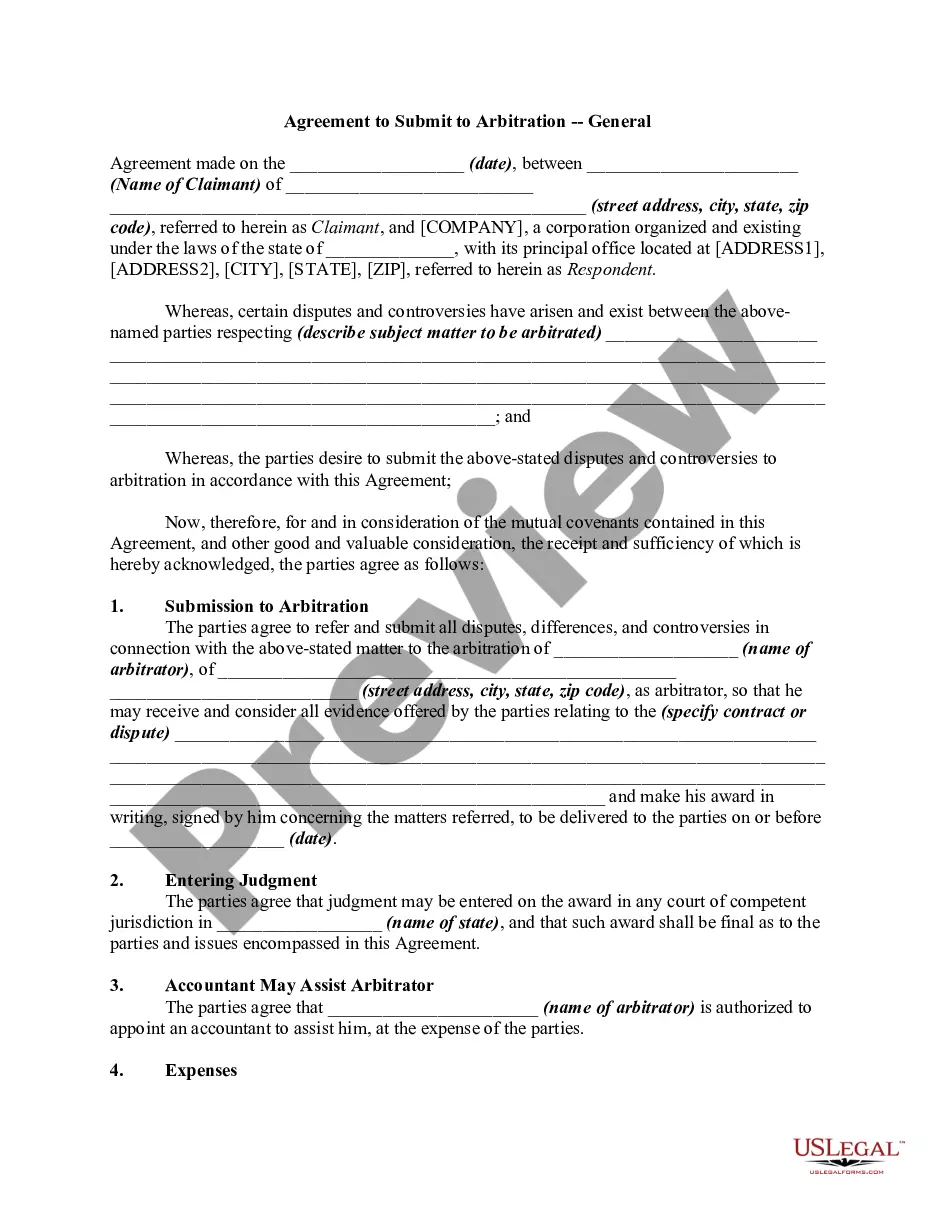
Minnesota Arbitration Submission Agreement
Description
How to fill out Arbitration Submission Agreement?
US Legal Forms - among the largest collections of legal documents in the USA - offers an extensive selection of legal document templates that you can download or print.
By using the website, you can access thousands of forms for business and personal purposes, categorized by groups, states, or keywords. You can find the latest forms like the Minnesota Arbitration Submission Agreement in just a few seconds.
If you have a membership, Log In and download the Minnesota Arbitration Submission Agreement from the US Legal Forms library. The Download button will appear on each form you view. You can access all previously downloaded forms from the My documents section of your account.
Complete the transaction. Use your credit card or PayPal account to process the payment.
Choose the format and download the form to your device. Edit. Fill out, modify, and print and sign the downloaded Minnesota Arbitration Submission Agreement. Each template you added to your account does not have an expiration date and is yours permanently. So, if you want to download or print another copy, just visit the My documents section and click on the form you need. Access the Minnesota Arbitration Submission Agreement with US Legal Forms, the most comprehensive library of legal document templates. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal requirements and regulations.
- Ensure you have chosen the correct form for your city/state.
- Click the Preview button to review the form's content.
- Check the form description to confirm that you have selected the correct form.
- If the form doesn't meet your needs, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- Once you're satisfied with the form, confirm your selection by clicking the Purchase now button.
- Then, choose the payment plan you prefer and provide your details to register for an account.
Form popularity
FAQ
We noted that arbitration clauses are made before any dispute arises. Submission agreements, however, are agreements to arbitrate made after the dispute has arisen.
In the submission agreement, the parties agree to submit only a specific dispute to arbitration. They can do so at the time the dispute arises, while the parties are engaged in negotiations for a resolution, or even if the dispute is already being actively litigated in court.
A submission agreement provides for the referral of disputes for resolution by arbitration. A submission agreement maybe used in circumstances where the parties have not previously included a dispute resolution clause in their contract and/or it may be used to supersede and replace prior dispute resolution agreements.
Arbitration can be binding (which means the participants must follow the arbitrator's decision and courts will enforce it) or nonbinding (meaning either party is free to reject the arbitrator's decision and take the dispute to court, as if the arbitration had never taken place). Binding arbitration is more common.
Submission Agreement means a written agreement wherein parties have agreed to submit all or certain disputes which have arisen or which may arise between them, to mediation.
What is binding arbitration? Binding arbitration involves the submission of a dispute to a neutral party who hears the case and makes a decision. Arbitration takes the place of a trial before a judge or jury.
Are Arbitration Agreements Legally Binding? Arbitration agreements are legally-binding if the case is disputed through binding arbitration. If the arbitration is non-binding, then you can pursue the case in court. If the arbitration is binding, then it is enforceable under law.
The arbitration agreement is valid only if signed by parties with full civil act capacity, and such parties must be competent, specifically: (i) A person with full civil act capacity is at least 18 years old and does not lose or limit her/his civil act capacity or difficulties in perception, mastery of acts.