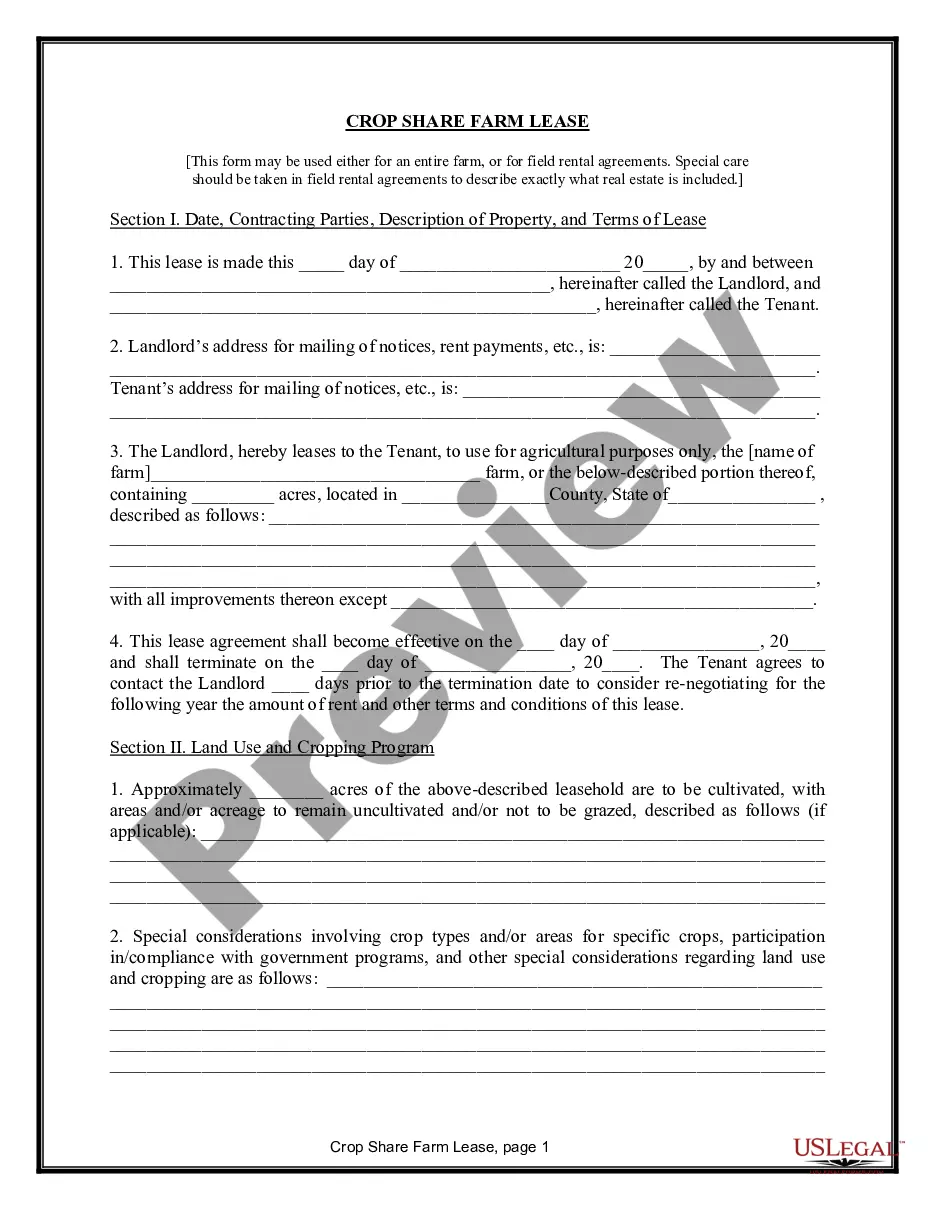
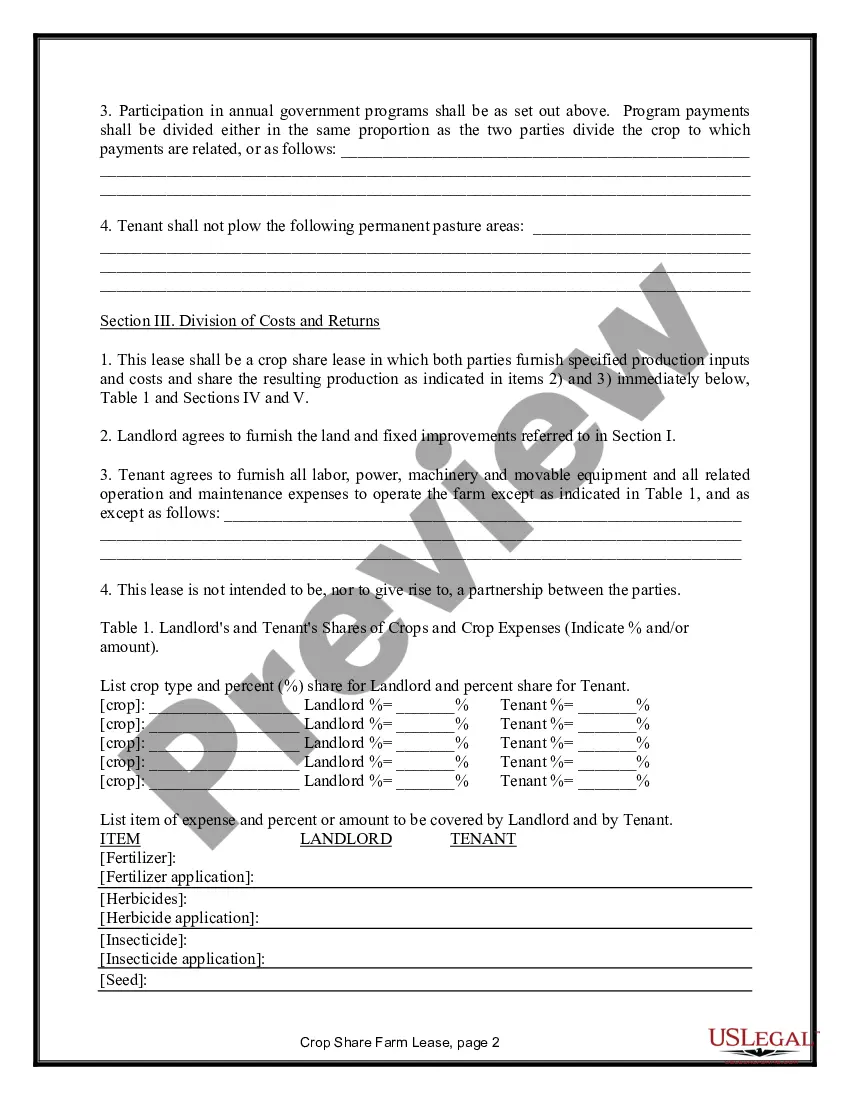
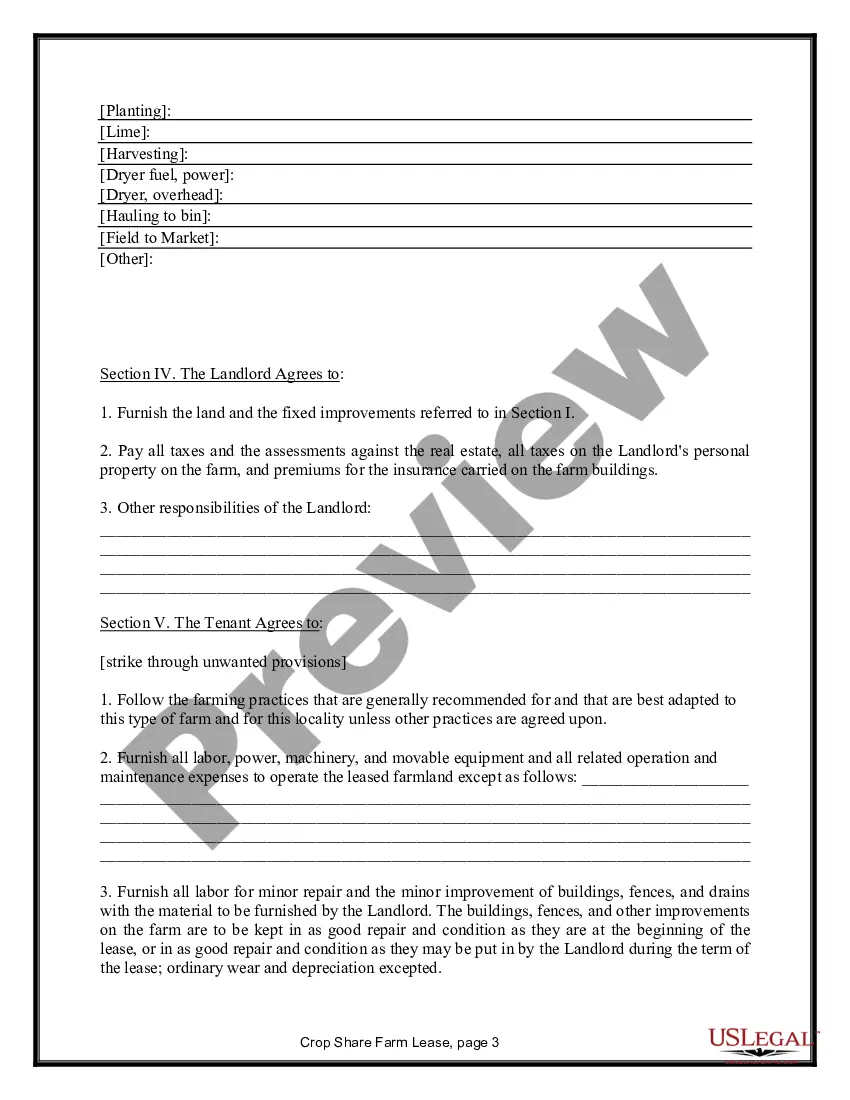
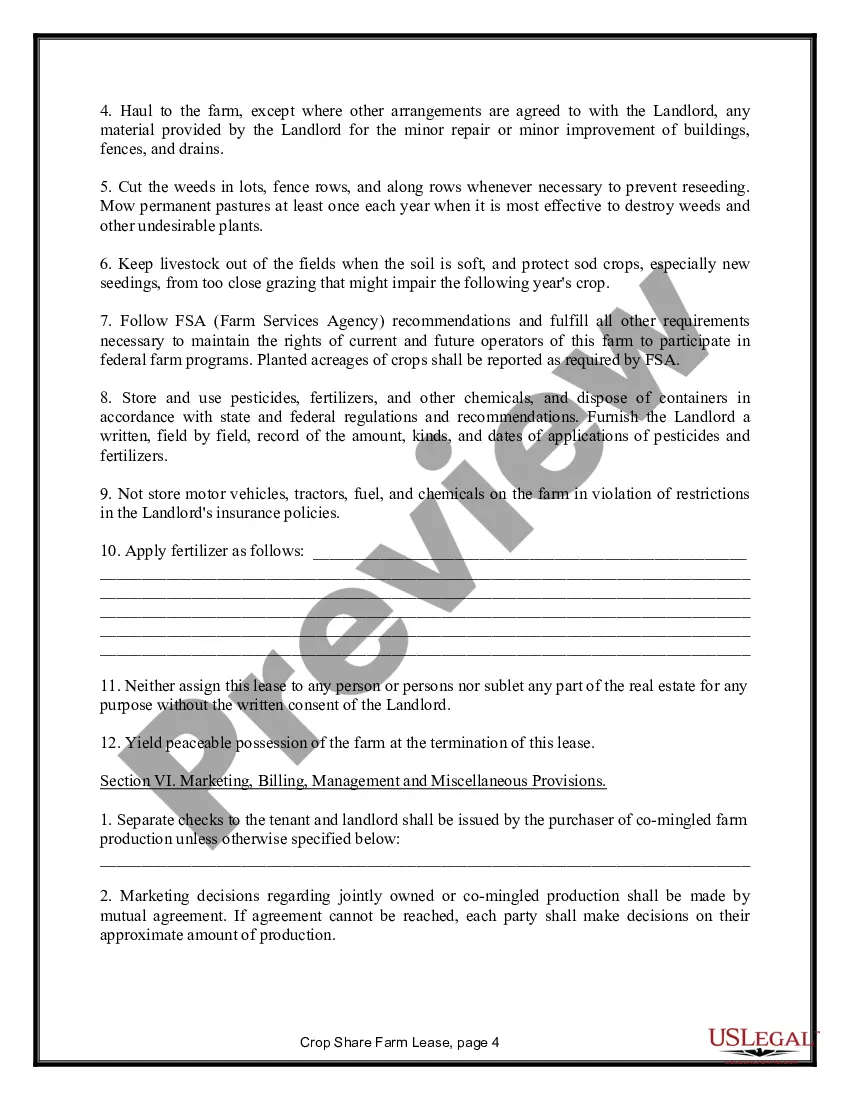
Maine Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share is an agreement between a landowner and a farmer in the state of Maine, where the landowner rents or leases their farmland to the farmer in exchange for a share of the produced crops. This type of lease or rental arrangement is common in the agricultural industry, allowing landowners to benefit from their land without actively engaging in farming, while farmers have access to land to cultivate crops. It is a mutually beneficial agreement that helps support and sustain local agriculture. There are a few different types of Maine Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share, including: 1. Traditional Crop Share: In this arrangement, the landowner and farmer agree on a specific percentage of the crop yield that will be shared between them. The landowner typically provides the land and sometimes equipment, while the farmer contributes labor, expertise, and machinery. At the end of the growing season, the total crop produced is divided based on the predetermined percentage, benefitting both parties. 