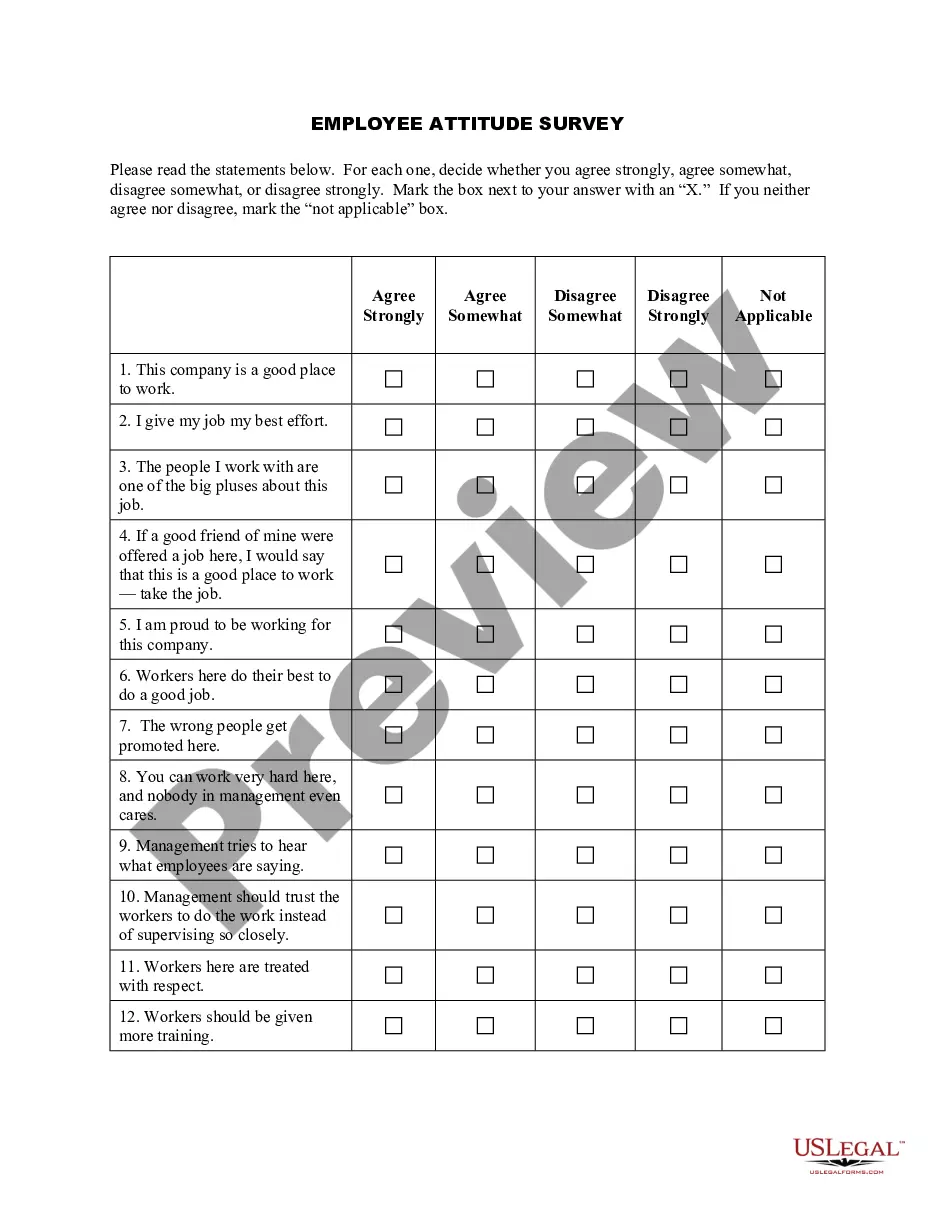
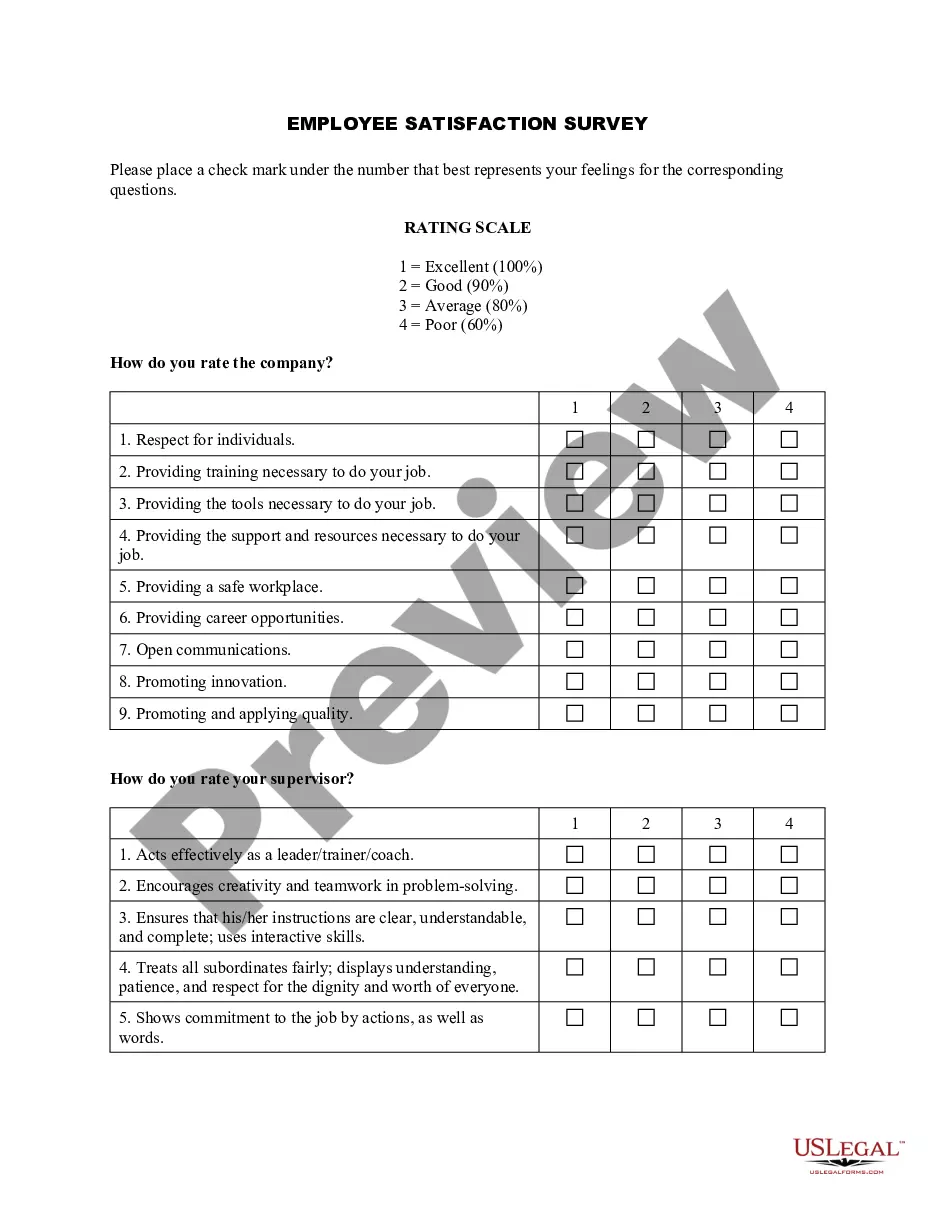
Minnesota Steps in Developing an Attitude Survey
Description
How to fill out Steps In Developing An Attitude Survey?
Finding the appropriate legal document template can be challenging. Clearly, there are numerous templates available online, but how do you find the legal form you require? Turn to the US Legal Forms website. This service offers a vast array of templates, including the Minnesota Steps in Creating an Attitude Survey, which can be utilized for both business and personal purposes. All forms are reviewed by experts and comply with state and federal guidelines.
If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click the Download button to obtain the Minnesota Steps in Creating an Attitude Survey. Use your account to search through the legal forms you have previously purchased. Visit the My documents section of your account to download another copy of the document you need.
If you are a first-time user of US Legal Forms, here are simple steps you should follow.
Choose the document format and download the legal document template to your device. Complete, modify, print, and sign the acquired Minnesota Steps in Creating an Attitude Survey. US Legal Forms is the largest repository of legal forms where you can find a variety of document templates. Use the service to obtain professionally crafted documents that meet state requirements.
- First, ensure that you have selected the correct form for your city/state.
- You can preview the form by using the Review button and read the form description to confirm it is the correct one for you.
- If the form does not meet your needs, utilize the Search box to find the suitable form.
- Once you are certain that the form is right, click the Purchase now button to procure the form.
- Select the pricing plan you desire and enter the required information.
- Create your account and pay for your order using your PayPal account or credit card.
Form popularity
FAQ
Six steps to good questionnaire design#1: Identify your research aims and the goal of your questionnaire.#2: Define your target respondents.#3: Develop questions.#4: Choose your question type.#5: Design question sequence and overall layout.#6: Run a pilot.
