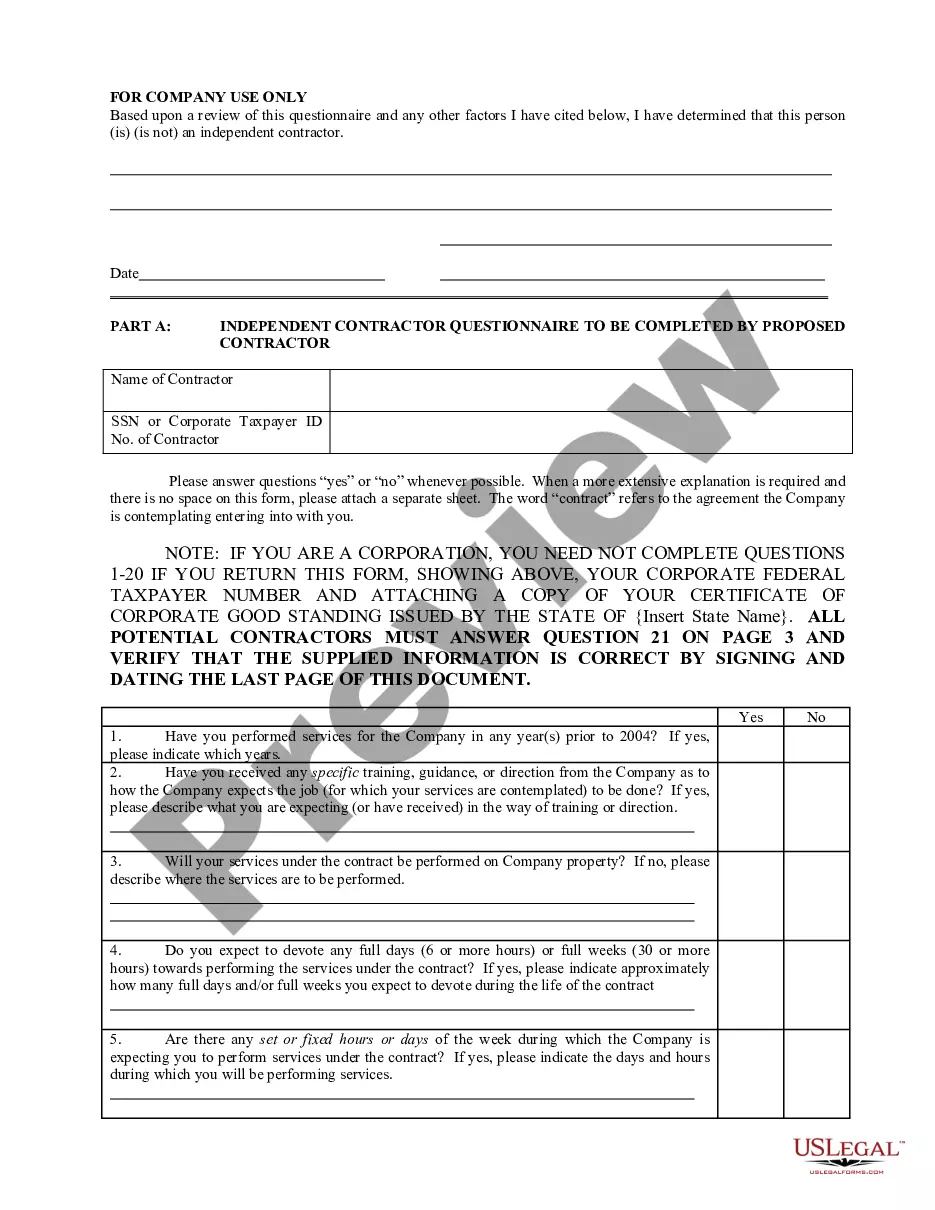
Michigan Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status
Description
How to fill out Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status?
US Legal Forms - one of the biggest collections of legal templates in the United States - offers a range of legal document templates that you can obtain or print. Through the website, you can discover thousands of forms for business and personal purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords.
You can access the latest versions of forms like the Michigan Determination of Self-Employed Contractor Status in just minutes.
If you already have an account, Log In and retrieve the Michigan Determination of Self-Employed Contractor Status from the US Legal Forms library. The Download button will appear on every form you view. You can review all previously saved forms in the My documents section of your account.
Process the transaction. Use your credit card or PayPal account to finalize the payment.
Select the format and download the form onto your device. Make changes. Fill out, modify, and print and sign the saved Michigan Determination of Self-Employed Contractor Status. Each template you add to your account has no expiration date and is yours to keep forever. Therefore, to obtain or print another copy, simply visit the My documents section and click on the form you require. Access the Michigan Determination of Self-Employed Contractor Status with US Legal Forms, the most extensive collection of legal document templates. Utilize numerous professional and state-specific templates that fulfill your business or personal needs and requirements.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for the city/county.
- Click the Review button to examine the form's content.
- Refer to the form description to confirm you have chosen the appropriate form.
- If the form does not meet your requirements, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- Once satisfied with the form, confirm your selection by clicking the Purchase now button.
- Then, select the payment option you prefer and provide your information to create an account.
Form popularity
FAQ
Becoming an independent contractor is one of the many ways to be classified as self-employed. By definition, an independent contractor provides work or services on a contractual basis, whereas, self-employment is simply the act of earning money without operating within an employee-employer relationship.
If you work for an employer, you're an employee. If you're self-employed, you're an independent contractor.
Self contracting means you are the one overseeing the project. You are in charge of everything including budgeting, getting permits, hiring the workers, getting inspections, and keeping everything organized and clean.
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
Four ways to verify your income as an independent contractorIncome-verification letter. The most reliable method for proving earnings for independent contractors is a letter from a current or former employer describing your working arrangement.Contracts and agreements.Invoices.Bank statements and Pay stubs.
An individual who performs services for remuneration under an exclusive contract that provides for the individual's control and direction by a person, firm, or corporation possessing a public service permit or by a certificated motor carrier transporting goods or property for hire is presumed to be covered by the
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
The IRS says that someone is self-employed if they meet one of these conditions: Someone who carries on a trade or business as a sole proprietor or independent contractor, A member of a partnership that carries on a trade or business, or. Someone who is otherwise in business for themselves, including part-time business
The basic test for determining whether a worker is an independent contractor or an employee is whether the principal has the right to control the manner and means by which the work is performed.
How to demonstrate that you are an independent worker on your resumeMention that time when you had to work on a project on your own.Talk about projects that required extra accountability.Describe times when you had to manage several projects all at once.More items...