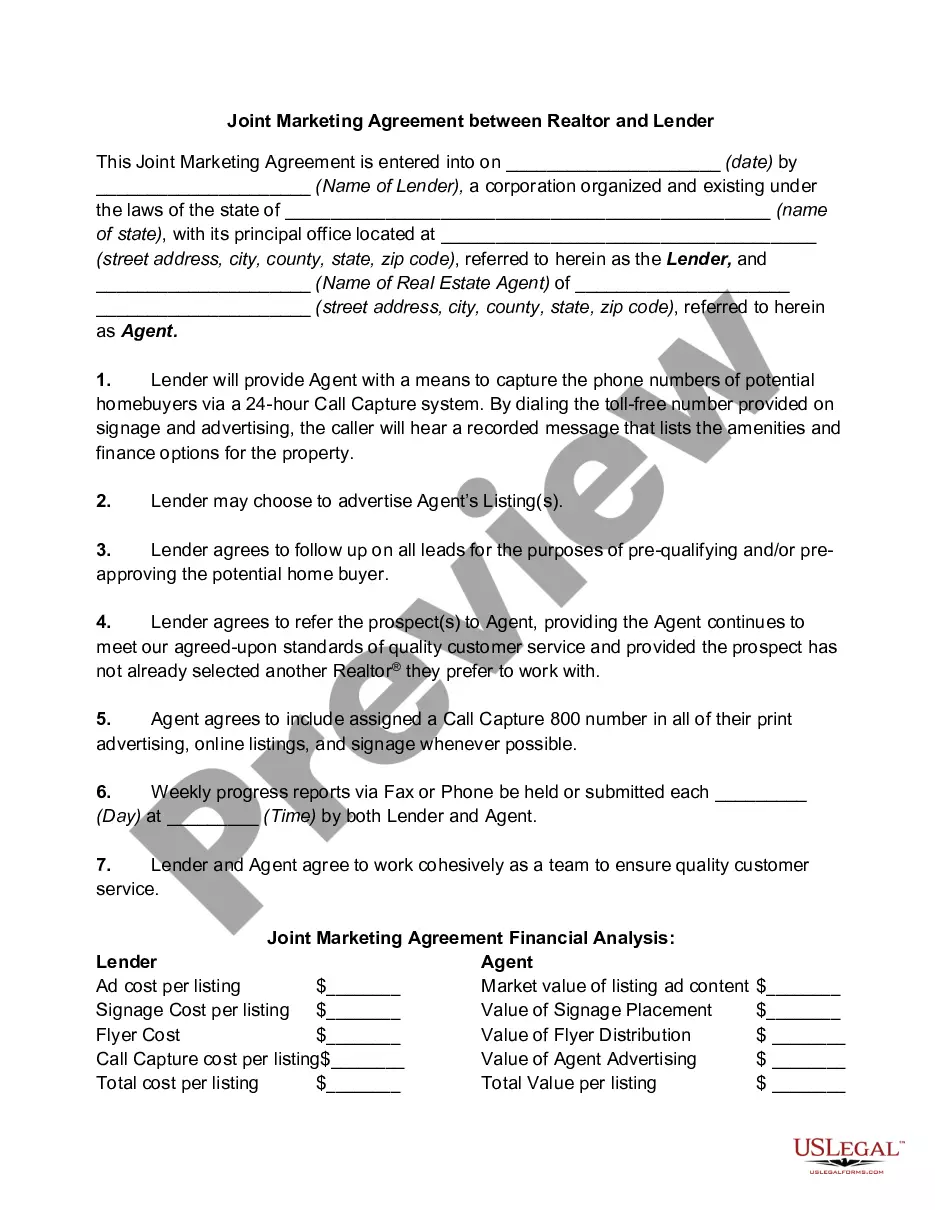
Maine Indemnification of Buyer and Seller of Business is a legal provision that acts as a protective measure for both parties involved in a business transaction. It outlines the responsibility and liability of the buyer and the seller, regarding any potential losses, damages, claims, or liabilities that may arise from their deal. In the context of business transactions, indemnification is a way to allocate the risk associated with potential issues, such as undisclosed liabilities, breach of warranties, or legal disputes, between the buyer and the seller. By including indemnification clauses in the agreement, both parties agree to compensate each other for any losses suffered due to certain specified events or actions. There are different types of indemnification provisions that can be included in a Maine business agreement: 1. General Indemnification: This type of indemnification clause requires the seller to indemnify the buyer against any losses, damages, or liabilities arising from pre-closing events or undisclosed risks related to the business or its assets. 2. Breach of Representation and Warranty Indemnification: In this type of indemnification, the seller agrees to compensate the buyer for any losses incurred if the seller's representations and warranties about the business or its assets prove to be false or misleading. 3. Tax Indemnification: This specific indemnification provision deals with potential tax liabilities related to the business. It requires the seller to indemnify the buyer against any tax debts or audits arising from the period before the sale. 4. Environmental Indemnification: This type of indemnification clause primarily focuses on potential environmental liabilities associated with the operations of the business or any prior non-compliant practices. The seller agrees to indemnify the buyer against any costs or penalties resulting from environmental damages or violations. 5. Intellectual Property Indemnification: If the business involves intellectual property assets, this indemnification clause protects the buyer from any claims or legal actions related to patent, copyright, trademark infringement, or any misappropriation of trade secrets. The seller agrees to indemnify the buyer for any resulting liabilities. It's important to note that the specific details of indemnification provisions, including the scope, limitations, conditions, and the indemnification period, are usually negotiated and included in the purchase agreement. The objective is to ensure that the buyer is adequately protected from any unforeseen risks or liabilities that may arise after the transaction is completed, while the seller is not unduly burdened with long-term obligations. Consulting with a legal professional experienced in Maine business law is recommended to ensure the indemnification provisions are properly tailored to the specific circumstances of the transaction.
