A deed of trust is a document which pledges real property to secure a loan, used instead of a mortgage in certain states. A deed of trust involves a third party called a trustee, usually an attorney of officer of the lender, who acts on behalf of the lender. When you sign a deed of trust, you in effect are giving a trustee title to the property, but you hold the rights and privileges to use and live in or on the property. If the loan becomes delinquent the beneficiary can file a notice of default and, if the loan is not brought current, can demand that the trustee begin foreclosure on the property so that the beneficiary (lender) may either be paid or obtain title. Unlike a mortgage, a deed of trust also gives the trustee the right to foreclose on your property without taking you to court first.
An agreement modifying a promissory note and deed of trust should be signed by both parties to the transaction and recorded in the office of the register of deeds and mortgages where the original deed of trust was recorded.
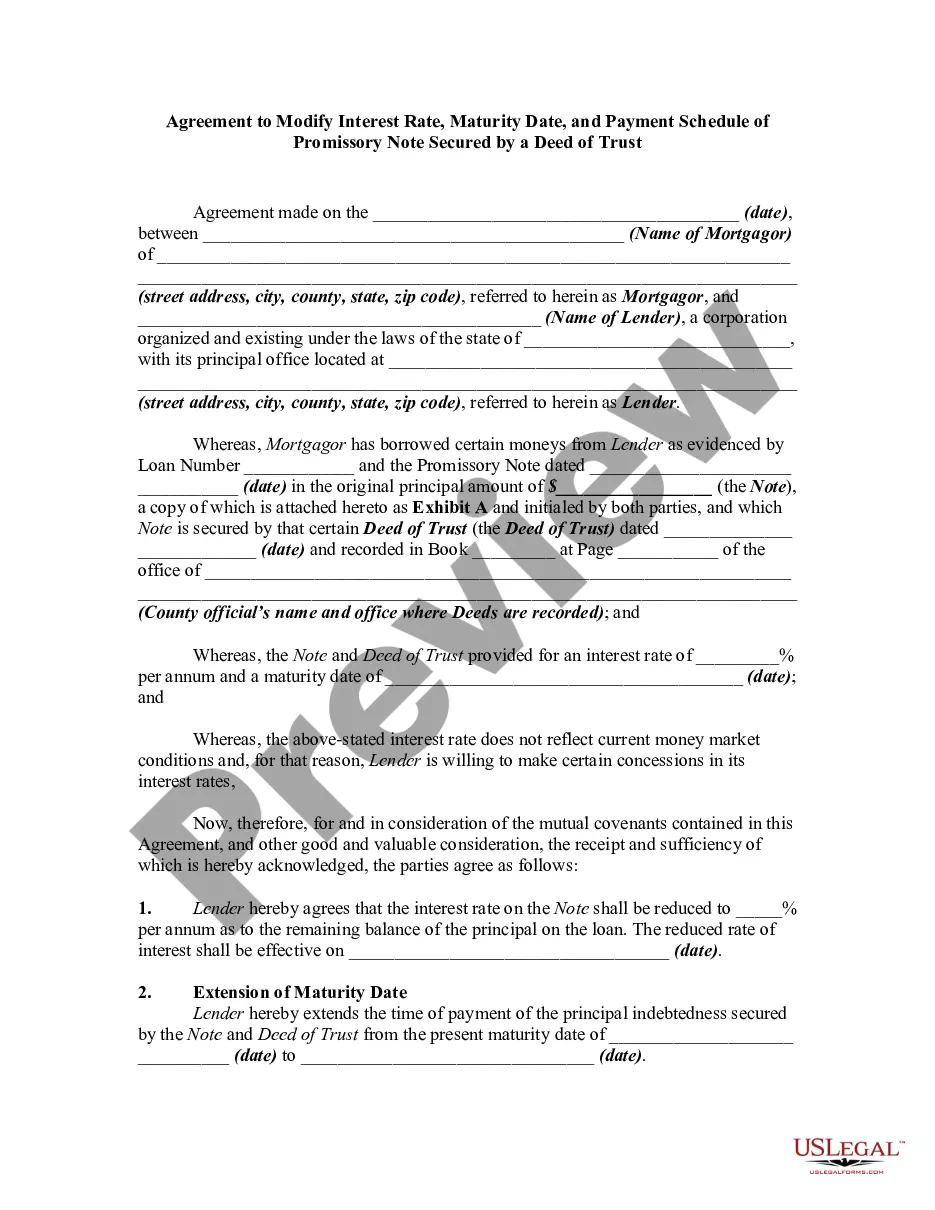
The Maryland Agreement to Change or Modify Interest Rate, Maturity Date, and Payment Schedule of Promissory Note Secured by a Deed of Trust is a legal document that allows parties involved in a promissory note to make amendments to certain aspects of the loan. It is important to understand the different types of modifications that can be made under this agreement. 1. Interest Rate Modification: This type of modification allows the parties to adjust the interest rate on the promissory note. It may be used to increase or decrease the interest rate, depending on the circumstances. This modification can be beneficial if the parties want to align the interest rate with current market rates or if the borrower is facing financial difficulties and needs a lower interest rate to afford the loan payments. 2. Maturity Date Extension: Another modification that can be made is to extend the maturity date of the loan. This alteration provides flexibility for the borrower in case they need more time to repay the loan or if they encounter unforeseen circumstances that hinder their ability to meet the original repayment deadline. By extending the maturity date, the borrower gains the opportunity to restructure their financial obligations and avoid defaulting on the loan. 3. Payment Schedule Modification: The payment schedule modification involves changing the terms and frequency of loan repayments. This can include alterations to monthly installments, the addition of a grace period, or changes to the due dates. This type of modification allows borrowers to adapt their repayment plan to better suit their financial situation, providing a higher chance of successful loan repayment and avoiding default. 