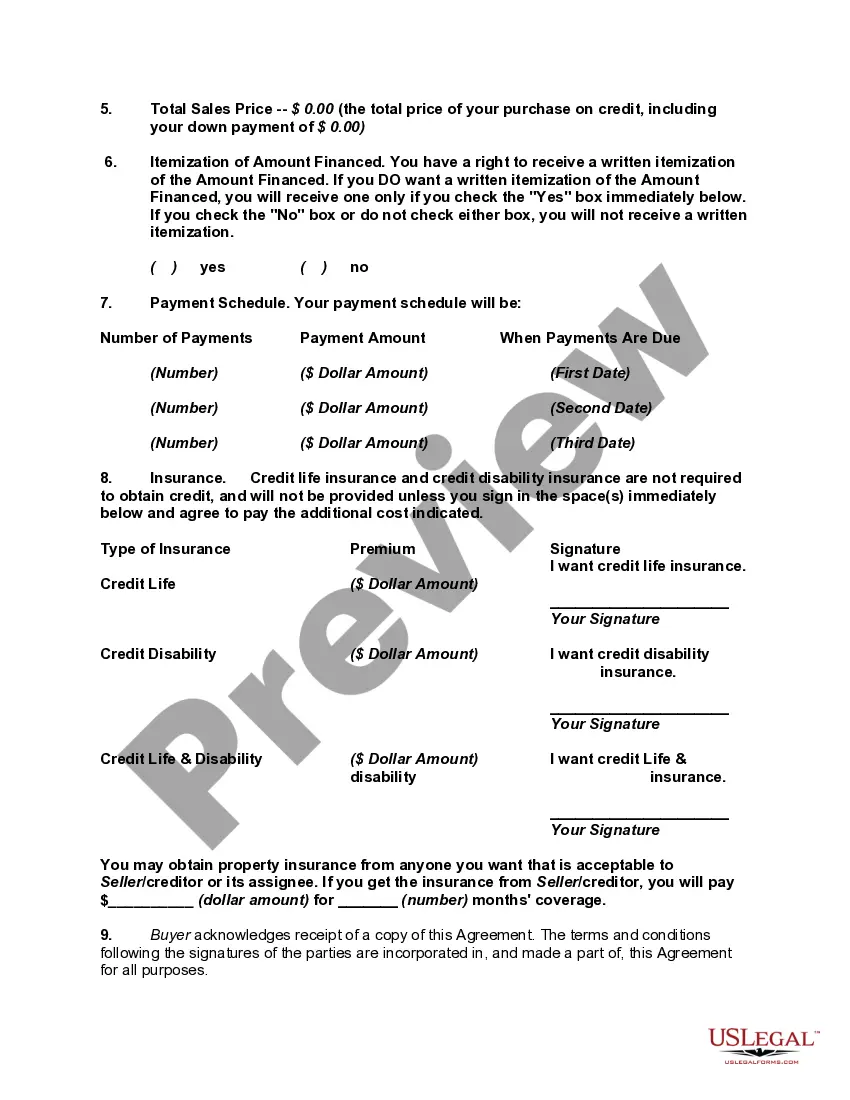
Disclosure of credit terms should have the content and form required under the federal Truth in Lending Act (15 U.S.C.A. §§ 1601 et seq.) and applicable regulations (Regulation Z, 12 C.F.R. § 226), and under state consumer credit laws to the extent that they differ from the federal Act. In connection with specified installment sales and other consumer credit transactions, these enactments require written disclosure and advice as to finance charges, annual percentage rates and other matters relating to credit. Under the federal Act, the disclosures may be set forth in the contract document itself or in a separate statement or statements.
A federal notice regarding preservation of the consumer's claims and defenses is required on all consumer credit contracts by Federal Trade Commission regulation. 16 C.F.R. § 433.2. The notice must appear in 10-point bold type or print and must be worded as set forth in the above form.
The Minnesota Security Agreement for Retail Installment Sale of Automobile, Car or Motor Vehicle is a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions for financing the purchase of a vehicle in Minnesota. This agreement is commonly used by car dealerships and financial institutions to secure their interest in the vehicle until the buyer completes the payment obligations. In this agreement, the buyer (debtor) agrees to make monthly installment payments to the seller (creditor) until the purchase price of the vehicle, including interest charges, is paid in full. The security agreement ensures that the creditor has a legal right to repossess the vehicle if the debtor defaults on the payments. Keywords: Minnesota Security Agreement, Retail Installment Sale, Automobile, Car, Motor Vehicle, legal document, terms and conditions, financing, purchase, Minnesota, car dealerships, financial institutions, secure, interest, buyer, seller, creditor, debtor, monthly installment payments, purchase price, interest charges, paid in full, repossess, default. Some types of Minnesota Security Agreements for Retail Installment Sale of Automobile, Car or Motor Vehicle may include: 1. Simple Security Agreement: This is a basic form that outlines the essential terms of the installment sale and security interest. It ensures that the creditor has the right to repossess the vehicle if the debtor fails to make payments. 2. Comprehensive Security Agreement: This type of agreement is more detailed and typically includes additional provisions, such as insurance requirements, maintenance responsibilities, and conditions for early repayment or refinancing. 3. Joint Security Agreement: In cases where there are multiple buyers involved in the purchase of a vehicle, this agreement defines the rights and obligations of each party. It clarifies how the security interest is shared among the buyers. 4. Subordination Agreement: This type of agreement is used when there are multiple liens on a vehicle, such as when the buyer already has an existing loan or lease. It establishes the priority of the security interest held by each creditor. 5. Extended Term Security Agreement: Sometimes, buyers require longer repayment periods. This agreement caters to such cases, allowing for an extended term with adjusted payment terms and interest rates. Keywords: types of Minnesota Security Agreements, simple security agreement, comprehensive security agreement, joint security agreement, subordination agreement, extended term security agreement, installment sale, security interest, repossession, payment default, insurance requirements, maintenance responsibilities, early repayment, refinancing, multiple buyers, liens, extended term, payment terms, interest rates.