Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable
Description
How to fill out Aging Of Accounts Payable?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest collections of legal documents in the United States - offers a diverse range of legal template options that you can download or print.
By using the site, you can find thousands of forms for business and personal purposes, organized by categories, states, or keywords. You can access the latest forms such as the Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable in just moments.
If you possess a monthly subscription, Log In and obtain the Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable from the US Legal Forms library. The Download button will appear on every form you review. You have access to all previously downloaded forms from the My documents section of your account.
Every template you added to your account does not have an expiration date and is yours permanently. Therefore, if you wish to download or print another copy, simply visit the My documents section and click on the form you desire.
Access the Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable with US Legal Forms, the most extensive collection of legal document templates. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that meet your business or personal needs and requirements.
- Ensure you have selected the correct form for your city/region. Click the Review button to examine the content of the form. Read the form details to confirm that you have chosen the right form.
- If the form does not meet your requirements, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find one that does.
- If you are satisfied with the form, confirm your choice by clicking the Buy now button. Then, choose the payment plan you wish and provide your details to register for an account.
- Process the payment. Use a credit card or PayPal account to finalize the transaction.
- Select the format and download the form to your device.
- Make changes. Complete, edit, print, and sign the downloaded Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable.
Form popularity
FAQ
To prepare an accounts payable aging report, first compile a list of all unpaid invoices along with their due dates. Then, categorize these invoices into time buckets, reflecting how long each one has been outstanding. Using tools available on platforms like USLegalForms can simplify this process, allowing you to generate a comprehensive Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable report that enhances your financial oversight.
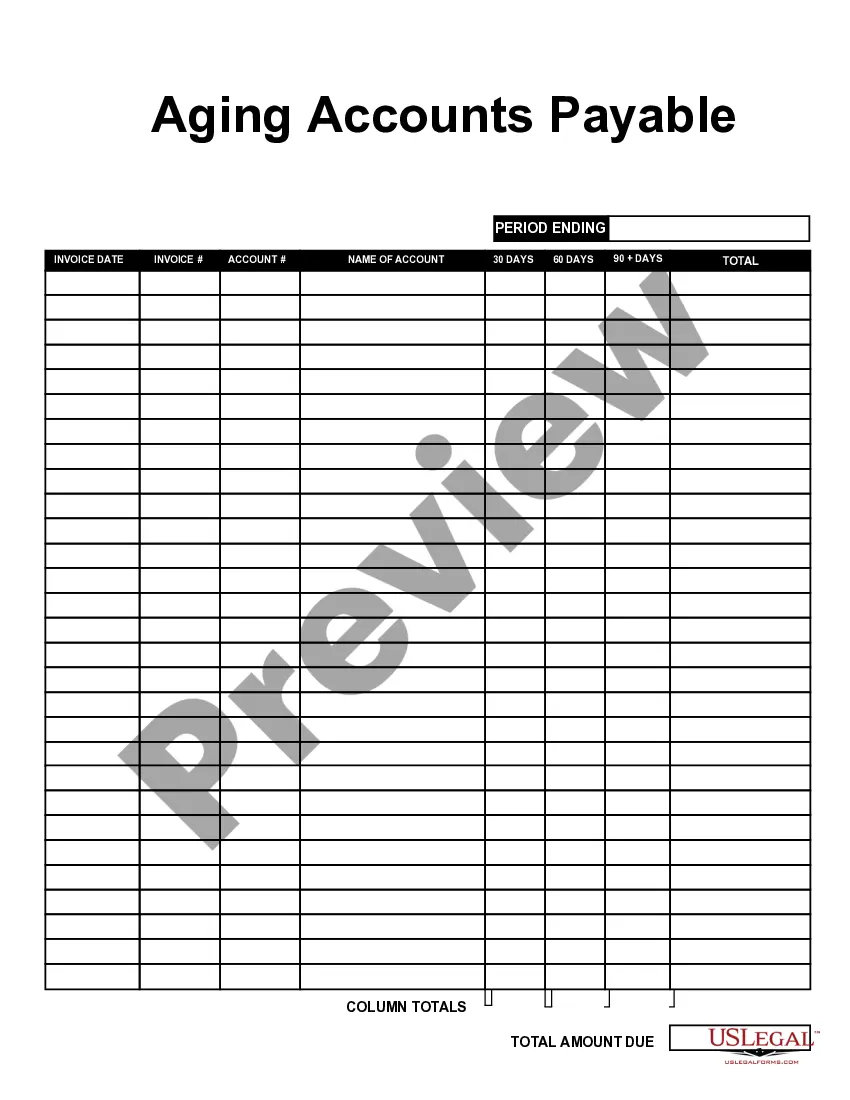
The aging schedule for accounts payable is a table that categorizes invoices based on their age, typically displayed in buckets such as 0-30 days, 31-60 days, 61-90 days, and so on. This schedule allows businesses to visualize their payment obligations and prioritize them accordingly. By maintaining an accurate aging schedule, companies can effectively manage their Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable and ensure timely payments.
AP aging is calculated by listing all outstanding invoices and categorizing them into groups based on how long they have been due. Each group usually represents a 30-day period, such as 0-30 days, 31-60 days, and so on. To efficiently manage Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable, businesses can utilize accounting software that automates this process and generates accurate aging reports.
The aging process of accounts payable involves reviewing and categorizing outstanding invoices according to specific time frames, typically in 30-day intervals. This structured analysis allows businesses to prioritize payments and make informed financial decisions. By focusing on the Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable, companies can streamline their payment processes and enhance their financial management.
In Minnesota, the average salary for an accounts payable clerk varies based on experience and location. Generally, an accounts payable clerk can expect to earn between $45,000 and $60,000 annually. This range reflects the growing importance of efficient Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable processes in businesses today. Utilizing platforms like US Legal Forms can help streamline accounts payable tasks, potentially enhancing salary prospects by increasing efficiency and accuracy.
The schedule of accounts payable is a detailed report that itemizes your company's financial obligations to vendors and suppliers. This schedule typically includes the due dates, payment amounts, and aging periods for each account. Keeping a well-organized schedule is essential for financial planning and maintaining good supplier relationships. Consider tools from US Legal Forms to help you manage this efficiently.
An aging schedule for Minnesota aging of accounts payable typically includes columns for each invoice, such as the vendor name, invoice number, invoice date, amount owed, and the aging categories. You can organize it by time frames, such as current, 1-30 days, 31-60 days, and over 60 days. This structured format allows for easy analysis and helps manage payments efficiently.
Yes, you can file your Minnesota state taxes online, which is often the easiest way to ensure accuracy and timely submission. Various online platforms, like uslegalforms, provide guided services for tax filing, helping you navigate aspects related to the Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable. Online filing can streamline the process significantly.
The M-1 tax form is specifically for partnerships and corporations that operate in Minnesota, used to report state income. This form helps in understanding tax liabilities and ensures accuracy in financial reporting concerning the Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable. Proper usage ensures compliance and clarity in your financial dealings.
Yes, you can deduct vehicle registration fees in Minnesota under certain conditions, particularly if the vehicle is used for business purposes. Knowing what you can deduct helps in managing financial records, including aspects tied to your Minnesota Aging of Accounts Payable. Always keep thorough records to substantiate your claims.