4. Combined Modifications: In certain cases, more than one modification may be required to address specific financial challenges faced by the borrower. For instance, a borrower may need to request an interest rate decrease, extension of the maturity date, and a revision of the payment schedule simultaneously. These combined modifications aim to alleviate financial burden, improve affordability, and prevent default on the promissory note. Overall, the Maryland Agreement to Change or Modify Interest Rate, Maturity Date, and Payment Schedule of Promissory Note Secured by a Deed of Trust offers borrowers and lenders the flexibility to adapt the terms of their loan agreement. It serves as a crucial tool for borrowers who need to modify their loans due to changing circumstances and assures lenders that the borrower remains committed to fulfilling their financial obligations.The Maryland Agreement to Change or Modify Interest Rate, Maturity Date, and Payment Schedule of Promissory Note Secured by a Deed of Trust is a legal document that allows parties involved in a promissory note to make amendments to certain aspects of the loan. It is important to understand the different types of modifications that can be made under this agreement. 1. Interest Rate Modification: This type of modification allows the parties to adjust the interest rate on the promissory note. It may be used to increase or decrease the interest rate, depending on the circumstances. This modification can be beneficial if the parties want to align the interest rate with current market rates or if the borrower is facing financial difficulties and needs a lower interest rate to afford the loan payments. 2. Maturity Date Extension: Another modification that can be made is to extend the maturity date of the loan. This alteration provides flexibility for the borrower in case they need more time to repay the loan or if they encounter unforeseen circumstances that hinder their ability to meet the original repayment deadline. By extending the maturity date, the borrower gains the opportunity to restructure their financial obligations and avoid defaulting on the loan. 3. Payment Schedule Modification: The payment schedule modification involves changing the terms and frequency of loan repayments. This can include alterations to monthly installments, the addition of a grace period, or changes to the due dates. This type of modification allows borrowers to adapt their repayment plan to better suit their financial situation, providing a higher chance of successful loan repayment and avoiding default. 4. Combined Modifications: In certain cases, more than one modification may be required to address specific financial challenges faced by the borrower. For instance, a borrower may need to request an interest rate decrease, extension of the maturity date, and a revision of the payment schedule simultaneously. These combined modifications aim to alleviate financial burden, improve affordability, and prevent default on the promissory note. Overall, the Maryland Agreement to Change or Modify Interest Rate, Maturity Date, and Payment Schedule of Promissory Note Secured by a Deed of Trust offers borrowers and lenders the flexibility to adapt the terms of their loan agreement. It serves as a crucial tool for borrowers who need to modify their loans due to changing circumstances and assures lenders that the borrower remains committed to fulfilling their financial obligations.