Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace
Description
How to fill out 21 Things To Do For A Safe Workplace?
If you want to complete, obtain, or produce authentic document templates, use US Legal Forms, the most extensive range of authentic forms available online.
Employ the website's straightforward and user-friendly search to locate the documents you require.
A selection of templates for business and personal purposes are organized by categories and states, or keywords.
Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, take advantage of the Search field at the top of the screen to find alternative versions of the authentic form template.
Step 4. After you find the form you want, click the Get now button. Select your preferred pricing option and enter your credentials to create an account.
- Utilize US Legal Forms to locate the Minnesota 21 Strategies for a Secure Workplace with just a few clicks.
- If you are currently a US Legal Forms user, Log In to your account and press the Download button to access the Minnesota 21 Strategies for a Secure Workplace.
- You can also reach documents you previously downloaded in the My documents section of your account.
- If this is your first time using US Legal Forms, follow the instructions below.
- Step 1. Make sure you have selected the form for the appropriate city/state.
- Step 2. Use the Review option to examine the content of the form. Don't forget to read the description.
Form popularity
FAQ
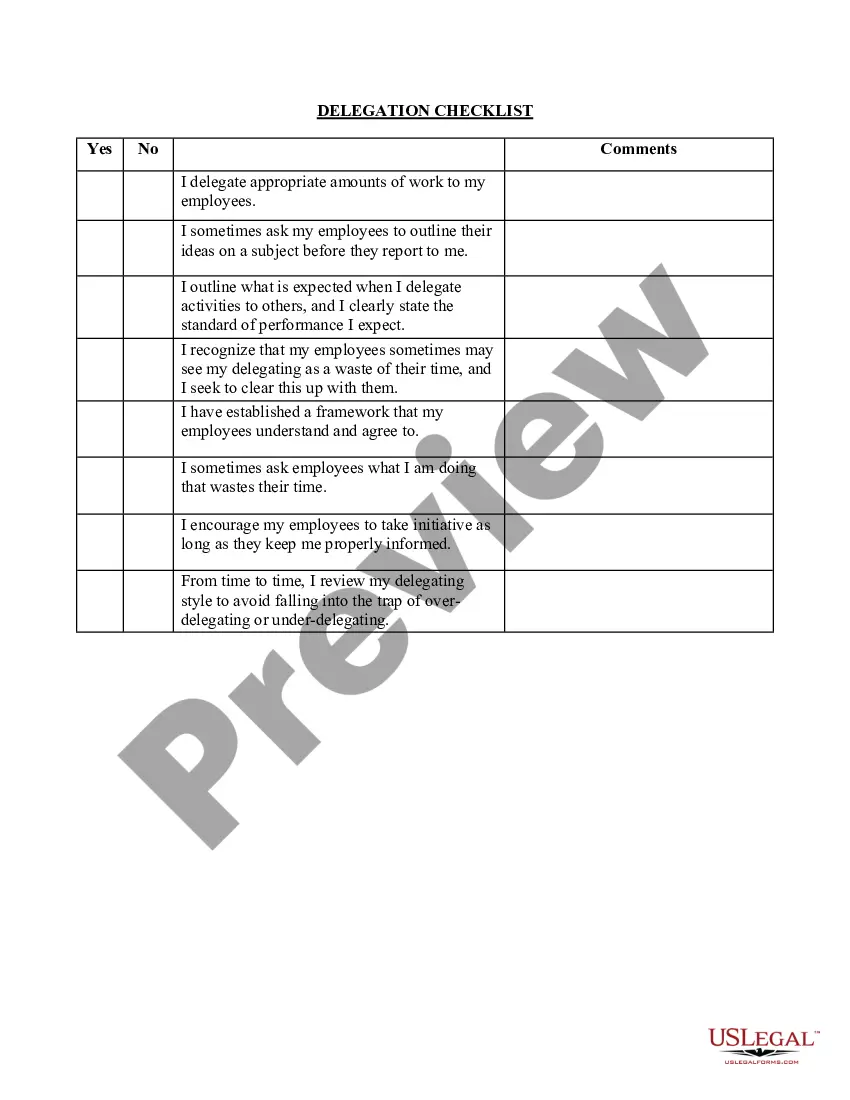
Maintaining safety in your working area involves regular checks and updates to safety procedures. It's essential to promote a culture of safety where all employees feel responsible for keeping the workspace secure. Conducting training sessions and refreshers can help maintain awareness. By incorporating the Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace into your routine, you ensure ongoing vigilance and safety.
Creating a safe working environment requires continuous evaluation and improvement. Implementing safety protocols and investing in employee training are critical steps. Listen to employee feedback and be willing to make changes based on their insights. Following the guidelines outlined in Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace reinforces your commitment to safety.
To ensure a safe work area, start by conducting regular safety inspections and promptly addressing any issues. Encourage team members to communicate their concerns and suggest improvements. Providing ongoing safety training equips employees with the skills to handle their tasks safely. By integrating Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace into your daily practices, you create a proactive approach toward safety.
Employers are required by law to provide a safe workplace under the Occupational Safety and Health Act. This legislation ensures that all workers are protected from recognized hazards. Compliance with these standards not only protects employees but also enhances productivity and morale. Incorporating the Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace can help employers meet their legal obligations.
The Minnesota Safe Program focuses on enhancing workplace safety through training and safety management. It provides resources and guidance to help organizations create safer environments. This program emphasizes proactive measures to minimize risks and protect workers. By understanding and following the Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace, employers can better comply with this program.
Ensuring safe working conditions involves regularly assessing the workplace for potential hazards. Establishing clear safety protocols and training employees on these standards are crucial steps. Furthermore, providing the right tools and safety equipment contributes significantly to minimizing risks. Implementing Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace supports a culture where safety comes first.
To create a safe workplace, it's essential to follow basic safety rules. Some key rules include wearing appropriate safety gear, reporting hazards immediately, and keeping work areas clean and organized. Regular breaks can also help prevent accidents caused by fatigue. Adhering to the Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace ensures both workers and employers prioritize safety.
Creating safe working conditions involves identifying potential hazards and implementing safety protocols. Employers should conduct regular safety training, maintain equipment, and encourage open communication about safety concerns. These actions align with the Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace, fostering a culture of safety that protects all employees.
New employees in Minnesota commonly fill out the I-9 form for employment eligibility and the W-4 form for federal tax withholding. Additionally, there may be state-specific forms depending on the employer. Completing these forms is essential for compliance and plays a role in the Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace.
Employers have a legal duty to provide a safe workplace for their employees. This includes identifying potential hazards, instituting safety measures, and providing necessary training. By fulfilling this responsibility, employers contribute to the Minnesota 21 Things to do for a Safe Workplace initiative, ensuring that employees work in a safe and healthy environment.