Maine Indemnification of Buyer and Seller of Business
Description
How to fill out Maine Indemnification Of Buyer And Seller Of Business?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest repositories of legal documents in the USA - provides a variety of legal document templates that you can download or print.
By using the website, you can find numerous forms for business and personal purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords.
You can access the latest versions of forms like the Maine Indemnification of Buyer and Seller of Business in just a few minutes.
Read through the form summary to confirm that you have chosen the correct document.
If the form does not meet your requirements, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- If you have a monthly membership, Log In to download the Maine Indemnification of Buyer and Seller of Business from the US Legal Forms library.
- The Download option will be visible on each form you view.
- You can access all previously downloaded forms in the My documents section of your account.
- If you are new to using US Legal Forms, here are simple steps to get started.
- Make sure you have selected the appropriate form for your city/state.
- Check the content of the form by clicking on the Preview option.
Form popularity
FAQ
A seller's indemnity clause sample typically includes clear language that specifies the seller's responsibility to indemnify the buyer against certain claims and losses. For example, it might state that the seller agrees to indemnify the buyer for any liabilities incurred due to breaches of representation and warranties related to the business sold. In the context of Maine Indemnification of Buyer and Seller of Business, having a well-defined sample can enhance the clarity of roles and obligations in the selling process. Utilizing resources like USLegalForms can help you draft a comprehensive indemnity clause.
The indemnification clause in real estate contracts serves to protect one party from potential losses caused by the other party's actions or omissions. In the context of Maine Indemnification of Buyer and Seller of Business, this clause typically outlines the conditions under which the seller must compensate the buyer for losses that may occur after the transaction. It can cover issues such as legal disputes, environmental problems, or undisclosed property defects. This clause is a vital component in ensuring a smoother real estate transaction.
An indemnity from the seller is a legal commitment made by the seller to protect the buyer from certain losses or claims that may arise after the sale. This assurance is crucial in the context of Maine Indemnification of Buyer and Seller of Business. Essentially, it ensures that if any unforeseen issues or disputes arise, the seller will cover the associated costs, giving the buyer peace of mind. This protection allows both parties to engage in the transaction with confidence.
Not having an indemnity clause can result in uncertainty and increased liability exposure for both buyers and sellers. In the Maine indemnification of buyer and seller of business, this lack of protection can create financial strain if unforeseen issues arise. Without this clause, one party may bear significant costs alone. Utilizing legal resources can help ensure your contracts include necessary protections.
If there is no indemnification clause in your contract, you may face risks related to financial losses and liabilities. In Maine indemnification of buyer and seller of business, this absence can leave both parties vulnerable during disputes. Consequently, unresolved issues may escalate and lead to costly legal battles. Taking advantage of comprehensive legal forms can prevent these pitfalls.
An indemnification clause is often necessary to protect both parties involved in a business transaction. When you include this clause in documents related to Maine indemnification of buyer and seller of business, you create safeguards against potential losses. This protection can enhance trust and lead to smoother negotiations. It is advisable to consult legal forms for tailored solutions.
A non indemnity clause refers to a provision in a contract that does not provide protection against losses or liabilities. In the context of Maine indemnification of buyer and seller of business, this means that parties agree not to cover each other for certain risks. This can lead to financial exposure if disputes arise. Understanding these clauses helps you make informed decisions during transactions.
Typically, the party responsible for an indemnity claim covers the associated costs. In the context of Maine indemnification of buyer and seller of business, if the indemnifying party is held liable, they will compensate the affected party for their losses. Clear agreements between buyers and sellers can help clarify these responsibilities, ensuring that both parties understand their obligations thus fostering a smoother transaction process.
Indemnification clauses can hold up in court, provided they are clearly written and adhere to state laws. In the realm of Maine indemnification of buyer and seller of business, courts typically enforce these clauses if they do not violate public policy. It’s essential to ensure that these clauses are legally sound to avoid potential challenges that could arise during disputes.
When a company agrees to indemnify you, it means they will bear the costs associated with legal claims or losses you might encounter while representing them. In the context of Maine indemnification of buyer and seller of business, this is vital for protecting the interests of buyers and sellers alike. This agreement serves as a foundation for trust, allowing individuals to engage in business without the constant worry of personal exposure to financial risk.
More info
By using our site and sending your request to one of our lawyer contacts, we will send the information you need to pay for the lawyer at the lowest possible price. You are paying a “fee” for a lawyer, but for your lawyers services you are getting much more than just money. We are a group of attorneys, so we know how much it costs to provide legal assistance and also how much it costs to pay for lawyers from all over the world! The only way you can know if a good lawyer is going to charge the same or even less than this is by using our site.