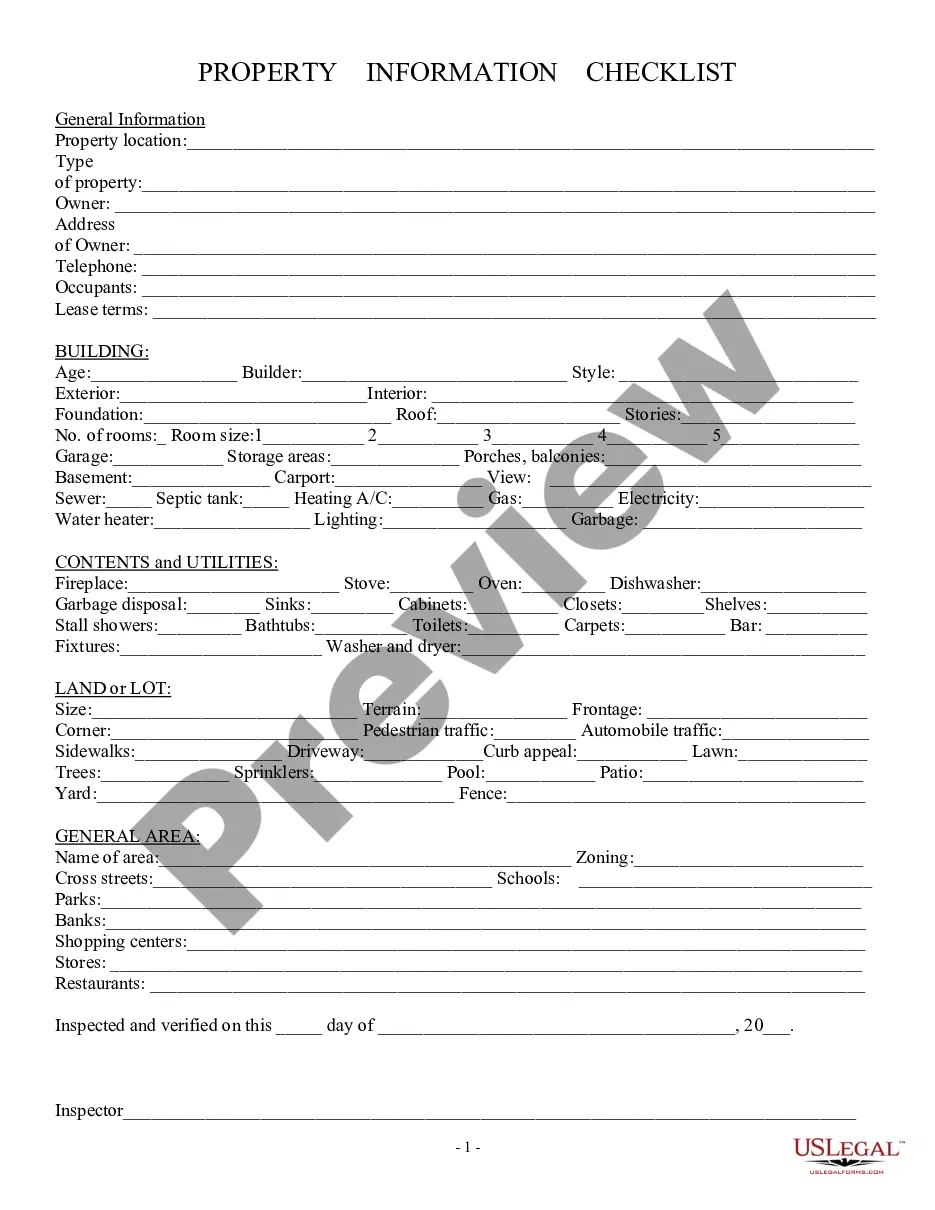
Maine Checklist of Information to Obtain For Evaluating Environmental Matters on Producing Properties
Description
How to fill out Checklist Of Information To Obtain For Evaluating Environmental Matters On Producing Properties?
You may commit hours on the web trying to find the authorized file template that meets the federal and state demands you require. US Legal Forms provides thousands of authorized kinds which can be analyzed by specialists. You can easily obtain or printing the Maine Checklist of Information to Obtain For Evaluating Environmental Matters on Producing Properties from our service.
If you have a US Legal Forms account, it is possible to log in and then click the Acquire button. Next, it is possible to full, edit, printing, or indicator the Maine Checklist of Information to Obtain For Evaluating Environmental Matters on Producing Properties. Each authorized file template you acquire is your own property permanently. To obtain another duplicate of the purchased develop, go to the My Forms tab and then click the corresponding button.
Should you use the US Legal Forms website the very first time, follow the simple recommendations beneath:
- Very first, make certain you have chosen the best file template for the county/area that you pick. Read the develop outline to ensure you have chosen the appropriate develop. If offered, make use of the Preview button to search with the file template at the same time.
- In order to discover another version of the develop, make use of the Research discipline to find the template that meets your needs and demands.
- After you have identified the template you want, click on Get now to move forward.
- Select the costs plan you want, key in your references, and register for a free account on US Legal Forms.
- Total the deal. You may use your credit card or PayPal account to purchase the authorized develop.
- Select the structure of the file and obtain it to the device.
- Make alterations to the file if required. You may full, edit and indicator and printing Maine Checklist of Information to Obtain For Evaluating Environmental Matters on Producing Properties.
Acquire and printing thousands of file layouts while using US Legal Forms web site, that offers the greatest selection of authorized kinds. Use professional and condition-distinct layouts to handle your organization or personal needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
In summary, the key elements of environmental impact assessment include scoping, baseline data collection, impact assessment, mitigation measures, monitoring and evaluation, and public participation.
A checklist for environmental impact assessment (EIA) is used to identify the potential environmental impacts of a proposed project or development. It is a simple and effective method for conducting preliminary assessments and screening proposed projects to determine if a full EIA is required.
7 Steps to Conducting a Mining EIA Environmental screening. Screening is the first stage in an EIA. ... Scoping. This second stage allows you to prioritize critical issues to keep in mind during an EIA while eliminating others. ... Impact assessment and mitigation. ... Impact management. ... EIA report. ... Review and licensing. ... Monitoring.
A NEPA EA is a comprehensive study that identifies environmental impacts of a land development action and analyzes a broad set of parameters including biodiversity, environmental justice, wetlands, air and water pollution, traffic, geotechnical risks, public safety issues and also hazardous substance issues.
A NEPA EA is a comprehensive study that identifies environmental impacts of a land development action and analyzes a broad set of parameters including biodiversity, environmental justice, wetlands, air and water pollution, traffic, geotechnical risks, public safety issues and also hazardous substance issues.
The EIA checklist is used to identify potential impacts that could result from the project and to determine if additional studies or mitigation measures are necessary to minimize those impacts.
The International Association for Impact Assessment (IAIA) defines an environmental impact assessment as "the process of identifying, predicting, evaluating and mitigating the biophysical, social, and other relevant effects of development proposals prior to major decisions being taken and commitments made".