Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use
Description
How to fill out Financial Statement Form - Universal Use?
Selecting the appropriate authentic document template can be a challenge. Naturally, there are numerous templates available online, but how do you locate the specific format you require? Utilize the US Legal Forms website. The service offers a plethora of templates, including the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use, which can be utilized for business and personal purposes.
All of the forms are verified by experts and comply with state and federal regulations.
If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click the Download button to acquire the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use. Use your account to search for the legal forms you have previously purchased. Proceed to the My documents tab of your account and retrieve another copy of the document you need.
Complete, edit, print, and sign the received Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use. US Legal Forms is the largest collection of legal forms where you can find a variety of document templates. Utilize the service to download professionally produced documents that adhere to state regulations.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are simple steps for you to follow.
- First, ensure that you have chosen the correct form for your city/county. You can preview the form using the Preview button and review the form description to confirm it is suitable for you.
- If the form does not meet your needs, use the Search field to find the correct form.
- Once you are certain the form is appropriate, click the Get now button to acquire the form.
- Select the payment option you prefer and enter the necessary information. Create your account and pay for your order using your PayPal account or credit card.
- Choose the file format and download the legal document template to your device.
Form popularity
FAQ
To prepare financial statements from a bank statement, start by reviewing your bank transactions for income and expenses. Categorize these transactions accurately into your financial statement. Utilizing the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use can help you systematically organize this information for a comprehensive overview.
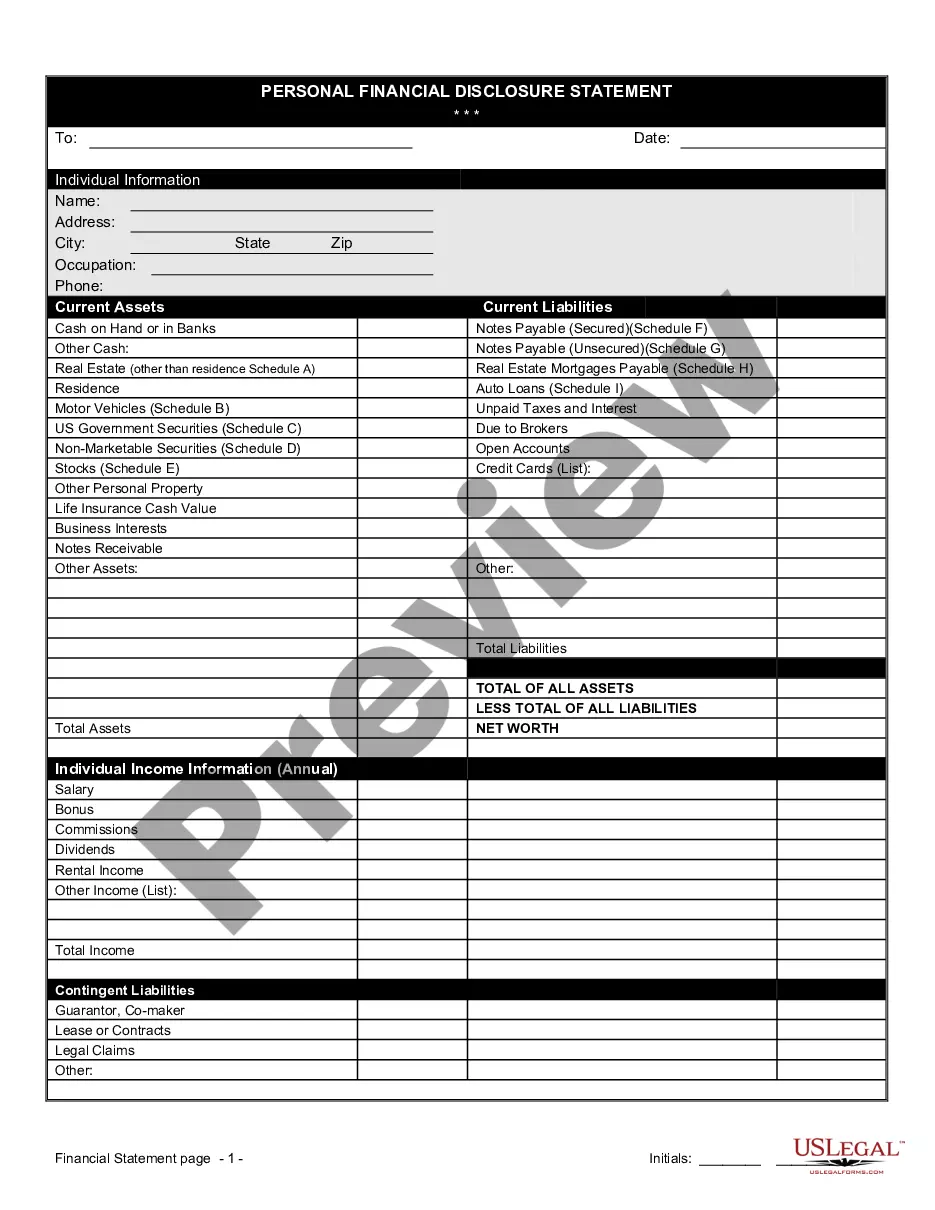
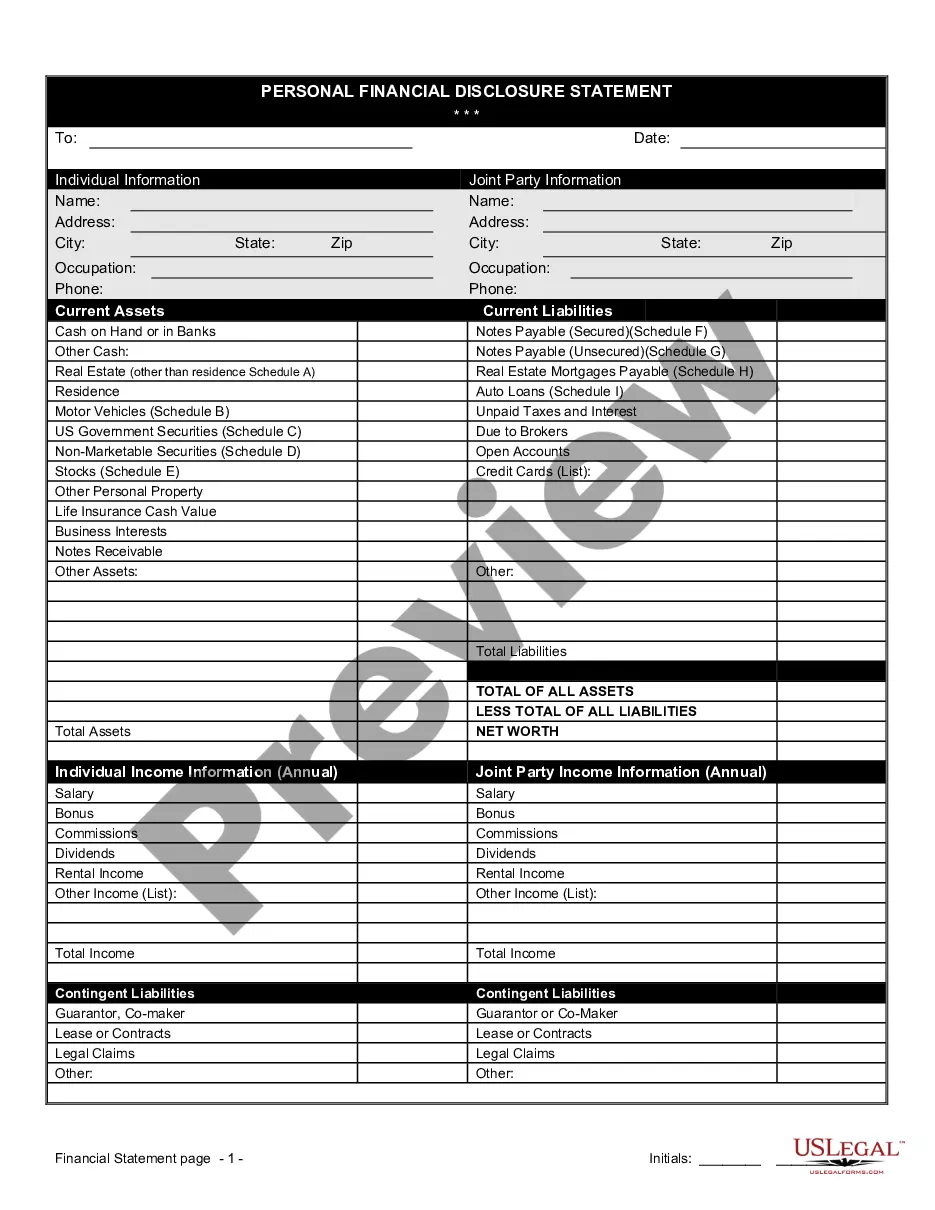
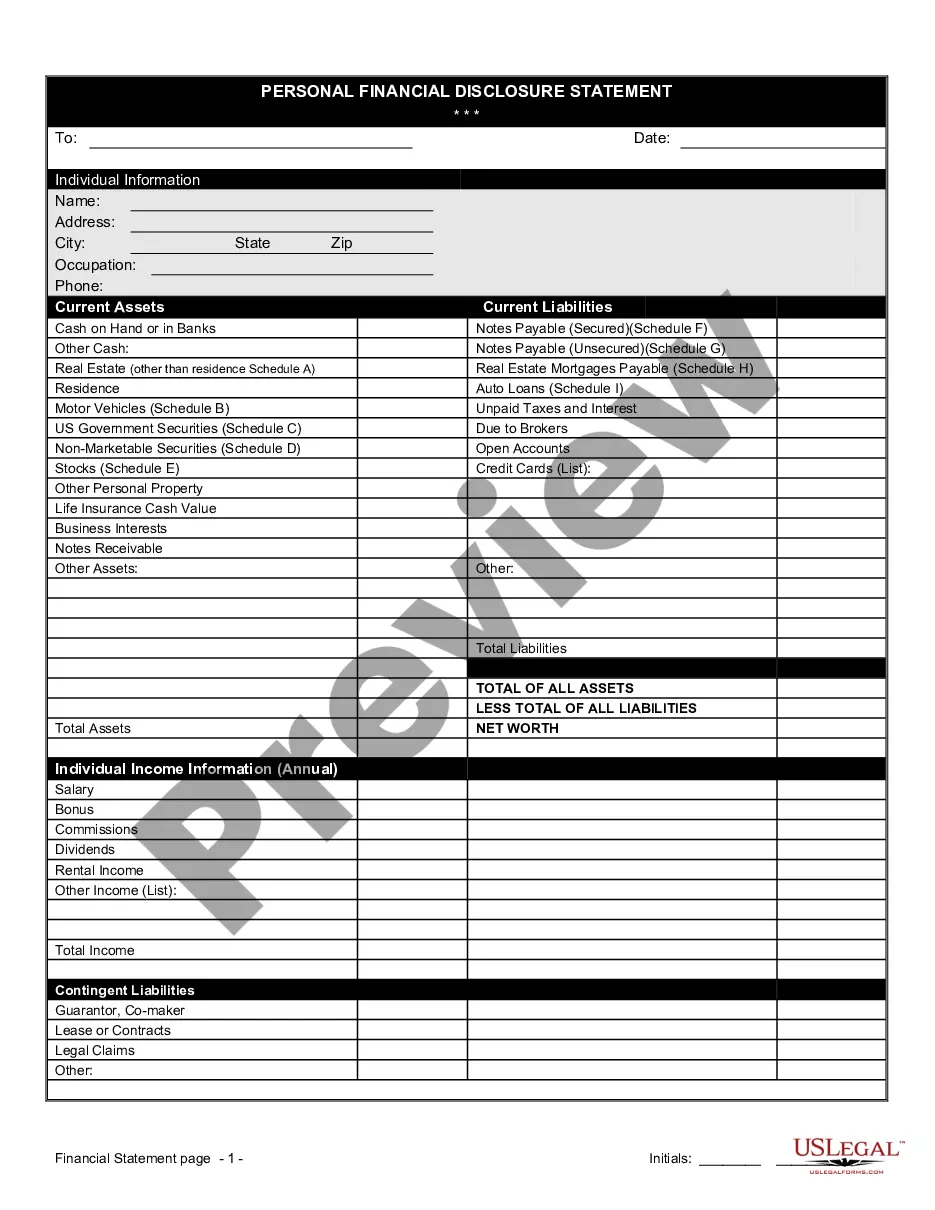
A financial affidavit for child support in Minnesota is a legal document that outlines an individual's financial situation to determine support obligations. It includes income, expenses, assets, and liabilities relevant to the case. For those navigating this process, the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use can be an effective tool for clarity and compliance.
