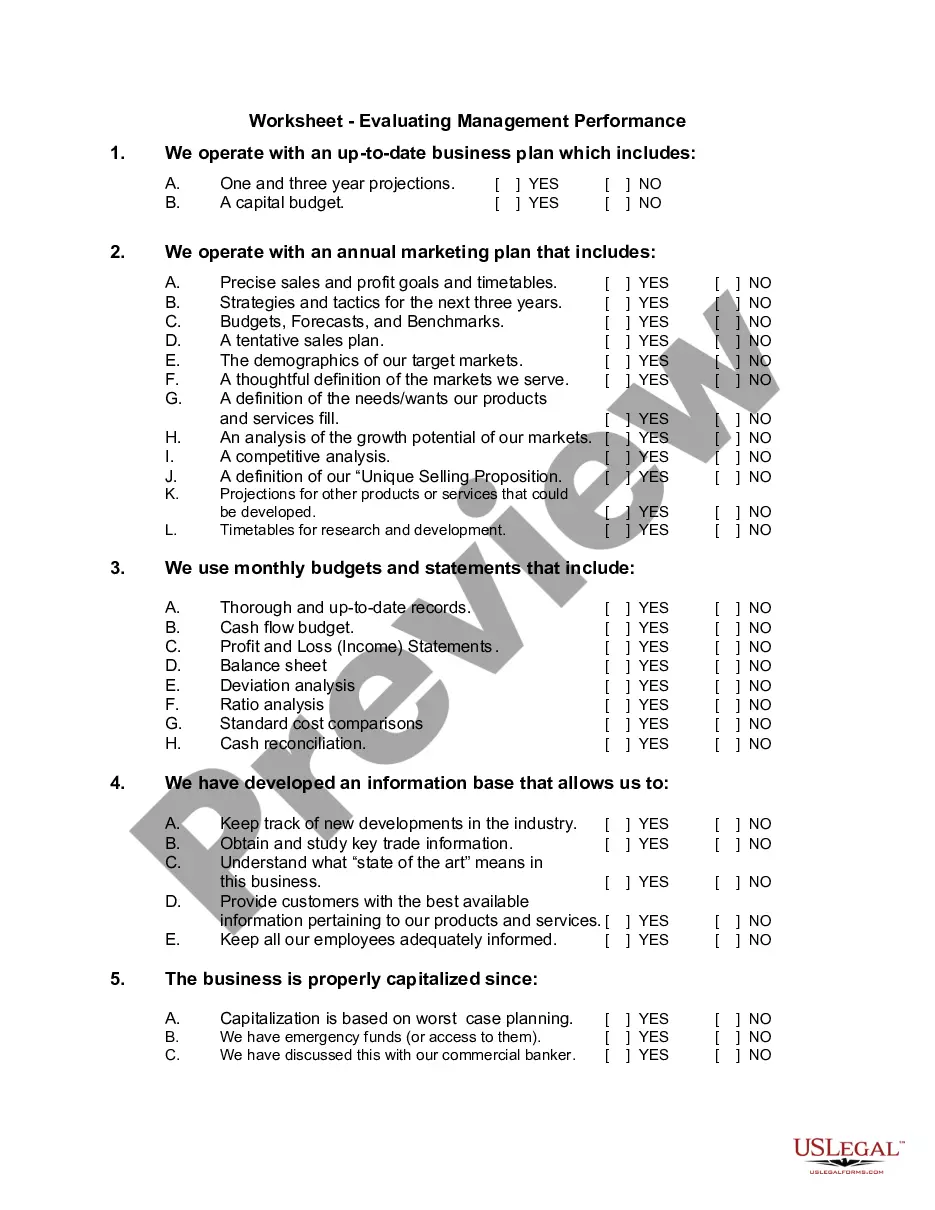
Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property
Description
How to fill out Triple Net Lease For Residential Property?
Selecting the optimal legal document format can be a challenge. Naturally, there are numerous templates available online, but how will you secure the legal form you require? Utilize the US Legal Forms website.
The platform offers a vast array of templates, including the Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property, suitable for both commercial and personal purposes. Each of the forms is vetted by professionals and complies with federal and state regulations.
If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click on the Download button to obtain the Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property. Use your account to browse the legal forms you have previously purchased. Navigate to the My documents tab of your account to retrieve another copy of the document you require.
US Legal Forms is the largest repository of legal forms where you can find various document templates. Use the service to obtain well-crafted papers that comply with state requirements.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/county. You can view the form via the Review button and examine the form summary to confirm it is suitable for you.
- If the form does not meet your expectations, use the Search field to find the appropriate form.
- Once you are confident the form is correct, click the Purchase now button to obtain the form.
- Choose the pricing plan you prefer and provide the necessary information.
- Create your account and complete the order using your PayPal account or credit card.
- Select the file format and download the legal document format to your device.
- Complete, modify, print, and sign the obtained Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property.
Form popularity
FAQ
One downside of a Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property is that you assume additional costs like property taxes, insurance, and maintenance. These expenses can fluctuate, affecting your monthly budget. Additionally, if the property requires significant repairs, you are responsible for those costs as well. It's essential to weigh these factors before entering into such a lease agreement.
One key disadvantage of a Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property is the potential for unforeseen financial responsibilities. Since tenants are responsible for taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs, they may encounter unexpected expenses that strain their budget. Moreover, this lease structure may require more active management and involvement in property issues. Understanding these factors can help tenants make informed decisions.
While a Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property can offer advantages, it also comes with risks. Tenants may face unexpected costs related to property upkeep or repairs, which can add financial strain. Market fluctuations can influence operating expenses, meaning that total costs can vary yearly. Therefore, it’s crucial for tenants to assess their ability to manage these potential financial impacts.
Tenants often choose a Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property because it provides a clear structure for costs. In this arrangement, tenants gain control over certain property expenses, such as taxes and insurance. This transparency can lead to lower base rent and a sense of ownership for tenants. Additionally, this lease type commonly attracts experienced renters who understand the financial responsibilities involved.
A triple net lease, specifically in the context of a Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property, designates that tenants are responsible for property expenses beyond the base rent. This includes property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs. This arrangement can often lead to lower rent prices and more control over property management for the tenant.
Qualifying for a triple net lease in Minnesota involves demonstrating financial stability and preparedness to handle property-related expenses. You should be ready to show your income and creditworthiness. Ensuring you understand the obligations of a Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property will also support your qualification process.
To get approved for a Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property, you typically need to provide your financial history and credit score. Landlords often look for stable income and a solid rental history. Additionally, demonstrating your ability to manage the costs associated with a triple net lease, like taxes and insurance, can strengthen your application.
While most residential leases typically do not follow a triple net structure, some agreements can be tailored in that way. A Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property may occur if the lease specifies that the tenant is responsible for all property-related expenses. Such arrangements are rare and often found in unique residential situations. It is beneficial to consult a legal professional to clarify if your lease falls under this category.
Triple net leases are not inherently bad for tenants, but they do require careful consideration. While they can offer lower base rent, tenants often face additional costs related to property upkeep, which could increase overall expenses. With a Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property, it’s essential that tenants are aware of these responsibilities and potential financial implications. Balancing these factors against the benefits of a lower rent may help tenants make an informed decision.
Triple net leases are most commonly associated with commercial properties like retail spaces and industrial buildings. However, you may also encounter a Minnesota Triple Net Lease for Residential Property under specific circumstances. Generally, these leases are less common in residential settings but can exist in unique arrangements. Understanding the nuances of your particular lease can help in evaluating its structure.