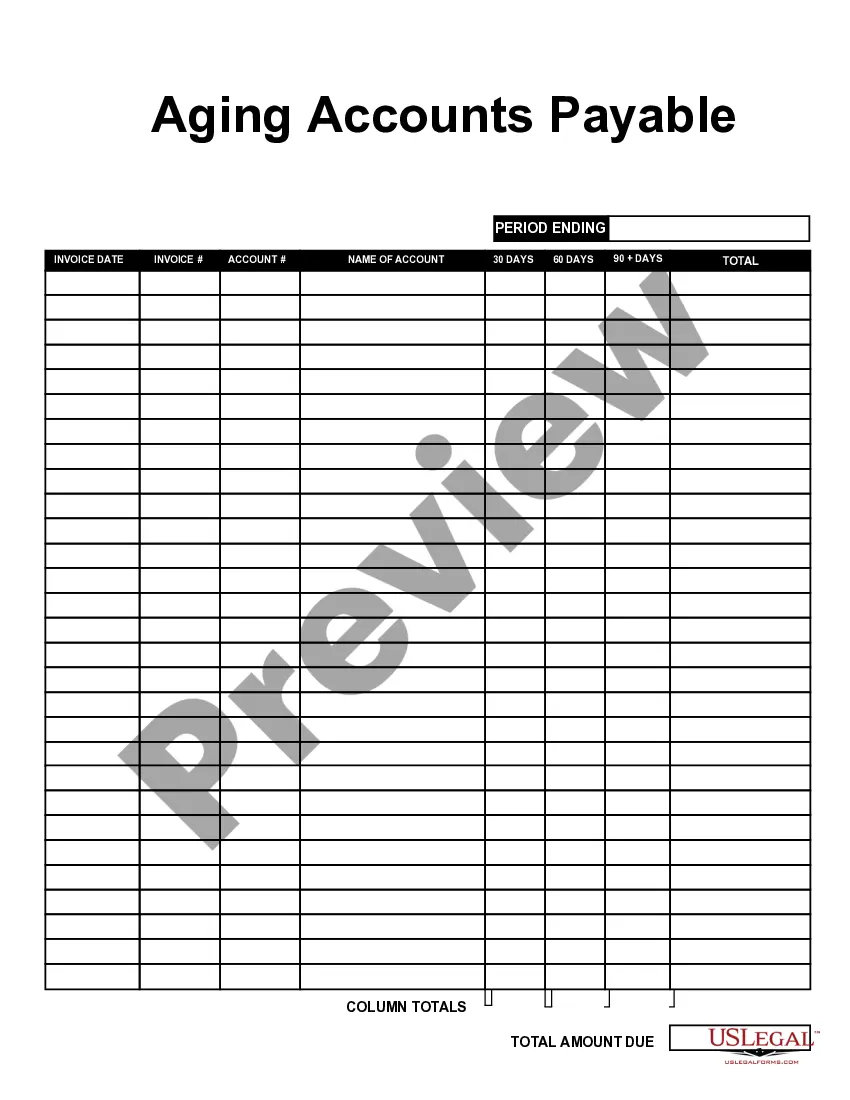
Maryland Aging Accounts Payable refers to the process of tracking and managing unpaid invoices and bills in the state of Maryland. It is a crucial aspect of financial management for businesses and organizations operating in Maryland. The term "aging" refers to categorizing outstanding invoices based on their due dates. This helps organizations monitor and prioritize their outstanding payments, ensuring timely payment and reducing any potential financial risks. The Maryland Aging Accounts Payable provides businesses with an overview of their unpaid invoices, allowing them to identify which invoices are overdue and need immediate attention. By categorizing invoices into specific time frames, typically 30 days, 60 days, 90 days, and beyond, it becomes easier to identify potentially problematic accounts. This categorization system helps organizations develop effective strategies to address late payments and take appropriate actions, such as sending reminders or initiating collection procedures. There are three primary types of Maryland Aging Accounts Payable: 1. Current Accounts Payable: This category includes invoices that are still within the agreed-upon payment terms, usually within 30 days. These invoices are considered current and do not pose an immediate risk to a business's financial health. 2. Past Due Accounts Payable: This category consists of invoices that have exceeded the agreed-upon payment terms, typically beyond 30 days. These invoices require immediate attention, as the longer they remain unpaid, the higher the risk of financial strain and damage to business relationships. 3. Delinquent Accounts Payable: Delinquent accounts refer to invoices that have significant outstanding balances and have remained unpaid for an extended period, usually beyond 90 days. These accounts pose a severe risk to businesses, as they indicate an ongoing issue with payment compliance and may require more aggressive collection efforts. Effectively managing Maryland Aging Accounts Payable helps businesses maintain healthy cash flow, improve vendor relationships, and mitigate financial risks. It allows organizations to identify potential cash flow bottlenecks, address payment disputes promptly, and negotiate favorable payment terms with suppliers. Utilizing software solutions or accounting systems tailored for tracking and managing accounts payable helps streamline the aging process, ensuring accurate reporting and efficient management of outstanding invoices in compliance with Maryland's financial regulations.
