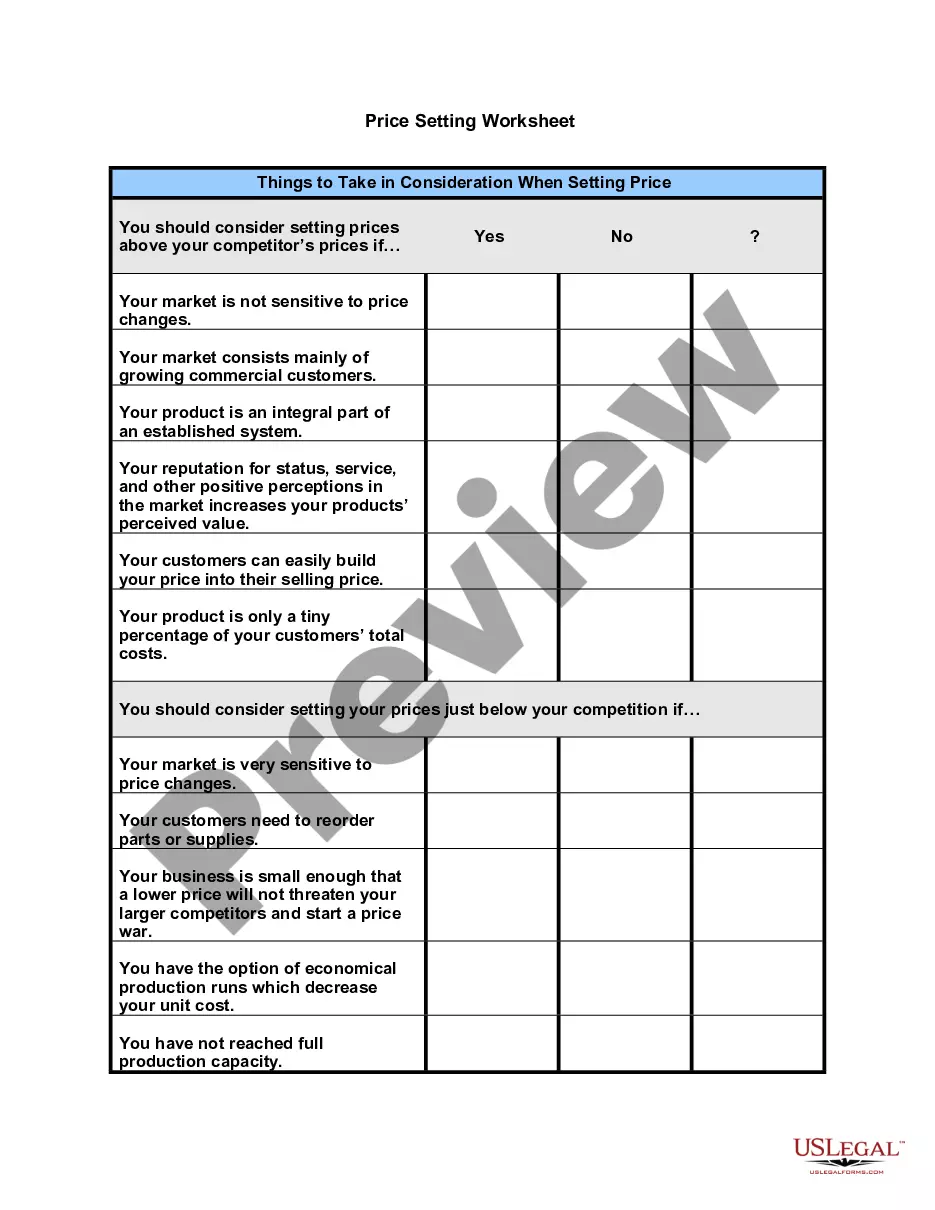
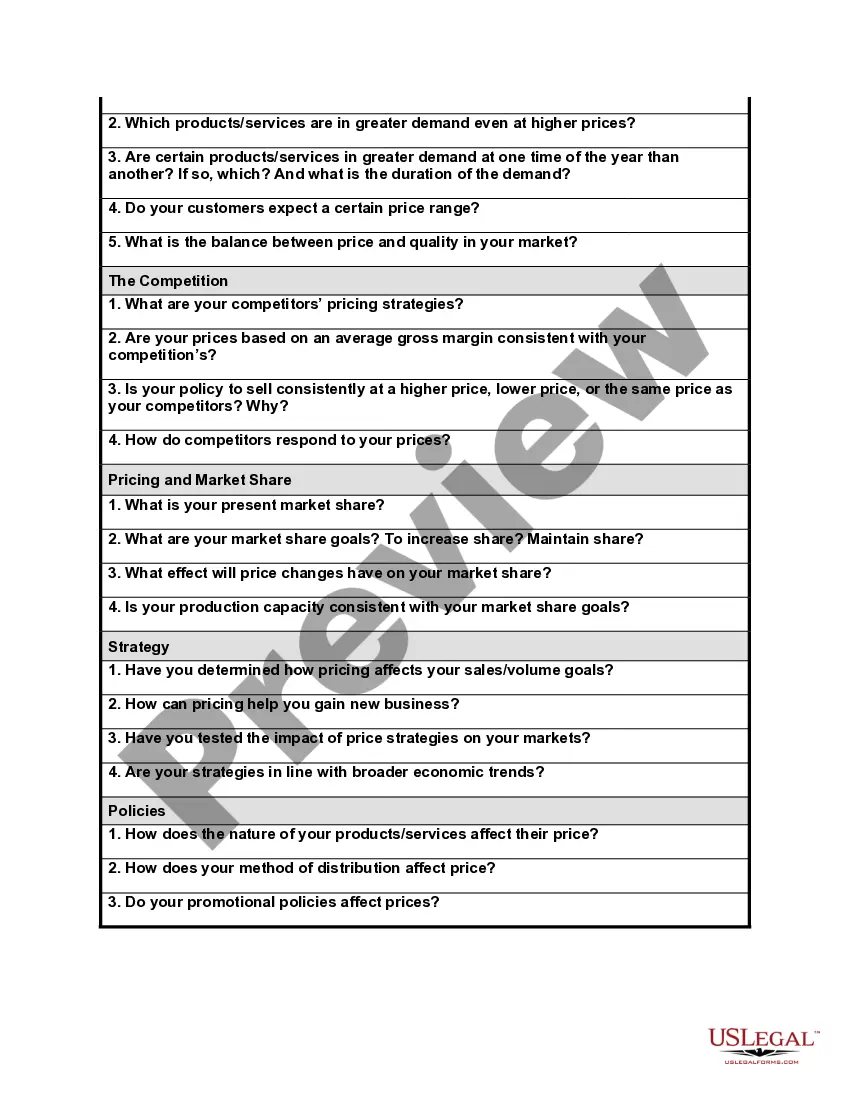
Maine Price Setting Worksheet
Description
How to fill out Price Setting Worksheet?
US Legal Forms - one of the most significant compilations of legal documents in the United States - offers a vast assortment of legal template formats that you can download or print.
By using the site, you can access thousands of forms for business and personal purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can obtain the latest documents like the Maine Pricing Worksheet within minutes.
If you already have a subscription, Log In and download the Maine Pricing Worksheet from the US Legal Forms collection. The Download button will appear on every document you view. You can find all previously saved documents in the My documents section of your account.
Make modifications. Fill out, edit, print, and sign the downloaded Maine Pricing Worksheet.
Every template you add to your account has no expiry date and belongs to you indefinitely. So, if you wish to download or print another copy, just navigate to the My documents section and click on the document you need.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, here are simple instructions to help you get started.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/state. Click the Review button to examine the contents of the form. Check the form summary to confirm you have chosen the correct document.
- If the form does not suit your needs, utilize the Search field at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- If you are satisfied with the document, finalize your choice by clicking the Buy Now button. Then, select your preferred pricing plan and provide your details to sign up for an account.
- Process the order. Use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
- Select the format and download the document to your device.
Form popularity
FAQ
NOTE: A nonresident individual working in Maine as an employee is not required to pay a Maine tax or file a Maine return on income from personal services unless that individual works in Maine for more than 12 days or, having worked in Maine for more than 12 days, earns or derives income from all Maine sources totaling
