A secured transaction is created when a buyer or borrower (debtor) grants a seller or lender (creditor or secured party) a security interest in personal property (collateral). A security interest allows a creditor to repossess and sell the collateral if a debtor fails to pay a secured debt.
The Truth-in-Lending Act (TILA) is part of the Federal Consumer Credit Protection Act. The purpose of the TILA is to make full disclosure to debtors of what they are being charged for the credit they are receiving. The Act merely asks lenders to be honest to the debtors and not cover up what they are paying for the credit. Regulation Z is a federal regulation prepared by the Federal Reserve Board to carry out the details of the Act. TILA applies to consumer credit transactions. Consumer credit is credit for personal or household use and not commercial use or business purposes.
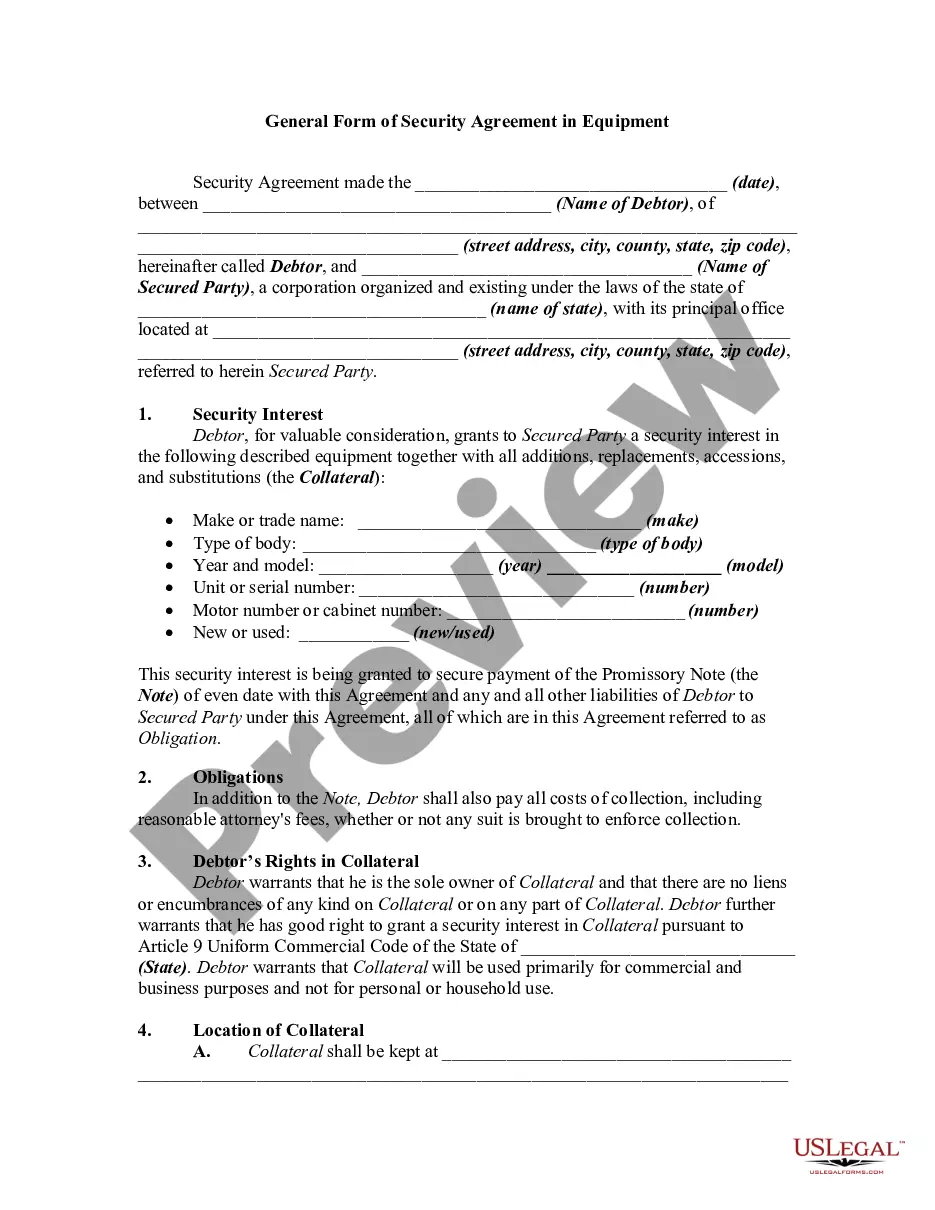
The Michigan General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment is a legal document that establishes a security interest in equipment to secure a loan or debt. It provides a detailed description of the rights and obligations of both the debtor and the creditor concerning the equipment. This agreement is essential in protecting the creditor's interest and ensuring that the debtor fulfills their obligations. The Michigan General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment includes several key elements. Firstly, it identifies the parties involved, including the debtor (borrower) and the creditor (lender). It also provides their relevant contact information, such as names, addresses, and phone numbers. Additionally, this agreement outlines the specific equipment that the security interest covers. It includes a comprehensive and detailed description of the equipment, including its make, model, serial number, and any unique identifiers. This description is crucial for establishing a clear understanding of which equipment the security interest applies to. The agreement also specifies the terms and conditions under which the equipment can be used or sold by the debtor. It outlines the debtor's responsibilities to maintain the equipment, keep it insured, and ensure it remains in good working condition. Furthermore, it may indicate restrictions on transferring or encumbering the equipment without the creditor's consent. Moreover, the agreement defines the remedies available to the creditor in case of default or non-payment by the debtor. It may include provisions for repossession and sale of the equipment to satisfy the outstanding debt. These provisions ensure that the creditor has a legal mechanism to recover their investment if the debtor fails to meet their obligations. It is important to note that while the Michigan General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment serves as a general template, specific types or variations of this agreement may exist. Some possible types include Michigan Specific Form of Security Agreement for Farm Equipment or Michigan Specific Form of Security Agreement for Construction Equipment. These types cater specifically to various industries where equipment plays a significant role in securing loans or debts. In summary, the Michigan General Form of Security Agreement in Equipment is a vital legal document that enables creditors to establish a security interest in equipment. It outlines the responsibilities and obligations of the debtor and creditor, details the equipment covered, and provides mechanisms for recourse in case of default. Different variations of this agreement may exist to cater to specific industries or types of equipment.