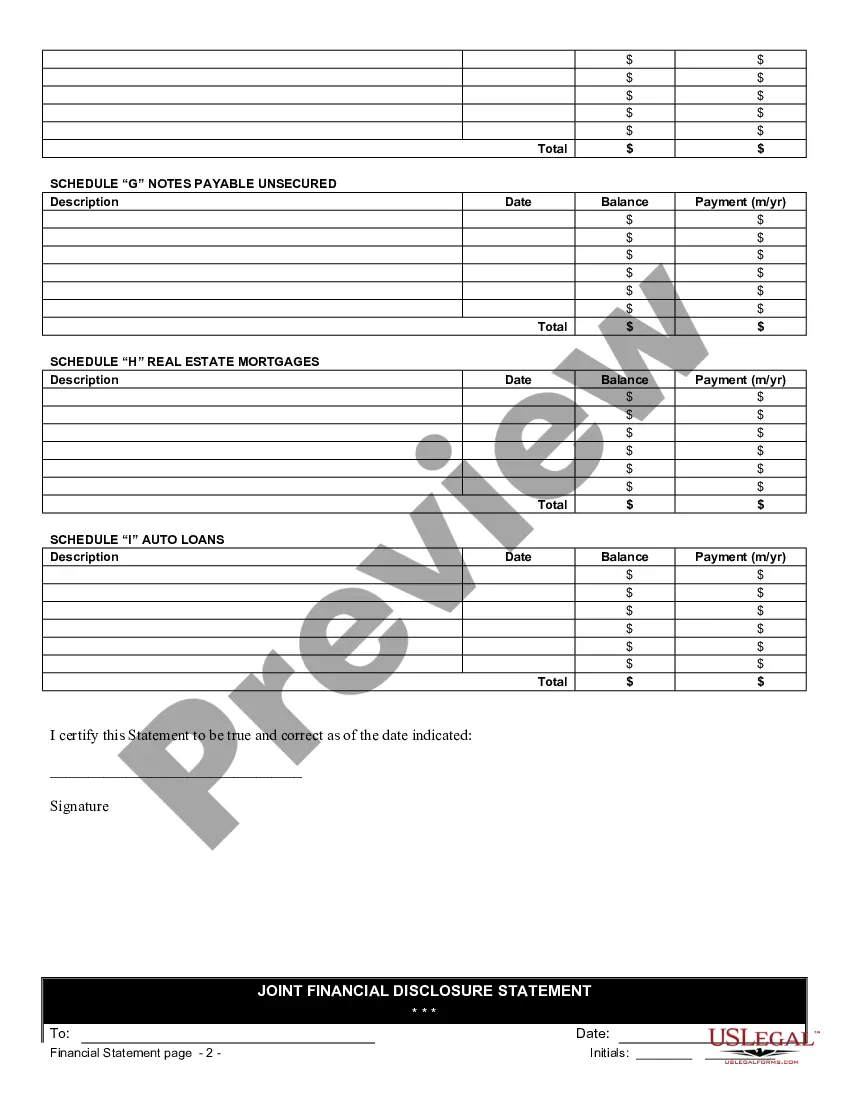
To fill out a financial statement, carefully read each section and input the necessary financial figures. Make sure to verify your information for accuracy, as it impacts the validity of the statement. Using the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use can assist you in filling it out correctly and comprehensively.
Filling out an SBA financial statement involves providing detailed information about your business's income, expenses, assets, and liabilities. Ensure you provide accurate figures for reliability, as lenders use this information for decision-making. Using the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use can enhance your accuracy and organization.
To complete a financial statement, gather your financial records, such as income statements and expense reports, and input the relevant data into the correct sections. Organize your assets, liabilities, and equity clearly. Utilizing the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use can streamline this process for clarity and efficiency.
An example of a financial statement is a balance sheet, which shows an individual’s or business’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific time. It's crucial for understanding one's financial health. For those needing a structured approach, consider using the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use.
Creating a financial statement involves collecting financial data, summarizing this information, and presenting it in an organized format. The Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use can guide you in structuring your statement effectively, ensuring all essential elements are included. For additional resources, consider exploring US Legal Forms for templates that best fit your financial documentation needs.
Business financial records, particularly for public companies, are generally available to the public. This transparency allows stakeholders to review a company's fiscal health. For those looking to create or analyze financial records, utilizing the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use can be an excellent starting point, ensuring uniformity and compliance.
To download a company's financial statement, visit the official website of the company or trusted financial databases. Most public companies provide downloadable versions of their financial statements. You may also want to check US Legal Forms for the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use, which can assist in tracking your own financial records efficiently.
Yes, public company financial statements are indeed public. They are required by law to disclose their financial health, making the Minnesota Financial Statement Form - Universal Use relevant for understanding these disclosures. You can easily access these documents through financial databases or directly on the respective company’s website.