If I live in Maine and work in New Hampshire do I have to file New Hampshire state taxes as well as my Maine State Taxes? No, you are not required to file a New Hampshire state return. The state of New Hampshire does not have an income tax.
If you need to change or amend an accepted Maine State Income Tax Return for the current or previous Tax Year you need to complete Form 1040ME. Form 1040ME is a Form used for the Tax Return and Tax Amendment. You can prepare a 2021 Maine Tax Amendment on eFile.com, however you can not submit it electronically.
If you file Form 1040-NR, use Schedule NEC (Form 1040-NR) to figure your tax on income that is not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business and to figure your capital gains and losses from sales or exchanges of property that is not effectively connected with a U.S. business.
Except for certain sales of a partnership interest on or after July 1, 2005, a nonresident generally does not have to pay Maine tax on interest, dividends, alimony, pensions or other income from intangible sources unless such income is from property employed in a business carried on in Maine.
Also, generally, a nonresident individual present in Maine for business for no more than 12 days and earning no more than $3,000 from business activity in Maine is not required to pay a Maine tax or file a Maine return on that income.
No matter how short a period you worked at a job, you still will need to include a W-2 from that employer to properly file your income taxes. The Internal Revenue Service requires that income from all jobs be included on your tax return, even if the job lasted only one or two days.
The IRS isn't concerned about how long you've had a job or how many jobs it takes you to reach the minimum income thresholds; once this amount is exceeded, you are required to file taxes. As a result of these thresholds, depending on what you made, you may have to file taxes if you only worked one month.
Single, under the age of 65 and not older or blind, you must file your taxes if: Unearned income was more than $1,100. Earned income was more than $12,400. Gross income was more than the larger of $1,100 or on earned income up to $12,050 plus $350.