Arbitration is a process in which the disputing parties choose a neutral third person, or arbitrator, who hears both sides of the dispute and then renders a decision. The big difference between mediation and arbitration is that a mediator helps the parties to fashion their own settlement, while an arbitrator decides the issue. An arbitrator is more like a judge than a mediator. The parties go into arbitration knowing that they will be bound by the decision. Arbitration is unlike litigation in that the parties choose the arbitrator, the proceedings are conducted in a private manner, and the rules of evidence and procedure are informal. Also, in arbitration, the arbitrators tend to be experts in the issues they are called on to decide. Arbitration has been the widest used ADR process in the business world, and would be especially desirable where the parties do not want to litigate an issue, but do want a binding decision. They can go into arbitration knowing that they can get a quick and relatively inexpensive decision, by which they agree they will be bound.
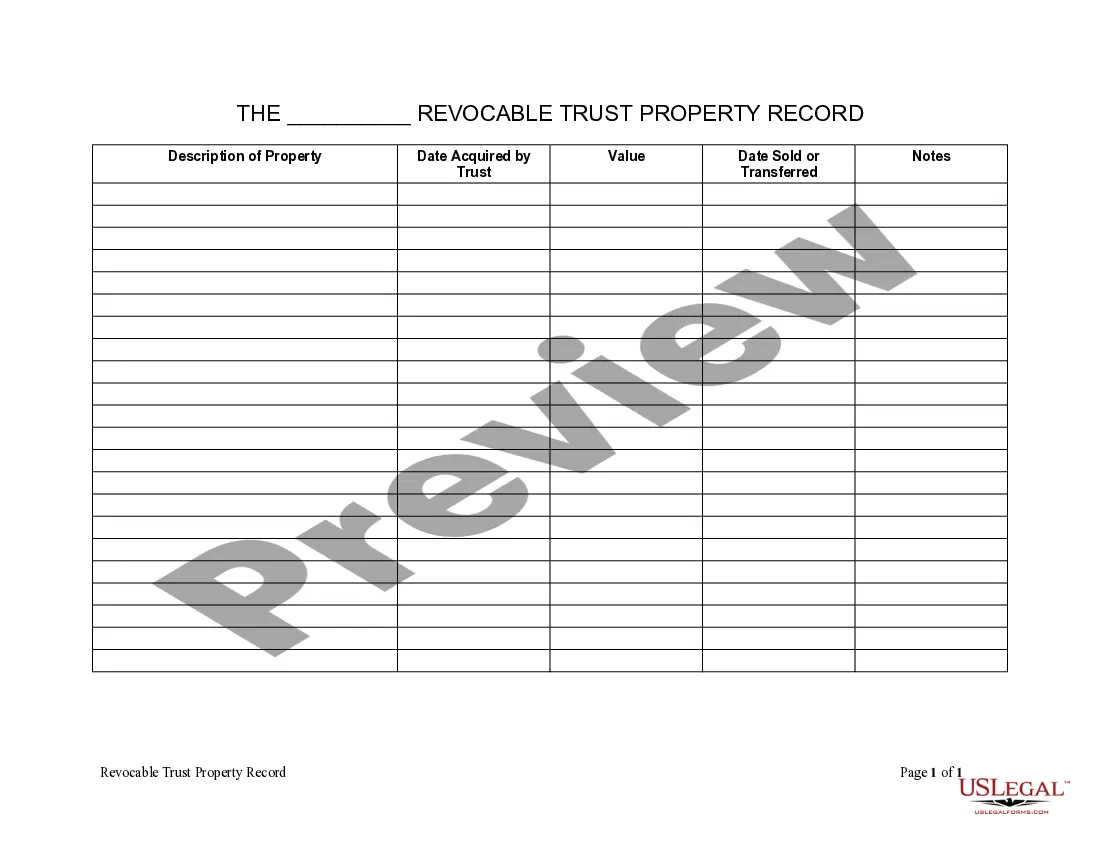
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.