Step 1: Determine the Survey Objectives, Resources, and Time Constraints.Step 2: Determine How The Questionnaire Will Be Administered.Step 3: Determine the Question Format.Step 4: Writing Clear Questions.Step 5: Designing the Question Flow.Step 6: Questionnaire Evaluation.Step 7: Obtain Client Approval.More items...
8 Steps to Designing an Ideal SurveySet your goals. Defining the purpose of your survey in clear, unambiguous terms is absolutely vital.Narrow down on your target population.Structure the survey.Select the mode of your survey.Choose the right question type.Formulate the questions.Introduce the survey.Take the field.
Developing a conceptual framework The first step of designing of a good questionnaire is to construct a conceptual framework. The researcher needs to be very clear about his research questions and what dependent and independent factors he intends to investigate.
To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps:Determine who will participate in the survey.Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person)Design the survey questions and layout.Distribute the survey.Analyze the responses.Write up the results.
10 Tips For Creating An Effective Online SurveyA short survey is better than a long one.Questions must be easy to understand and answer.Group questions according to topic.Place sensitive questions at the end.Avoid irrelevant questions.Reassure your respondents that their data is secure.Spend time on your design.More items...
In substantive surveys, survey attitude is often measured by including just a single question about the survey experience. With a single question, however, it is not possible to assess its validity or reliability.
7 Steps to Create a Community Feedback Survey. Set your objectives.Set Your Objectives.Write Your Survey Questions.Test, Test, Test!Send It To Members.Collect Responses.Analyze the Responses.Act on the Results.
There are five points you need to include in your survey introduction:Your organization.The goal of the survey.How much time this will take.Anonymity/privacy of personal information (link to your privacy statement)Relevant instructions.
10 best practices for creating effective surveysDefine a clear, attainable goal for your survey.Keep the more personal questions to the end.Don't let your survey get too long.Focus on using closed-ended questions.Consider including a survey incentive.Don't ask leading questions.Keep your answer choices balanced.More items...