Minnesota Workplace Safety Rules
Description
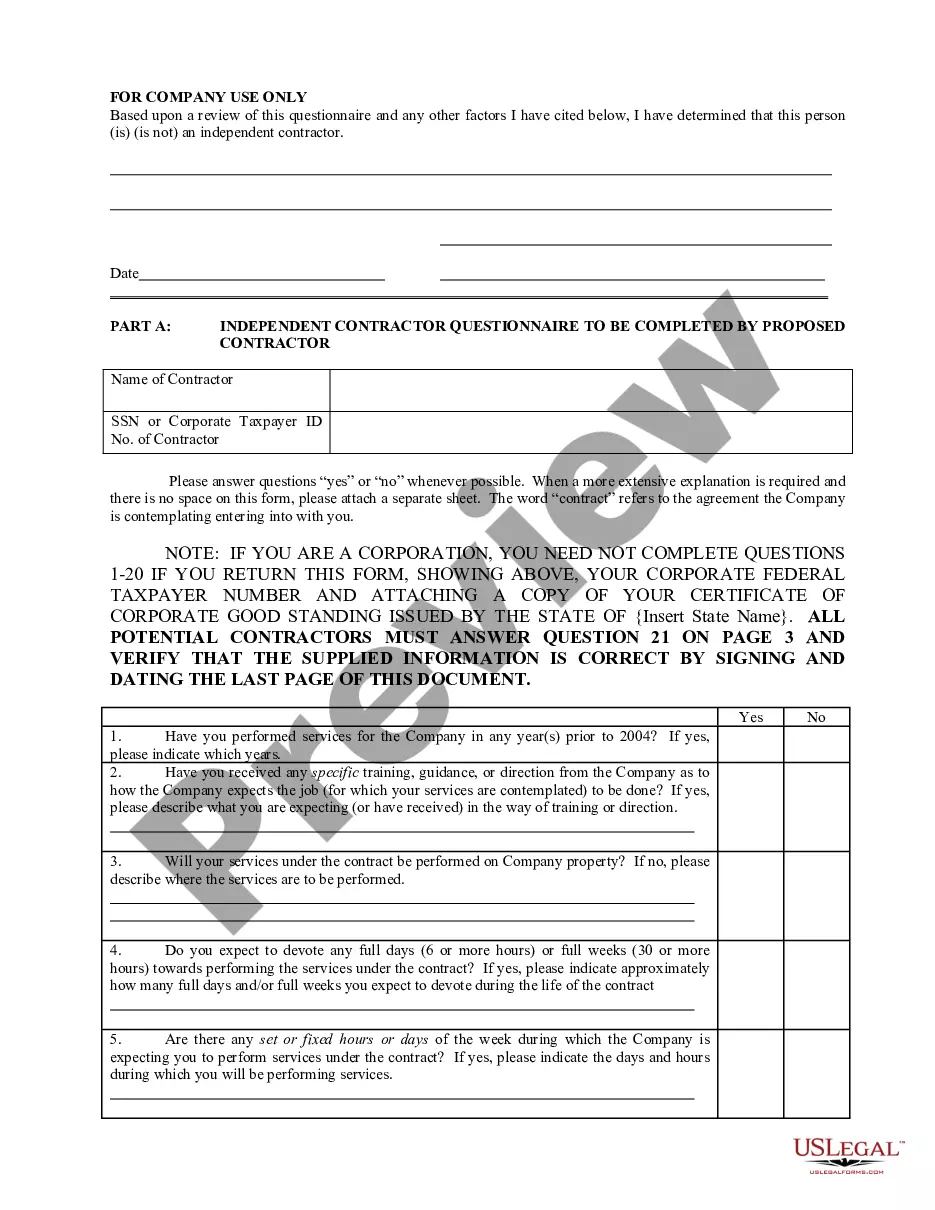
How to fill out Workplace Safety Rules?
Are you presently in a circumstance that requires files for either organizational or personal responsibilities almost every time.
There are numerous legal document templates accessible online, but locating reliable ones isn’t straightforward.
US Legal Forms provides thousands of form templates, including the Minnesota Workplace Safety Rules, designed to meet federal and state regulations.
Once you have the appropriate form, click on Purchase now.
Choose the pricing plan you desire, complete the required information to create your account, and process your order using PayPal or credit card. Select a convenient file format and download your copy. Access all the document templates you've purchased in the My documents section. You can obtain another copy of the Minnesota Workplace Safety Rules at any time, simply click the desired form to download or print the document template. Utilize US Legal Forms, the most extensive collection of legal forms, to save time and avoid errors. This service provides professionally crafted legal document templates for various purposes. Create your account on US Legal Forms and start simplifying your life.
- If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and have an account, simply Log In.
- Then, you can download the Minnesota Workplace Safety Rules template.
- If you do not have an account and wish to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps.
- Find the form you need and ensure it is for the correct city/county.
- Use the Preview button to check the form.
- Review the details to ensure you have selected the correct form.
- If the form is not what you’re looking for, utilize the Search feature to find the form that meets your requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
Applying safety in the workplace involves several proactive steps, such as conducting regular risk assessments and providing comprehensive training to all employees. Establishing clear safety protocols and encouraging open communication about concerns can foster a culture of safety. Additionally, integrating Minnesota Workplace Safety Rules into daily operations ensures a consistent approach to workplace safety across various industries.
The three most cited violations by OSHA include fall protection, hazard communication, and scaffolding standards. These frequent violations indicate areas where workplaces commonly overlook safety protocols. Understanding and adhering to these areas can significantly improve compliance with Minnesota Workplace Safety Rules and protect workers.
Some good example of risk management control measures include: Give employees longer rest breaks or shortening the length of each shift. Move the location of a work process to an area that is less crowded. Change how a work process is performed to reduce the risk of injury.
7 Safety Rules to Avoid Workplace InjuryUse the proper tool for the job.Always wear the proper PPE for the work task.Never work on live equipment.Make sure chemicals are properly labeled and stored.Communicate safety hazards to other personnel.Stop work when needed to address hazards.
The OSHA recommendations include seven core elements for a safety and health program: management leadership; worker participation; hazard identification and assessment; hazard prevention and control; education and training; program evaluation and improvement; and communication and coordination for host employers,
Regulations on walking/working surfaces.Means of egress (exiting), which includes emergency evacuation plans.Occupational noise exposure.Hazardous handling of materials.Protective equipment, such as eye, face, and respiratory protection.Sanitation.Requirement of first aid supplies on-site.More items...
Provide a workplace free from serious recognized hazards and comply with standards, rules and regulations issued under the OSH Act. Examine workplace conditions to make sure they conform to applicable OSHA standards. Make sure employees have and use safe tools and equipment and properly maintain this equipment.
Top Ten Workplace Safety Tips Reduce Workplace Stress. Use Tools and Machines Properly. Use Mechanical Aids When Possible. Wear Protective Equipment. Stay Sober. Be Aware of Your Surroundings. Correct Posture Protects Your Back. Be Alert and Awake.More items...
Examples of OSHA standards include require- ments to provide fall protection, prevent trenching cave-ins, prevent exposure to some infectious diseases, ensure the safety of workers who enter confined spaces, prevent exposure to such harmful substances as asbestos and lead, put guards on machines, provide respirators or
OSHA's 7 Core Elements of an Effective Safety and Health ProgramManagement Leadership.Worker Participation.Hazard Identification & Assessment.Hazard Prevention & Control.Education & Training Program.Evaluation & Improvement.Management of Contractors / Staffed Employees.