A patent is a grant of a property right by the Government to an inventor. The United States Constitution gives Congress the right to provide for patent protection in legislation in order to encourage useful inventions. The patent itself provides a detailed description of the invention, and how it is used or how to make it. Thus, if you obtain a patent you cannot keep the matter secret, which is the province of Trade Secret Law. A patent enables the owner to exclude others from making, using or selling the invention for the life of the patent.
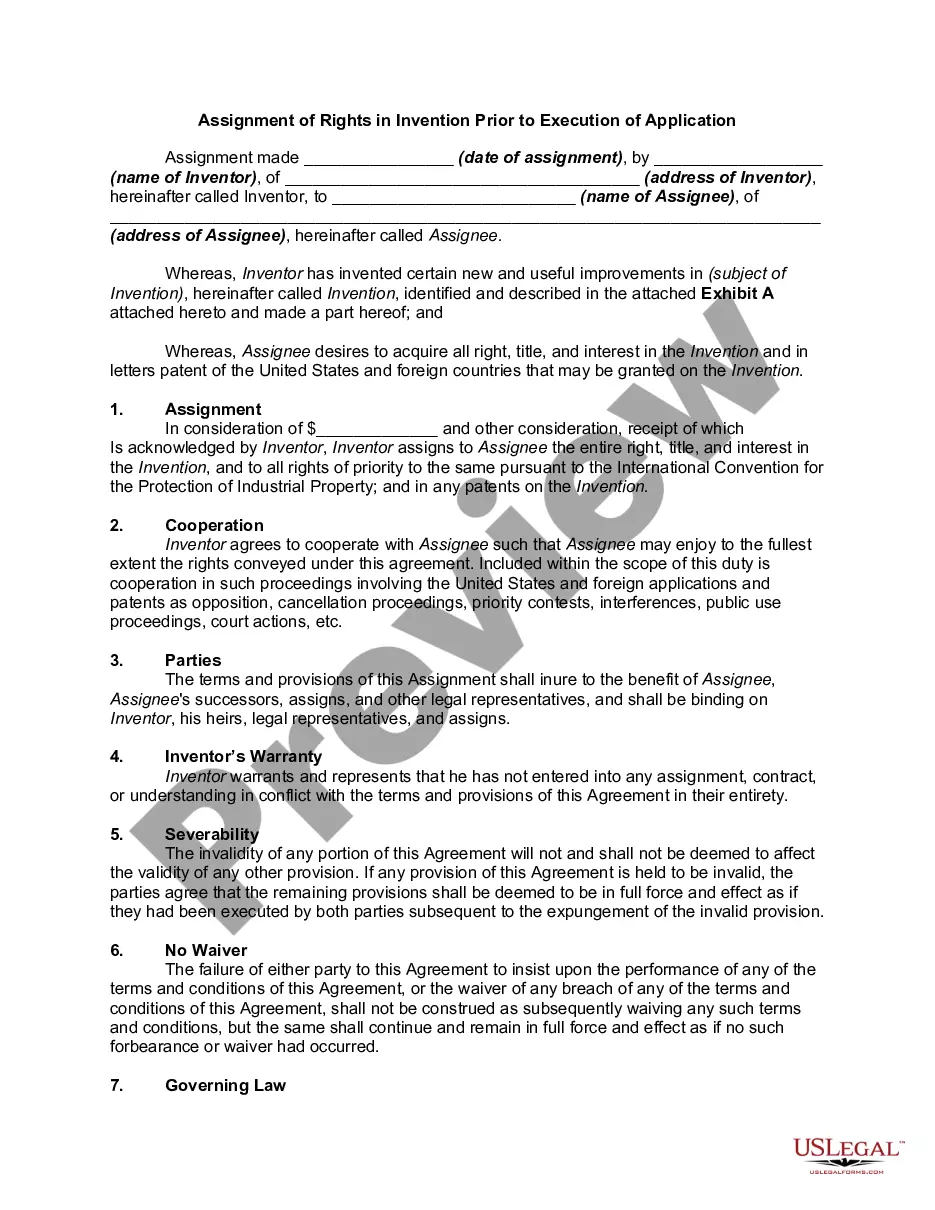
Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application
Description
How to fill out Assignment Of Rights In Invention Prior To Execution Of Application?
