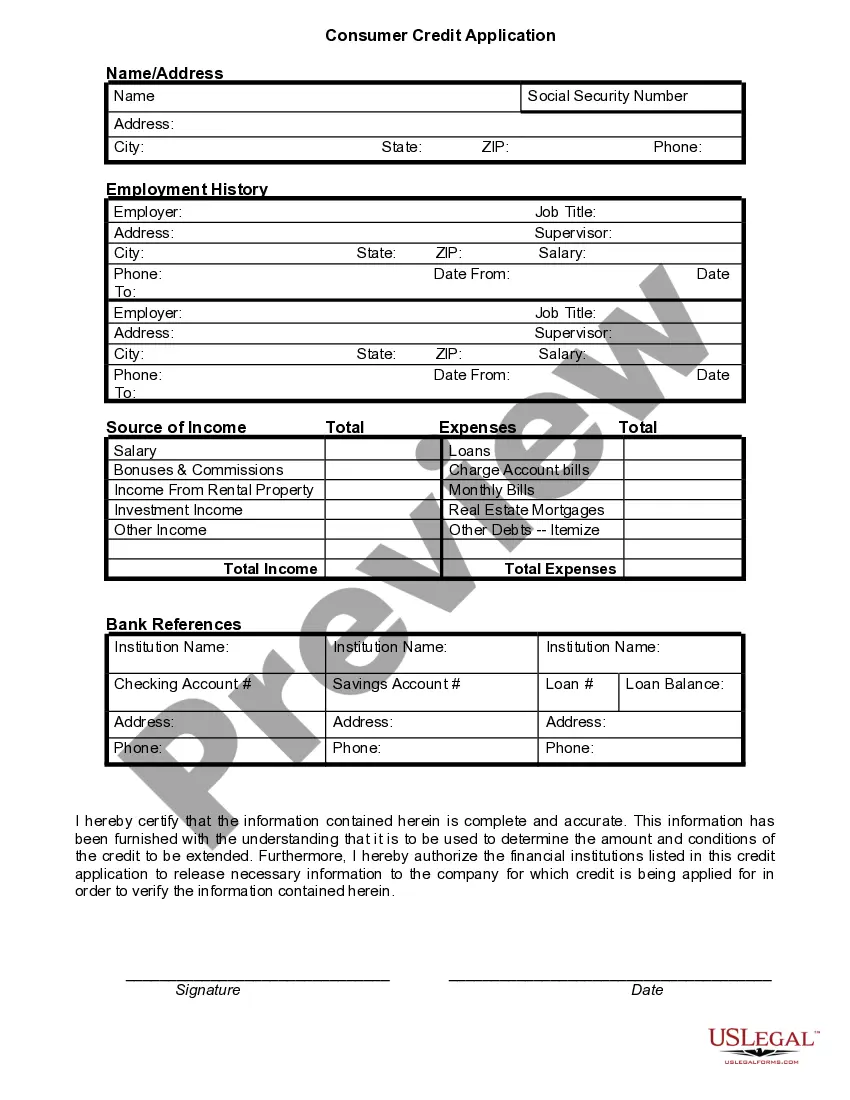
This form is a generic example that may be referred to when preparing such a form for your particular state. It is for illustrative purposes only. Local laws should be consulted to determine any specific requirements for such a form in a particular jurisdiction.
A Minnesota Contract for Construction of a Commercial Building refers to a legally binding agreement between a property owner (referred to as the "owner" or "client") and a contractor (referred to as the "builder" or "contractor"). This construction contract establishes the terms and conditions under which a commercial building project will be executed, ensuring a clear understanding of the project scope, timeline, costs, and responsibilities of both parties involved. Keywords: Minnesota, Contract for Construction, Commercial Building Different types of Minnesota Contracts for Construction of a Commercial Building may include: 1. Lump Sum Contract: This is the most common type of construction contract, where the contractor agrees to perform the entire construction project for a fixed, agreed-upon price. 2. Cost Plus Contract: In this type of contract, the owner agrees to pay the contractor for all costs incurred during the construction project, including materials, labor, and overhead expenses. A predetermined fee or percentage may be added to cover the contractor's profit margin. 3. Design-Build Contract: This contract method involves a single entity responsible for both the design and construction of the commercial building project. The contractor takes on the responsibility of hiring architects, engineers, and subcontractors, streamlining the process and reducing potential conflicts. 4. Construction Manager at Risk (CAR) Contract: In this type of contract, the construction manager is involved early in the design process and performs construction risk management services. The construction manager assumes responsibility for cost estimation, scheduling, and coordinating the subcontractors, ensuring the project is completed within the budget and timeframe. 5. Construction Management Contract (CMC): This contract involves hiring a construction management firm that acts as the owner's representative. The construction manager assists in project planning, coordinating subcontractors, overseeing construction activities, and monitoring budget and schedule compliance while providing regular reports to the owner. 6. Unit Price Contract: The unit price contract details the cost of specific items or work units based on predetermined rates, making it suitable for projects where quantities may vary. Payments are calculated by multiplying the unit price by the actual quantities of the work done. In each of these contract types, it is essential to clearly define the project scope, timeline, payment structure, change order procedures, warranties, termination clauses, dispute resolution mechanisms, and other pertinent terms to ensure a successful and smooth construction project in Minnesota.A Minnesota Contract for Construction of a Commercial Building refers to a legally binding agreement between a property owner (referred to as the "owner" or "client") and a contractor (referred to as the "builder" or "contractor"). This construction contract establishes the terms and conditions under which a commercial building project will be executed, ensuring a clear understanding of the project scope, timeline, costs, and responsibilities of both parties involved. Keywords: Minnesota, Contract for Construction, Commercial Building Different types of Minnesota Contracts for Construction of a Commercial Building may include: 1. Lump Sum Contract: This is the most common type of construction contract, where the contractor agrees to perform the entire construction project for a fixed, agreed-upon price. 2. Cost Plus Contract: In this type of contract, the owner agrees to pay the contractor for all costs incurred during the construction project, including materials, labor, and overhead expenses. A predetermined fee or percentage may be added to cover the contractor's profit margin. 3. Design-Build Contract: This contract method involves a single entity responsible for both the design and construction of the commercial building project. The contractor takes on the responsibility of hiring architects, engineers, and subcontractors, streamlining the process and reducing potential conflicts. 4. Construction Manager at Risk (CAR) Contract: In this type of contract, the construction manager is involved early in the design process and performs construction risk management services. The construction manager assumes responsibility for cost estimation, scheduling, and coordinating the subcontractors, ensuring the project is completed within the budget and timeframe. 5. Construction Management Contract (CMC): This contract involves hiring a construction management firm that acts as the owner's representative. The construction manager assists in project planning, coordinating subcontractors, overseeing construction activities, and monitoring budget and schedule compliance while providing regular reports to the owner. 6. Unit Price Contract: The unit price contract details the cost of specific items or work units based on predetermined rates, making it suitable for projects where quantities may vary. Payments are calculated by multiplying the unit price by the actual quantities of the work done. In each of these contract types, it is essential to clearly define the project scope, timeline, payment structure, change order procedures, warranties, termination clauses, dispute resolution mechanisms, and other pertinent terms to ensure a successful and smooth construction project in Minnesota.