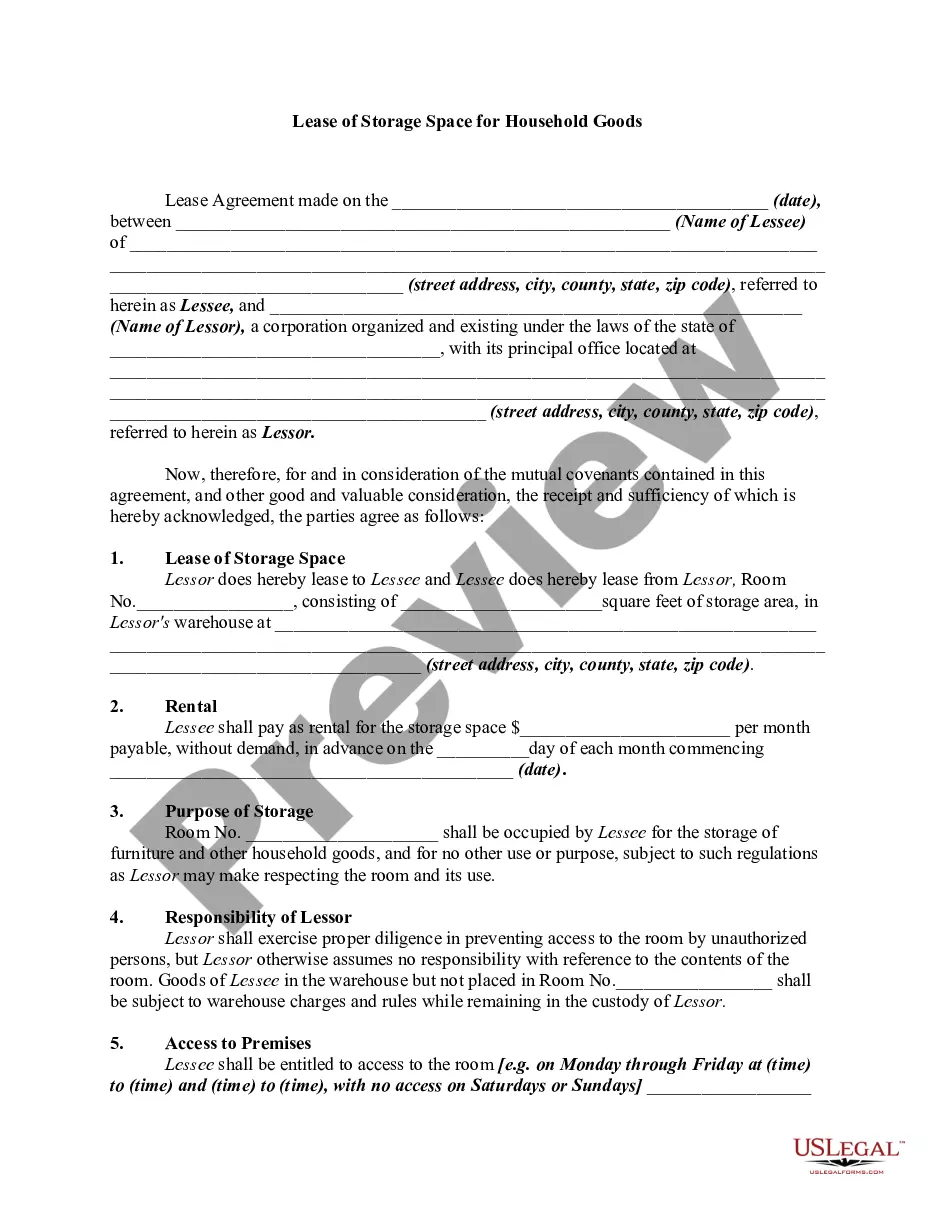
While most warehousing contracts create bailments of the stored goods, other types of agreements may be made covering the subject matter. Of these, the most important are leases of storage space. The essential factor distinguishing a lease of storage space from a bailment of goods is the storer's retaining possession and control over the goods. It cannot be conclusively presumed that a lease rather than a bailment is intended merely because the contract provides for the storing of goods in a certain space in the warehouse. This is true even though the goods are to be placed in a separate room to which the storer is given a key. However, if under the agreement the warehouseman has no control over the storer's access to the premises where the goods are stored, it is generally held that there is a lease of storage space. Of course, the instrument should be drafted to clarify the legal relationship that the parties desire.
Maryland Lease of Storage Space for Household Goods is a legal agreement entered into between a landlord (the storage facility owner) and a tenant (the individual or business seeking storage space) to outline the terms and conditions of storing household goods in Maryland. This lease agreement governs the relationship and responsibilities of both parties. The Maryland Lease of Storage Space for Household Goods is specifically designed to cater to the storage needs of residential customers requiring a secure and convenient place to keep their belongings. It offers various types of storage units tailored to meet different requirements, ensuring the safekeeping of household goods for short or long durations. Two common types of Maryland Lease of Storage Space for Household Goods include: 1. Residential Storage Units: These units are specifically designed to accommodate the household goods of individuals or families who need a temporary storage solution. Whether it is due to moving, downsizing, remodeling, or deployment, residential storage units provide a secure and climate-controlled environment to keep furniture, appliances, clothing, and other personal belongings. 2. Business Storage Units: This type of storage space is suitable for commercial purposes. Businesses can utilize these units to store excess inventory, office furniture, equipment, files, archives, or any other items requiring extra space. The business storage units are often equipped with additional features like 24/7 access, surveillance systems, and customizable storage options to cater to diverse business needs. The Maryland Lease of Storage Space for Household Goods typically covers essential aspects such as: 1. Rental Terms: The lease agreement defines the duration of the lease, start and end dates, and any renewal options. It lays out the rental charges, frequency of payment, and acceptable payment methods. 2. Unit Description and Use: The lease explicitly describes the storage unit's size, location, and specifications, ensuring the tenant understands the allocated space. It also outlines the permitted uses of the unit, such as storage of household goods, non-hazardous items, or specific categories allowed by the facility. 3. Access and Security: The agreement specifies the tenant's rights regarding access to the storage facility, whether it's limited by specific hours or granted 24/7 access. It may mention security measures employed by the landlord, like video surveillance, security guards, or access control systems, ensuring the safety of stored goods. 4. Insurance: The lease agreement may address the tenant's responsibility for obtaining insurance coverage to protect their stored goods against potential damage or loss. It may require proof of insurance or offer options to purchase insurance through the storage facility. 5. Non-Payment and Lien Rights: The agreement covers provisions related to non-payment of rent, late fees, and the landlord's lien rights in case of default. It highlights the consequences, such as potential sale or disposal of the stored goods to recover outstanding dues. 6. Termination: The terms and conditions of lease termination are outlined, including notice periods, requirements for removing stored items, and any associated fees or penalties. It is crucial for both landlords and tenants to carefully review and understand the Maryland Lease of Storage Space for Household Goods. Seeking legal advice or assistance may be beneficial to ensure compliance with Maryland's laws and regulations surrounding storage space leasing.