2. Custom Farming Crop Share: This type of lease or rental agreement is more flexible, where the landowner compensates the farmer based on specific services provided rather than sharing the crop yield. The farmer performs various farming activities such as soil preparation, planting, harvesting, and maintenance, while the landowner may contribute financially or through other means. 3. Variable Lease or Rental Agreement: In certain cases, farms may adopt a variable crop share agreement wherein the percentage of crop share fluctuates depending on factors such as market conditions, weather patterns, or input costs. This type of lease allows for adjustment and fair distribution of risks and rewards between the landowner and farmer. 4. Organic Crop Share Lease: With the growing demand for organic produce, some farmers and landowners may enter into an organic farm lease or rental agreement. In this case, the farmer commits to using organic farming practices, and the landowner benefits from the premium prices associated with organic crops. 5. Equitable Crop Share Lease: This type of crop share lease is designed to ensure a fair distribution of risks and rewards between the landowner and farmer. It accounts for various factors such as labor, capital investment, land quality, and market conditions to determine an equitable sharing ratio that benefits both parties. Maine Farm Lease or Rental — Crop Share provides opportunities for landowners to utilize their land resources and simultaneously support the farming community. It enables farmers to access land for cultivation without the need for large capital investments, ultimately promoting sustainable agriculture and food production in the state of Maine.
Maine Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share
Description
How to fill out Maine Farm Lease Or Rental - Crop Share?
Choosing the right lawful papers design could be a battle. Obviously, there are plenty of web templates available on the Internet, but how can you get the lawful type you need? Take advantage of the US Legal Forms site. The service offers 1000s of web templates, including the Maine Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share, that can be used for organization and personal needs. All the varieties are examined by experts and meet state and federal demands.
In case you are already signed up, log in for your bank account and then click the Obtain option to have the Maine Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share. Use your bank account to check from the lawful varieties you possess bought earlier. Visit the My Forms tab of the bank account and obtain yet another version in the papers you need.
In case you are a fresh customer of US Legal Forms, listed below are basic instructions so that you can follow:
- Very first, make sure you have selected the right type for the area/region. It is possible to check out the form utilizing the Review option and look at the form explanation to make sure this is the best for you.
- In the event the type will not meet your expectations, make use of the Seach discipline to discover the right type.
- Once you are certain that the form is proper, go through the Get now option to have the type.
- Opt for the pricing strategy you desire and enter in the essential information and facts. Design your bank account and purchase an order making use of your PayPal bank account or bank card.
- Opt for the submit file format and acquire the lawful papers design for your product.
- Full, revise and print out and indication the received Maine Farm Lease or Rental - Crop Share.
US Legal Forms may be the greatest collection of lawful varieties in which you will find a variety of papers web templates. Take advantage of the company to acquire appropriately-manufactured files that follow status demands.