Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use: A Comprehensive Guide Introduction: The Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use plays a vital role in the land-use planning and zoning process within the state. This application allows individuals, businesses, or organizations to request permission for specific uses of land that may deviate from existing zoning regulations or land-use limitations. In this detailed description, we will explore the purpose, process, and different types of Massachusetts Applications for Conditional Use, highlighting relevant keywords throughout. Purpose: The primary objective of the Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use is to provide a streamlined and structured approach for applicants seeking to obtain permits for land-use activities that would typically be considered non-compliant with existing zoning regulations. This application process enables individuals, businesses, or organizations to present their proposals and justifications for the requested conditional use, ensuring that the development or activity aligns with the municipality's overall objectives and standards. Process: The process of applying for a Massachusetts Conditional Use Permit generally includes the following steps: 1. Identifying the project: The applicant must clearly outline the nature and scope of the proposed conditional use, including details such as the property location, existing zoning, and the specific regulations the project seeks to deviate from. 2. Preliminary meetings: It is advisable to engage in preliminary discussions with relevant municipal authorities, planning boards, or zoning boards to ensure a complete understanding of the application process, requirements, and potential challenges. 3. Completing the application form: The Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use form requires detailed information regarding the applicant, project description, site plans, environmental impacts, community benefits, and any requested variances or waivers. 4. Submitting the application: The completed application, along with all supporting documentation, must be submitted to the appropriate municipal department or board, accompanied by the required fees. 5. Public hearing: In most cases, a public hearing is conducted, allowing community members to voice their opinions and concerns related to the proposed conditional use. Applicants are often required to present their project in detail during the hearing. 6. Review and decision: Following the public hearing, the municipal planning or zoning board reviews the application, considering factors such as impact on neighboring properties, traffic, noise, environmental concerns, and compliance with the municipality's overall land-use plan. The board makes a decision to approve, deny, or modify the requested conditional use. Different Types: While the specifics of the Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use vary across municipalities, there are typically different types of conditional uses that applicants can apply for. Some common types include: 1. Commercial conditional use: This type allows for non-residential land use, such as retail stores, offices, or hotels, in areas designated primarily for residential purposes. 2. Industrial conditional use: This type permits industrial activities in areas typically zoned for commercial or residential purposes, subject to meeting specific requirements and mitigating potential adverse impacts. 3. Waterfront conditional use: This category pertains to development or activities along waterfronts, beaches, or coastal areas, encompassing considerations like conservation, recreational access, and preservation of natural resources. 4. Planned unit development conditional use: This type involves applications for mixed-use developments or projects that incorporate a range of land uses, such as housing, commercial spaces, and recreational amenities, creating more integrated and sustainable communities. Conclusion: The Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use serves as a crucial tool for managing land-use activities that deviate from existing zoning regulations. By providing a transparent and structured process, it ensures that proposed projects meet the community's objectives while balancing potential impacts on the surrounding environment, infrastructure, and quality of life. Aspiring applicants should closely review the specific requirements, guidelines, and procedures of their respective municipality to ensure a successful application process.
Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use
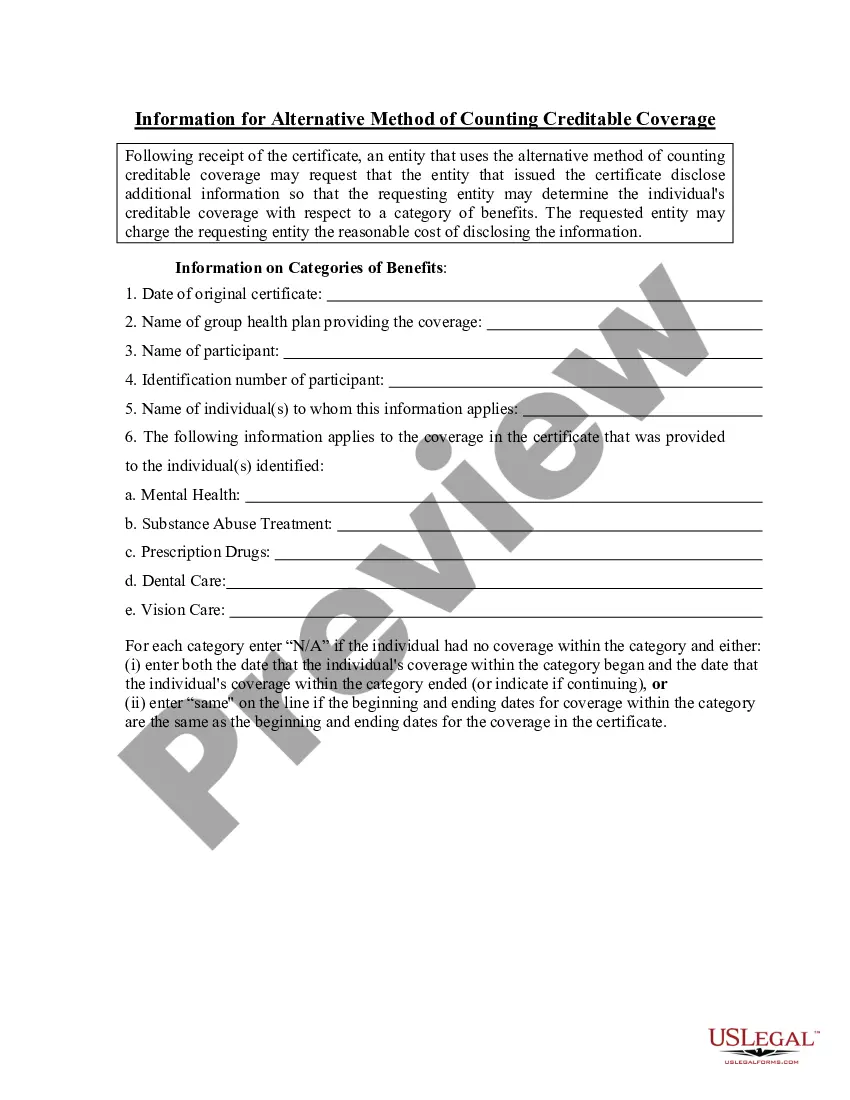
Description
How to fill out Massachusetts Application For Conditional Use?
If you need to comprehensive, obtain, or produce legitimate papers web templates, use US Legal Forms, the biggest assortment of legitimate types, that can be found on the web. Use the site`s simple and handy research to obtain the documents you require. Different web templates for organization and specific reasons are categorized by classes and says, or keywords. Use US Legal Forms to obtain the Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use in just a few mouse clicks.
Should you be already a US Legal Forms consumer, log in to the profile and then click the Acquire switch to obtain the Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use. You may also entry types you earlier saved from the My Forms tab of the profile.
If you use US Legal Forms the first time, follow the instructions listed below:
- Step 1. Be sure you have chosen the form to the proper city/region.
- Step 2. Take advantage of the Preview solution to look through the form`s information. Do not overlook to see the information.
- Step 3. Should you be not happy with the kind, make use of the Look for industry towards the top of the screen to discover other versions from the legitimate kind design.
- Step 4. When you have discovered the form you require, go through the Purchase now switch. Select the costs prepare you prefer and include your credentials to sign up to have an profile.
- Step 5. Process the purchase. You can use your credit card or PayPal profile to accomplish the purchase.
- Step 6. Pick the file format from the legitimate kind and obtain it in your product.
- Step 7. Total, edit and produce or indicator the Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use.
Every legitimate papers design you get is your own property permanently. You possess acces to every single kind you saved inside your acccount. Select the My Forms segment and pick a kind to produce or obtain once again.
Compete and obtain, and produce the Massachusetts Application for Conditional Use with US Legal Forms. There are many skilled and express-specific types you may use for your organization or specific needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
Boston's Zoning Code dictates the appropriate heights, densities, and uses allowed in different areas of the City. This section includes resources to help you understand Boston's Zoning Code, the BPDA's involvement with zoning, and more.
Hear this out loud PauseWhat is a Conditional Use Permit? A "Conditional Use" is a land use that is provided for in the Zoning Ordinance, but requires specific case-by-case approval by the City Council. A Conditional Use may be appropriate for a particular site, but only if the impacts of the use on the neighborhood can be mitigated.
Divide the GROSS FLOOR AREA by the BUILDABLE LAND AREA. The result is the Floor Area Ratio (FAR).
? With a land area of 48.4 square miles Boston comprises 0.6% of the 7,824 square miles that make up the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
Hear this out loud PauseWhat is a Conditional Use Permit (CUP)? Zoning districts contain land uses that are permitted and conditional. A conditional use is a use allowed in a zoning district only after specific requirements have been met and the Planning and Zoning Commission has attached conditions of approval.
A minimum of fifteen feet from the front building line, except applicable only above a height of sixty-five feet. A minimum of fifteen feet from the rear building line, except applicable only above a height of ninety feet.
Hear this out loud PauseA minimum of fifteen feet from the front building line, except applicable only above a height of sixty-five feet. A minimum of fifteen feet from the rear building line, except applicable only above a height of ninety feet.
Hear this out loud PauseWHAT IS A CONDITIONAL USE PERMIT? ACONDITIONAL USE PERMIT (CUP) allows a city or county to consider special uses which may be essential or. desirable to a particular community, but which are not allowed as a matter of right within a zoning district, through a public hearing process.