Maryland Ratification
Description
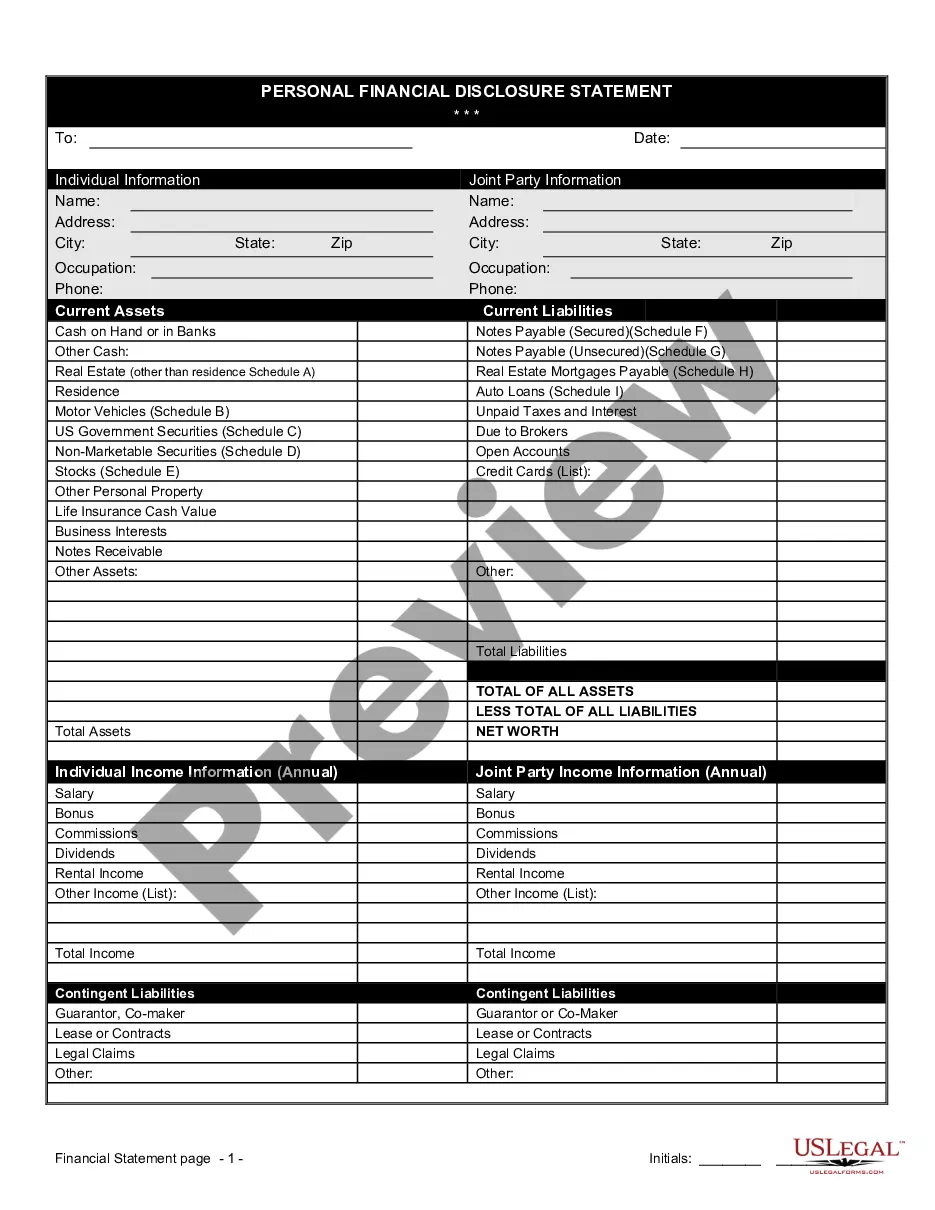
How to fill out Ratification?
Are you currently within a place where you require papers for either business or person functions nearly every day? There are tons of legal file themes available on the Internet, but getting versions you can trust isn`t simple. US Legal Forms delivers a huge number of type themes, like the Maryland Ratification, that happen to be created in order to meet federal and state demands.
Should you be already informed about US Legal Forms website and possess a free account, simply log in. Afterward, you may obtain the Maryland Ratification design.
Should you not offer an account and need to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps:
- Obtain the type you need and ensure it is to the right area/county.
- Use the Review key to analyze the form.
- See the information to ensure that you have selected the right type.
- In the event the type isn`t what you`re trying to find, utilize the Search industry to obtain the type that meets your requirements and demands.
- Once you find the right type, click Buy now.
- Select the pricing plan you desire, fill in the desired details to make your bank account, and purchase your order using your PayPal or Visa or Mastercard.
- Decide on a practical document structure and obtain your copy.
Locate each of the file themes you possess purchased in the My Forms menu. You can get a further copy of Maryland Ratification whenever, if necessary. Just go through the essential type to obtain or printing the file design.
Use US Legal Forms, probably the most substantial assortment of legal kinds, to save lots of efforts and avoid errors. The assistance delivers professionally manufactured legal file themes that can be used for an array of functions. Make a free account on US Legal Forms and start generating your lifestyle a little easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
Maryland joined the Union on April 28, 1788, as the seventh state. The area of Maryland was part of the original territory of the United States. It was chartered as a colony in 1632.
Maryland joined the Union on April 28, 1788, as the seventh state. The area of Maryland was part of the original territory of the United States. It was chartered as a colony in 1632.
Because of disputes over representation, voting, and the western lands claimed by some states, ratification was delayed. When Maryland ratified it on March 1, 1781, the Congress of the Confederation came into being.
Maryland ratified the U.S. Constitution on April 28, 1788; it was the seventh of the original 13 states to join the Union.
Marylanders were given further incentive to ratify when Virginia agreed to relinquish its western land claims, and so the Maryland legislature ratified the Articles of Confederation on March 1, 1781.
Despite Washington's fears to the contrary, Maryland proved a strong Federalist state. Only 12 out of 76 men elected to the ratifying convention could be called Anti-Federalist, and their principal goal was to amend the Constitution, not defeat it.
Maryland: April 28, 1788. South Carolina: . New Hampshire: June 21, 1788 (With this state's ratification, the Constitution became legal.) Virginia: June 25, 1788.