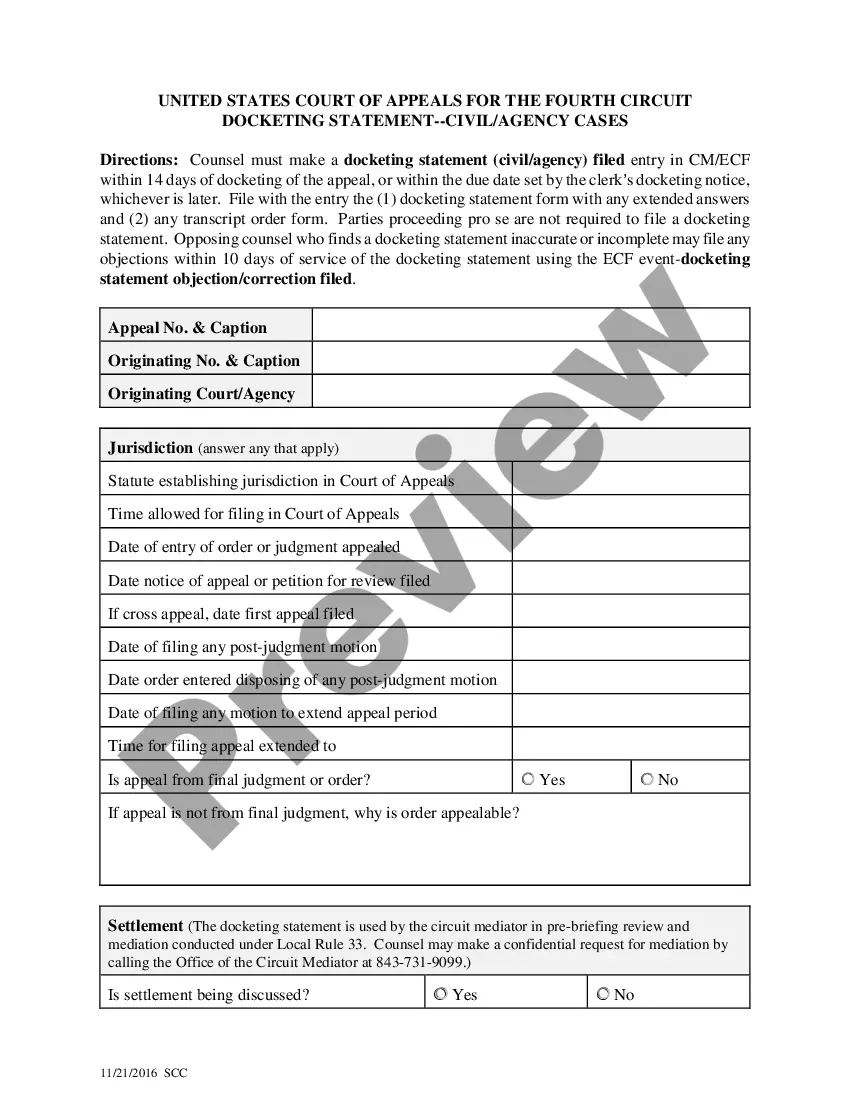
Michigan EULA — End User License Agreement is a legal contract between the software owner and the end user that outlines the terms and conditions under which the software can be used. It is a vital document that governs the rights and limitations of the software usage, ensuring that both parties are protected. The Michigan EULA — End User License Agreement sets out the scope of the software license and grants the end user certain rights to use the software within defined parameters. It typically addresses issues such as the permitted use, installation, copying, modification, and distribution of the software. By agreeing to the EULA, the end user acknowledges and accepts these terms, establishing a binding agreement. There are various types of Michigan EULA — End User License Agreements, each designed to cater to specific software usage scenarios. Some common examples include: 1. Commercial Software EULA: This type of EULA is applicable for software purchased or licensed for commercial purposes. It contains provisions related to payment terms, warranty disclaimers, intellectual property rights, and restrictions on use. 2. Open Source Software EULA: Open source software typically follows a different licensing model. The EULA for open source software, such as GNU General Public License (GPL), grants users the freedom to use, modify, and distribute the software. It outlines the conditions under which the software can be shared or distributed. 3. Software as a Service (SaaS) EULA: SaaS agreements pertain to cloud-based software services. These agreements specify the terms and conditions of the service, data privacy, service level expectations, and liability limitations. 4. Mobile App EULA: Mobile app developers often require an EULA to govern the use of their applications. This EULA covers the installation, usage, data collection, and privacy aspects specific to mobile devices. 5. Freeware or Shareware EULA: Freeware or shareware EULAs designate the terms of use for software that is made available to users at no cost. It may have limitations on redistribution, usage restrictions, and disclaimers of warranties. It is important for both software owners and end users in Michigan to familiarize themselves with the specific EULA that governs the software they are dealing with, as each EULA may differ in its terms and conditions. Understanding the implications and obligations outlined in the EULA ensures compliance and fosters a positive user experience.
Michigan EULA - End User License Agreement
Description
How to fill out Michigan EULA - End User License Agreement?
Choosing the best authorized file web template might be a battle. Naturally, there are plenty of web templates available on the net, but how would you obtain the authorized kind you want? Utilize the US Legal Forms internet site. The assistance offers a large number of web templates, such as the Michigan EULA - End User License Agreement, which you can use for company and personal needs. Every one of the varieties are inspected by professionals and meet federal and state demands.
Should you be already signed up, log in to the bank account and click the Down load option to have the Michigan EULA - End User License Agreement. Make use of your bank account to search from the authorized varieties you may have ordered in the past. Check out the My Forms tab of your bank account and obtain one more version of your file you want.
Should you be a whole new end user of US Legal Forms, listed here are easy guidelines so that you can adhere to:
- Initial, make sure you have chosen the proper kind for the metropolis/county. You can check out the shape utilizing the Review option and read the shape explanation to ensure it is the right one for you.
- In the event the kind is not going to meet your expectations, make use of the Seach field to obtain the right kind.
- Once you are certain that the shape is suitable, go through the Acquire now option to have the kind.
- Opt for the rates prepare you need and enter in the needed details. Build your bank account and pay money for your order using your PayPal bank account or credit card.
- Opt for the submit structure and down load the authorized file web template to the product.
- Full, change and print out and sign the obtained Michigan EULA - End User License Agreement.
US Legal Forms will be the most significant catalogue of authorized varieties in which you can discover various file web templates. Utilize the company to down load professionally-manufactured paperwork that adhere to express demands.