Minnesota Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status In Minnesota, distinguishing between employees and independent contractors is crucial for tax and legal purposes. Determining whether an individual is an employee or a self-employed contractor depends on several factors outlined by the Minnesota Department of Revenue and other relevant authorities. This detailed description will provide a comprehensive overview of the criteria used to determine self-employed contractor status in Minnesota, along with key keywords associated with the topic. 1. Definition of a Self-Employed Contractor: A self-employed contractor is an individual who operates as an independent business entity, providing services to other businesses or clients, without being classified as an employee. They have the freedom to control how and when they perform their work, and they are responsible for their own taxes and benefits. 2. Criteria for Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status: To classify an individual as a self-employed contractor, the following factors are taken into consideration in Minnesota: a) Control and independence: The level of control the individual has over their work, including the ability to set their own schedule, choose assignments, and provide services to multiple clients. Keywords: control, independence, work arrangement, scheduling, client choice. b) Nature of the relationship: The extent to which the work performed by the individual is a core part of the hiring company's business. If the individual's services are integral to the primary business operations, they are more likely to be classified as an employee. Keywords: nature of work, core business, integral, business operations. c) Contractual agreements: The presence of a written contract between the hiring entity and the individual, outlining the terms of the working arrangement, payment structure, and duration of the engagement. Keywords: written contract, agreement, terms, payment, duration. d) Financial aspects: Whether the individual has a significant investment in their own tools, equipment, or workspace, and whether they have the opportunity to make a profit or incur a loss based on their expertise and business decisions. Keywords: investment, tools, equipment, workspace, profit and loss. e) Skills and specialization: The individual's level of skill, specialization, or professional licenses that distinguish them from regular employees. Keywords: skills, specialization, professional licenses, expertise. 3. Different Types of Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status in Minnesota: In Minnesota, there are no specific types or categories of self-employed contractor status. Instead, the determination is made on a case-by-case basis, evaluating the above-mentioned criteria. Overall, the determination of self-employed contractor status in Minnesota revolves around the level of control, independence, and business aspects associated with an individual's work. It is essential for both businesses and individuals to carefully assess their working relationship to ensure proper classification, as misclassification can lead to legal and tax consequences. It is advisable to consult with an attorney or a tax professional for accurate guidance and to stay updated on any changes in Minnesota laws or regulations related to determining self-employed contractor status.
Minnesota Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status
Description
How to fill out Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status?
You can invest time on-line attempting to find the authorized record format that fits the state and federal needs you will need. US Legal Forms provides a huge number of authorized types which are evaluated by professionals. You can easily acquire or print out the Minnesota Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status from your support.