US Legal Forms - one of the most notable repositories of legal templates in the United States - offers a broad selection of legal document formats that you can download or print.
By utilizing the website, you will access thousands of forms for commercial and personal purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can find the most recent forms like the Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application within minutes.
If you hold a monthly subscription, Log In and download the Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application from your US Legal Forms library. The Download button will appear on every form you view. You have access to all previously downloaded forms in the My documents section of your account.
Proceed with the transaction.
Use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the purchase. Choose the format and download the form to your system. Edit it. Fill out, modify, print, and sign the downloaded Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application. Each template you save in your account has no expiration date, meaning you own it permanently. Therefore, if you wish to download or print another copy, simply go to the My documents section and click on the form you need. Access the Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application with US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive collections of legal document templates. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal needs and requirements.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for the city/state.
- Click the Preview button to examine the content of the form.
- Read the description of the form to confirm you have chosen the right one.
- If the form does not meet your needs, use the Search section at the top of the page to find the one that does.
- If you are satisfied with the form, confirm your choice by clicking the Purchase Now button.
- Then, select the payment plan you prefer and provide your information to create an account.
Form popularity
FAQ
Whether your employer owns your invention often depends on the terms of your employment contract and the specifics of state law, particularly regarding Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application. Generally, if you develop an invention using company resources or during work hours, your employer may have claims to ownership. However, personal projects created outside of work time usually remain yours. Engaging with legal resources like US Legal Forms can help clarify your rights and obligations regarding ownership and assignments.
A confidentiality and invention assignment agreement with Amazon outlines the terms under which an inventor agrees to share their ideas with the company while ensuring that their rights are protected. This type of agreement is essential in the context of Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, as it protects your intellectual property while allowing you to collaborate with Amazon. It also provides assurances that your confidential information stays secure. To navigate this process efficiently, consider using US Legal Forms for clear and concise agreement templates.
An invention assignment is a legal document that allows an inventor to transfer ownership rights of their invention to another party. In the context of Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, this document ensures that any rights to the invention are formally recognized and documented. By signing an assignment, you provide clarity and security regarding ownership, which can be crucial for both individuals and businesses. Utilizing US Legal Forms can help you create a tailored invention assignment that suits your specific needs.
The assignment of invention refers to the legal process where an inventor transfers the ownership rights of an invention to another party, typically an employer or a company. This agreement ensures that the entity purchasing the rights has complete control over the invention's use and commercialization. Understanding the Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application is essential to navigate these agreements effectively.
Deciding whether to patent or trademark depends on the nature of your invention. A patent protects your invention's functionality, while a trademark protects the brand identity associated with your product. If your focus is on an innovative process or product, the Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application will be critical for patenting, ensuring your rights are secured.
Gaining rights to an invention often starts with documenting your creation and understanding your employment agreements. If you work for a company, it is vital to review any assignment agreements in place, such as the Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application. These agreements dictate whether the rights belong to you or your employer.
Legal rights to inventions typically stem from patent law, which grants inventors exclusive rights to their creations for a certain period. To secure these rights, inventors must apply for and obtain a patent, establishing their claim to the invention. The Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application is essential in this context, as it outlines who holds the rights before filing a patent.
Licensing your invention involves granting permission to another party to use, make, or sell your invention in exchange for royalties or other compensation. To start, you should prepare a licensing agreement detailing the terms of use. Utilizing the Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application can help clarify ownership and rights, making the licensing process smoother.
When you execute a confidentiality and invention assignment agreement with the company, you are legally agreeing to protect its confidential information and assign your rights to any inventions created during your employment. This means any inventions or innovations you create within your work scope belong to the company. The Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application is crucial here, as it specifies the legal ownership of your inventions.
An employee assignment agreement is a legal contract that specifies that any inventions created by an employee during their work will belong to the employer. This type of agreement is crucial for businesses to secure intellectual property developed by their staff. When navigating the Maine Assignment of Rights in Invention Prior to Execution of Application, having a clear employee assignment agreement helps clarify ownership and protect innovative contributions.