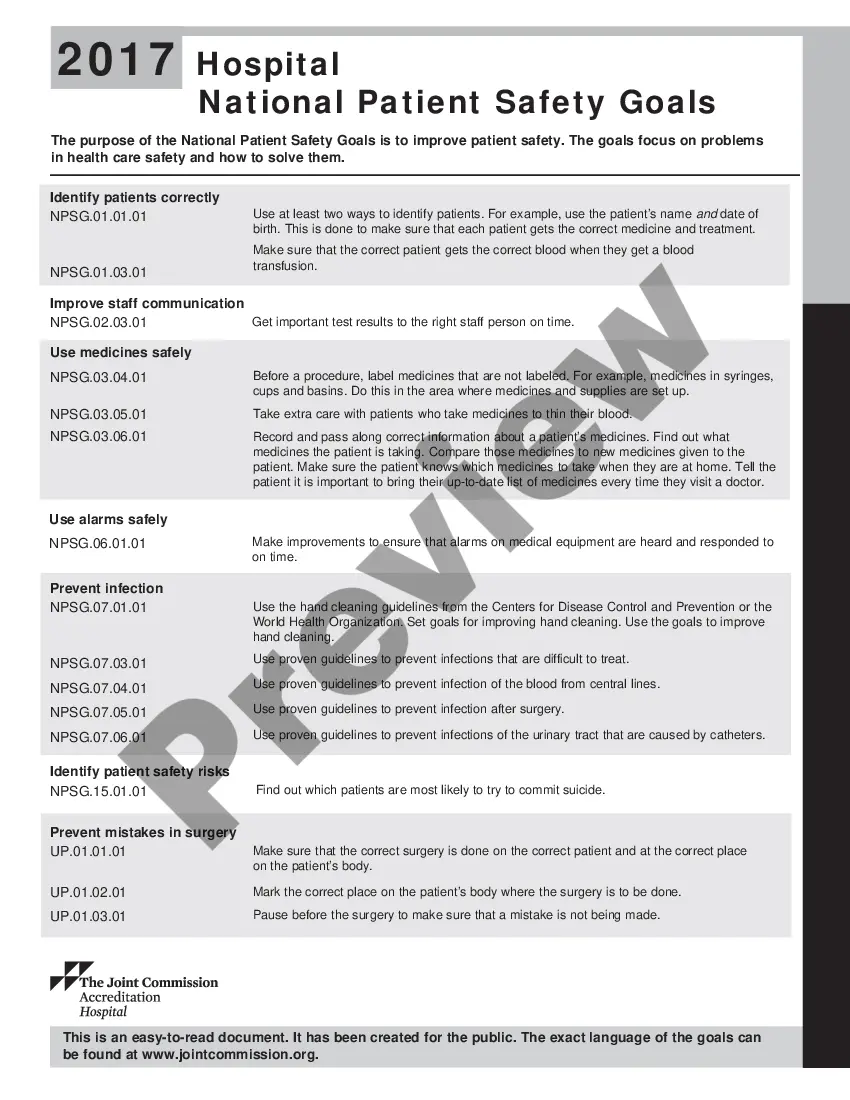
The Minnesota Hospital National Patient Safety Goals (Nests) are a set of guidelines and recommendations established by The Joint Commission to ensure the safety and well-being of patients in healthcare settings within Minnesota. These goals are designed to address critical areas of patient safety and provide a framework for healthcare organizations to improve their processes and systems. The Nests in Minnesota focus on various aspects of patient care and safety, aiming to minimize risks, prevent errors, and enhance the overall quality of healthcare delivery. Here are some key goals and their corresponding objectives: 1. Identify patients correctly: This goal emphasizes the importance of patient identification processes to ensure accurate and safe care delivery. Healthcare organizations are encouraged to implement measures like patient identification bands, questioning patients, and using two patient identifiers (name, date of birth, etc.) to minimize potential errors or mistaken identity. 2. Improve staff communication: Effective communication plays a vital role in enhancing patient safety. Hospitals are encouraged to establish clear lines of communication among staff members, utilizing standardized hand off processes to reduce miscommunication and ensure accurate transfer of patient information. 3. Use medications safely: Medication errors can have serious consequences. The Nests aim to reduce medication-related mistakes by encouraging healthcare organizations to establish processes, such as conducting medication reconciliation, educating patients about their medications, and implementing electronic prescribing systems to minimize errors. 4. Prevent infection: Infections acquired during healthcare facility stay are a significant concern. Hospitals are advised to adhere to infection prevention guidelines, promote hand hygiene practices, implement specific precautions for contagious patients, and monitor compliance with proper sterilization and disinfection procedures. 5. Prevent falls: Patient falls can result in injuries and further complications. The Nests urge hospitals to conduct fall risk assessments upon admission, implement patient-centered interventions, such as proper bed height, assistance devices, and non-slip flooring to prevent falls, and educate both patients and families about fall prevention strategies. 6. Ensure surgical site safety: Surgical procedures carry inherent risks, and the focus is on reducing surgical errors and complications. Hospitals are encouraged to implement surgical time-outs, verify the correct site and procedure with the patient, and follow proper infection prevention protocols during surgery. These are just a few examples of the Minnesota Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. Healthcare organizations across the state should review and incorporate these goals into their patient safety programs to improve the quality of care and enhance patient outcomes. By prioritizing these goals, hospitals can strive towards creating a safe and reliable healthcare environment for all patients in Minnesota.
Minnesota Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Minnesota Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
If you wish to total, down load, or printing legal record templates, use US Legal Forms, the biggest variety of legal types, that can be found on-line. Use the site`s easy and hassle-free lookup to obtain the files you need. A variety of templates for business and individual uses are sorted by categories and claims, or key phrases. Use US Legal Forms to obtain the Minnesota Hospital National Patient Safety Goals in just a few mouse clicks.
When you are currently a US Legal Forms customer, log in to your account and then click the Obtain button to get the Minnesota Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. You can even access types you in the past delivered electronically from the My Forms tab of your account.
If you use US Legal Forms for the first time, follow the instructions listed below:
- Step 1. Be sure you have chosen the form for the appropriate metropolis/country.
- Step 2. Use the Review option to look over the form`s information. Do not forget about to read the outline.
- Step 3. When you are unhappy with the develop, utilize the Search industry towards the top of the display to locate other variations of your legal develop design.
- Step 4. Upon having found the form you need, click on the Buy now button. Pick the prices plan you choose and include your qualifications to sign up to have an account.
- Step 5. Procedure the financial transaction. You should use your credit card or PayPal account to finish the financial transaction.
- Step 6. Find the structure of your legal develop and down load it on your own product.
- Step 7. Complete, change and printing or indicator the Minnesota Hospital National Patient Safety Goals.
Each and every legal record design you acquire is your own for a long time. You might have acces to each develop you delivered electronically in your acccount. Click the My Forms segment and select a develop to printing or down load once again.
Be competitive and down load, and printing the Minnesota Hospital National Patient Safety Goals with US Legal Forms. There are thousands of specialist and status-distinct types you can use for your personal business or individual needs.