If you already have a US Legal Forms account, you may log in and click the Obtain option. Next, you may comprehensive, change, print out, or indicator the Minnesota Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status. Each and every authorized record format you acquire is the one you have permanently. To get one more version associated with a obtained form, go to the My Forms tab and click the related option.
If you are using the US Legal Forms website for the first time, adhere to the basic guidelines under:
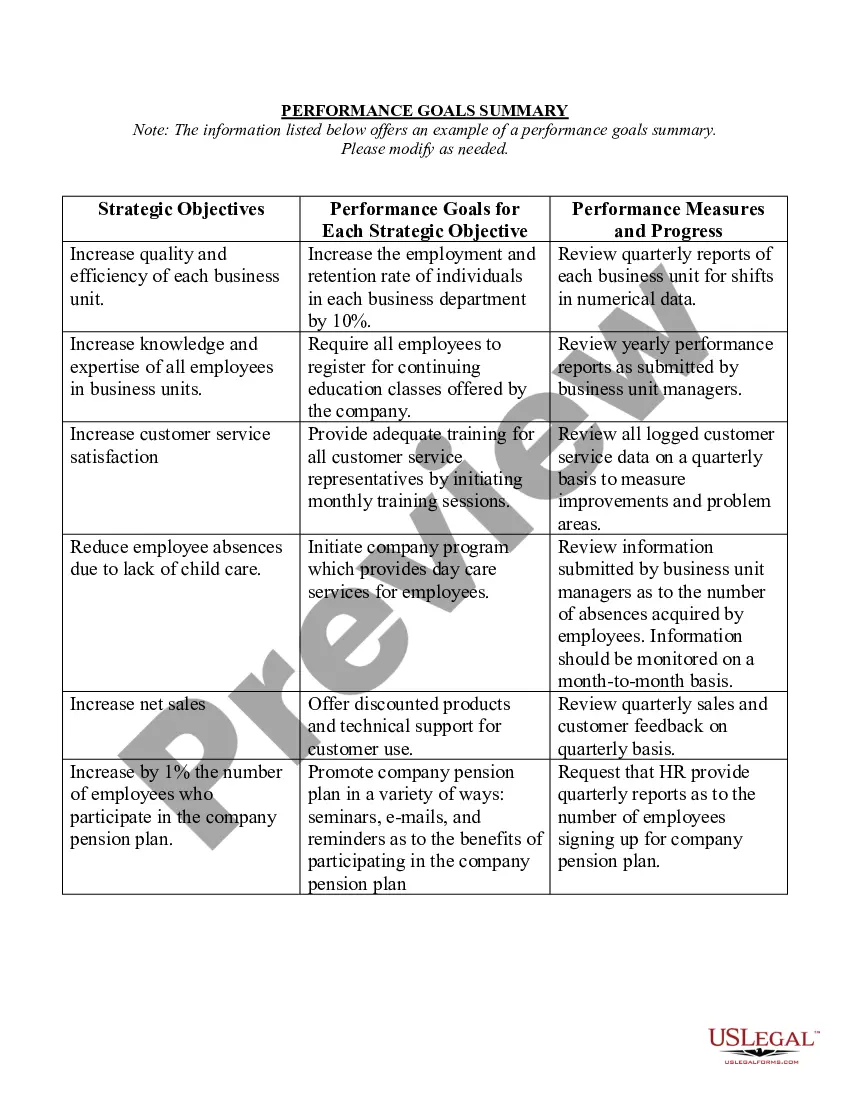
- First, make certain you have selected the proper record format for that state/metropolis of your choosing. Read the form description to ensure you have picked out the appropriate form. If accessible, take advantage of the Preview option to look from the record format also.
- In order to find one more variation of the form, take advantage of the Search industry to get the format that meets your requirements and needs.
- When you have found the format you need, just click Get now to move forward.
- Pick the prices prepare you need, type in your accreditations, and register for a merchant account on US Legal Forms.
- Complete the transaction. You may use your bank card or PayPal account to purchase the authorized form.
- Pick the structure of the record and acquire it to your product.
- Make changes to your record if needed. You can comprehensive, change and indicator and print out Minnesota Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status.
Obtain and print out a huge number of record templates while using US Legal Forms website, which provides the largest selection of authorized types. Use skilled and state-certain templates to take on your small business or individual needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
A worker is an independent contractor if you have the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not how to work is performed. Independent contractors pay self-employment tax on their earnings.
Independent contractors provide goods or services according to the terms of a contract they have negotiated with an employer. Independent contractors are not employees, and therefore they are not covered under most federal employment statutes.
The basic test for determining whether a worker is an independent contractor or an employee is whether the principal has the right to control the manner and means by which the work is performed.
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
A 1099 (Miscellaneous Income) form issued by the business. A narrated conversation with the employer. For FS, self-employed clients can be certified once without income verification. At the time of certification, explain to the client - in writing - that they must begin keeping income records.
What Is an Independent Contractor? An independent contractor is a self-employed person or entity contracted to perform work foror provide services toanother entity as a nonemployee. As a result, independent contractors must pay their own Social Security and Medicare taxes.
How to demonstrate that you are an independent worker on your resumeMention that time when you had to work on a project on your own.Talk about projects that required extra accountability.Describe times when you had to manage several projects all at once.More items...
Independent contractors are self-employed workers who provide services for an organisation under a contract for services. Independent contractors are not employees and are typically highly skilled, providing their clients with specialist skills or additional capacity on an as needed basis.
Four ways to verify your income as an independent contractorIncome-verification letter. The most reliable method for proving earnings for independent contractors is a letter from a current or former employer describing your working arrangement.Contracts and agreements.Invoices.Bank statements and Pay stubs.