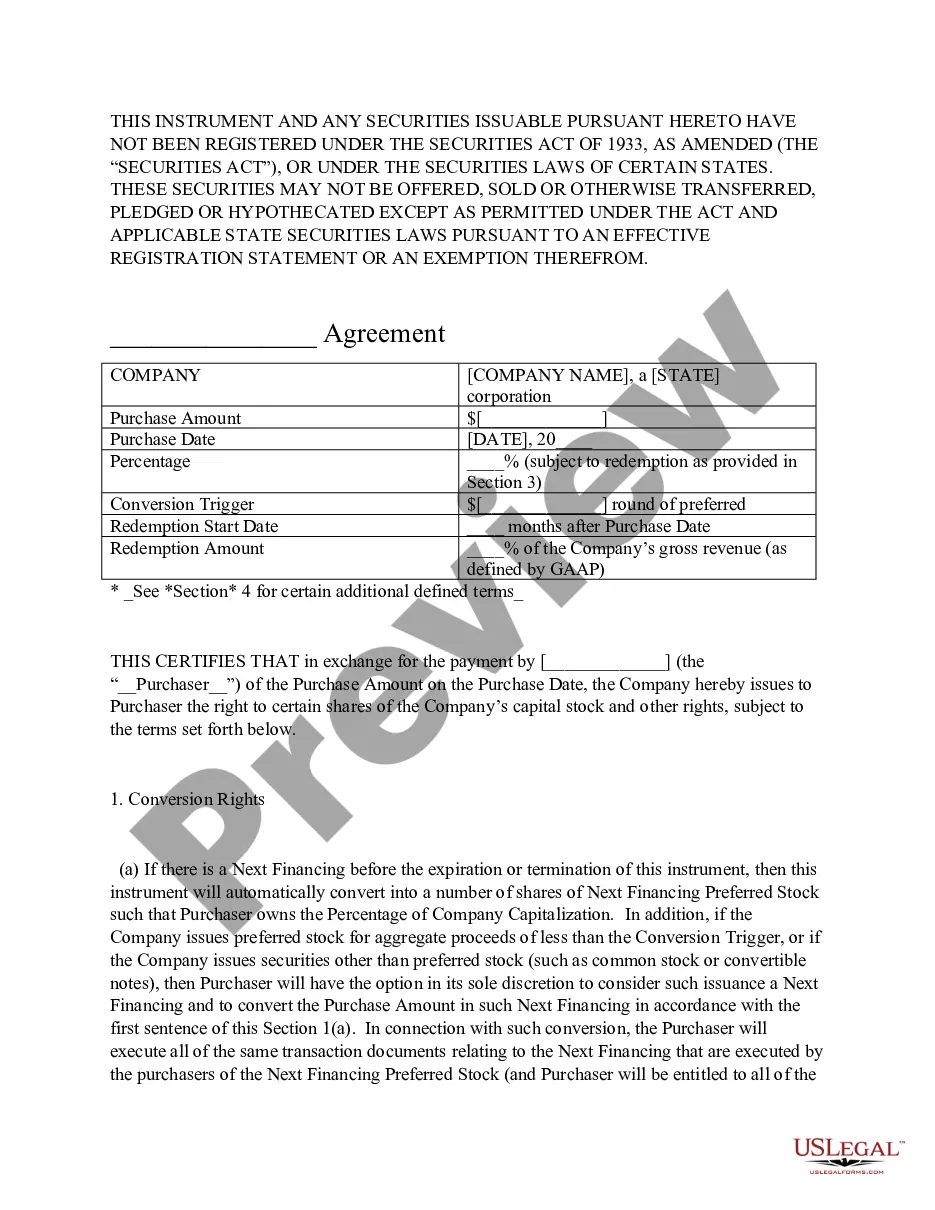
Massachusetts Terms for Private Placement of Series Seed Preferred Stock
Description
How to fill out Terms For Private Placement Of Series Seed Preferred Stock?
US Legal Forms - one of many largest libraries of authorized types in the United States - delivers a wide range of authorized papers templates you may acquire or printing. Making use of the site, you will get thousands of types for business and individual purposes, categorized by classes, suggests, or search phrases.You can get the latest types of types just like the Massachusetts Terms for Private Placement of Series Seed Preferred Stock in seconds.
If you already possess a membership, log in and acquire Massachusetts Terms for Private Placement of Series Seed Preferred Stock from your US Legal Forms collection. The Down load switch can look on each develop you look at. You get access to all previously acquired types inside the My Forms tab of your respective accounts.
If you wish to use US Legal Forms initially, here are easy instructions to obtain started off:
- Be sure to have picked out the correct develop for your personal area/county. Click on the Review switch to examine the form`s content material. Browse the develop explanation to ensure that you have selected the right develop.
- When the develop doesn`t suit your specifications, utilize the Look for field near the top of the display to obtain the one that does.
- If you are pleased with the form, confirm your decision by clicking the Acquire now switch. Then, opt for the rates plan you like and provide your references to register to have an accounts.
- Process the purchase. Use your credit card or PayPal accounts to finish the purchase.
- Pick the file format and acquire the form on your own system.
- Make alterations. Complete, change and printing and sign the acquired Massachusetts Terms for Private Placement of Series Seed Preferred Stock.
Every single design you included with your money lacks an expiry particular date and is yours eternally. So, in order to acquire or printing another backup, just visit the My Forms area and click about the develop you will need.
Get access to the Massachusetts Terms for Private Placement of Series Seed Preferred Stock with US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive collection of authorized papers templates. Use thousands of professional and status-particular templates that satisfy your small business or individual requirements and specifications.
Form popularity
FAQ
These fundraising rounds allow investors to invest money into a growing company in exchange for equity/ownership. The initial investment?also known as seed funding?is followed by various rounds, known as Series A, B, and C. A new valuation is done at the time of each funding round.
Series A funding comes after there is already a product and obvious traction. Seed funding is usually the first round of funding and raises a small amount of capital. In series A, the startup receives more capital to support future growth.
Hear this out loud PauseA Series AA Round is a round of startup financing using a class of preferred stock called the ?Series AA Preferred Shares.? Series AA is also known as ?Seed? because it comes before Series A. Series AA terms are usually not as onerous as Series A terms, and the valuation is typically lower.
The first round of stock offered during the seed or early stage round by a portfolio company to the venture investor or fund. This stock is convertible into common stock in certain cases such as an IPO or the sale of the company.
Hear this out loud PauseSeries Seed Preferred Stock is a type of preferred stock issued by startups during their early stage of development. Preferred stock is a hybrid security that combines elements of both debt and equity.
Hear this out loud PauseThe first round of stock made available to the public by a startup is referred to as Series A preferred stock. This type of stock is generally offered for purchase during the seed stage of a new startup and can be converted into common stock in the event of an initial public offering or sale of the company.