Maryland Aging Accounts Payable
Description
How to fill out Aging Accounts Payable?
Choosing the best lawful papers web template might be a struggle. Of course, there are a variety of web templates accessible on the Internet, but how will you discover the lawful develop you will need? Make use of the US Legal Forms site. The support provides a huge number of web templates, such as the Maryland Aging Accounts Payable, which can be used for business and private requires. All of the types are checked out by professionals and satisfy federal and state specifications.
Should you be currently listed, log in for your bank account and click the Obtain switch to get the Maryland Aging Accounts Payable. Make use of your bank account to look throughout the lawful types you may have bought earlier. Check out the My Forms tab of your respective bank account and have one more version of the papers you will need.
Should you be a new customer of US Legal Forms, listed below are easy recommendations for you to stick to:
- Initially, ensure you have selected the proper develop for your personal town/state. You can check out the shape utilizing the Preview switch and read the shape description to make sure it will be the right one for you.
- If the develop does not satisfy your expectations, take advantage of the Seach area to find the proper develop.
- When you are certain that the shape is suitable, go through the Buy now switch to get the develop.
- Opt for the costs plan you need and type in the required info. Create your bank account and purchase the transaction utilizing your PayPal bank account or bank card.
- Opt for the document file format and obtain the lawful papers web template for your gadget.
- Complete, edit and print and indicator the attained Maryland Aging Accounts Payable.
US Legal Forms is the largest catalogue of lawful types for which you can find different papers web templates. Make use of the service to obtain skillfully-made files that stick to condition specifications.
Form popularity
FAQ
The accounts payable turnover in days shows the average number of days that a payable remains unpaid. To calculate the accounts payable turnover in days, simply divide 365 days by the payable turnover ratio. Therefore, over the fiscal year, the company takes approximately 60.53 days to pay its suppliers.
The Accounts Payable Aging Report lists vendors to which you owe money in the rows. The columns separate your bills by how many days they are overdue, with the first column being bills that are not overdue, and the fifth column being bills that are more than 90 days overdue.
To prepare accounts receivable aging report, sort the unpaid invoices of a business with the number of days outstanding. This report displays the amount of money owed to you by your customers for good and services purchased.
How to create an accounts receivable aging reportStep 1: Review open invoices.Step 2: Categorize open invoices according to the aging schedule.Step 3: List the names of customers whose accounts are past due.Step 4: Organize customers based on the number of days outstanding and the total amount due.
The accounts payable turnover in days shows the average number of days that a payable remains unpaid. To calculate the accounts payable turnover in days, simply divide 365 days by the payable turnover ratio. Therefore, over the fiscal year, the company takes approximately 60.53 days to pay its suppliers.
An accounts payable aging report (or AP aging report) is a vital accounting document that outlines the due dates of the bills and invoices a business needs to pay. The opposite of an AP aging report is an accounts receivable aging report, which offers a timeline of when a business can expect to receive payments.
Simply put, accounts payable aging reports gives you an overview of what your business owes for supplies, inventory, and services. A quick glance at this report reveals the identities of your creditors, how much money is owed to each creditor and how long that money has been owed.
An accounts payable aging report (or AP aging report) is a vital accounting document that outlines the due dates of the bills and invoices a business needs to pay. The opposite of an AP aging report is an accounts receivable aging report, which offers a timeline of when a business can expect to receive payments.
AP Aging ReportsGo to Reports on the top menu.Choose Vendors and Payables.Select A/P Aging Detail.Tick the Customize Report tab.In the Dates field choose Custom.Enter the date for April in the From and To field.Tap OK.16-Feb-2021
When you pay off an invoice, remove the current or past due amount from your report. For example, say you paid off the $100 invoice that's 61 90 days past due for Vendor 3. After you pay Vendor 3 the $100, make sure you change the 61 90 days column to say $0.