Maryland General Assignment
Description
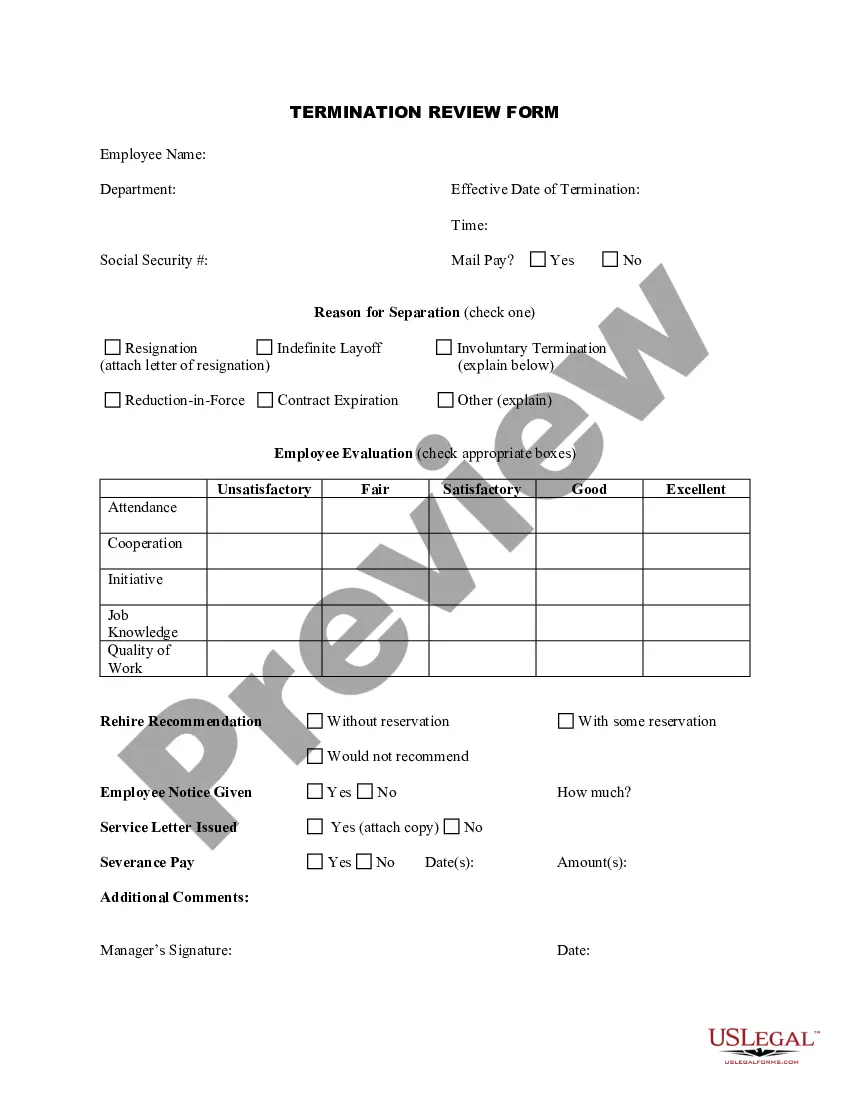
How to fill out General Assignment?
Have you ever been in a location where you require documents for either business or personal matters nearly all the time.
There are numerous legal document templates available online, but finding forms you can trust is not easy.
US Legal Forms provides thousands of form templates, such as the Maryland General Assignment, designed to comply with state and federal regulations.
Once you find the correct form, click on Get now.
Select the pricing plan you want, provide the necessary information to create your account, and pay for the order using your PayPal or Visa or MasterCard.
- If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and have an account, simply Log In.
- After that, you can download the Maryland General Assignment template.
- If you do not have an account and want to start using US Legal Forms, follow these instructions.
- Find the form you need and make sure it is for the correct city/state.
- Utilize the Preview option to view the form.
- Check the details to confirm that you have selected the correct form.
- If the form does not meet your needs, use the Search field to find the form that suits your requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
The main responsibility of the General Assembly is to legislate, meaning it creates and amends laws for the state of Maryland. This includes budget approval, policy development, and oversight of state programs. Engaging with the Maryland General Assembly allows you to influence changes that matter to you. Your participation can drive impactful legislation.
The primary power of the Maryland General Assembly lies in its ability to enact laws that govern the state. This legislative body has the authority to propose, debate, and finalize legislation affecting various sectors. Effectively, it serves as the voice of the citizens, reflecting their needs and interests. Understanding this power helps residents better engage with the law-making process.
Filing articles of organization in Maryland involves submitting the necessary documents to the Maryland State Department of Assessments and Taxation. You can complete this process online or via mail, ensuring you include all required information. USLegalForms provides templates for these documents, streamlining the process for you. This support makes it easier to establish your business legally.
You can obtain Maryland tax forms through the official Maryland State Revenue Administration website. The site provides downloadable forms and instructions tailored to your tax situation. For added convenience, the USLegalForms platform offers templates related to tax documentation that can simplify your filing process. Using these resources can help ensure you meet your tax obligations effectively.
Maryland's state government is responsible for administering public services such as education, health care, and infrastructure development. Additionally, it oversees various programs that aim to enhance the quality of life for residents. Engaging with initiatives spearheaded by the Maryland General Assembly can lead to improvements in these essential areas. Community involvement amplifies these efforts.
You can submit your testimony to the Maryland General Assembly by contacting your local legislator or their office directly. It is advisable to prepare a concise statement outlining your views on relevant legislation. You might also consider using the USLegalForms platform to access templates that facilitate the submission process. This approach increases your likelihood of effectively contributing to the discussion.
The Maryland General Assembly is responsible for creating laws that govern the state. It plays a crucial role in shaping policies that impact the daily lives of residents. Through this legislative process, the Assembly addresses various issues, ranging from education to transportation. Engaging with the Maryland General Assembly can empower citizens to participate in law-making.
The Maryland General Assembly is composed of elected officials known as delegates and senators, along with support staff and analysts. These individuals collaborate to review, amend, and pass legislation that impacts citizens’ rights and responsibilities. The synergy among these members is crucial for effective governance, particularly on matters related to the Maryland General Assignment. You can explore available resources on platforms like US Legal Forms to familiarize yourself with the roles within the Assembly.
The Maryland General Assembly is the legislative authority in the state, tasked with crafting laws and adopting budgets that serve the people. It plays a crucial role in shaping policies that affect daily life, from education to public safety. Understanding the workings of the General Assembly is essential for grasping topics like the Maryland General Assignment. For those interested in participating in or tracking legislative developments, resources such as US Legal Forms can be invaluable.
In Maryland, the single subject rule mandates that each bill must focus on one main topic. This rule intends to prevent unrelated issues from being bundled together, ensuring more transparent legislation. By adhering to this rule, lawmakers can build a clearer understanding of the Maryland General Assignment matters at hand. When seeking clarity on legislative processes, consider utilizing platforms like US Legal Forms for access to relevant documents and insights.