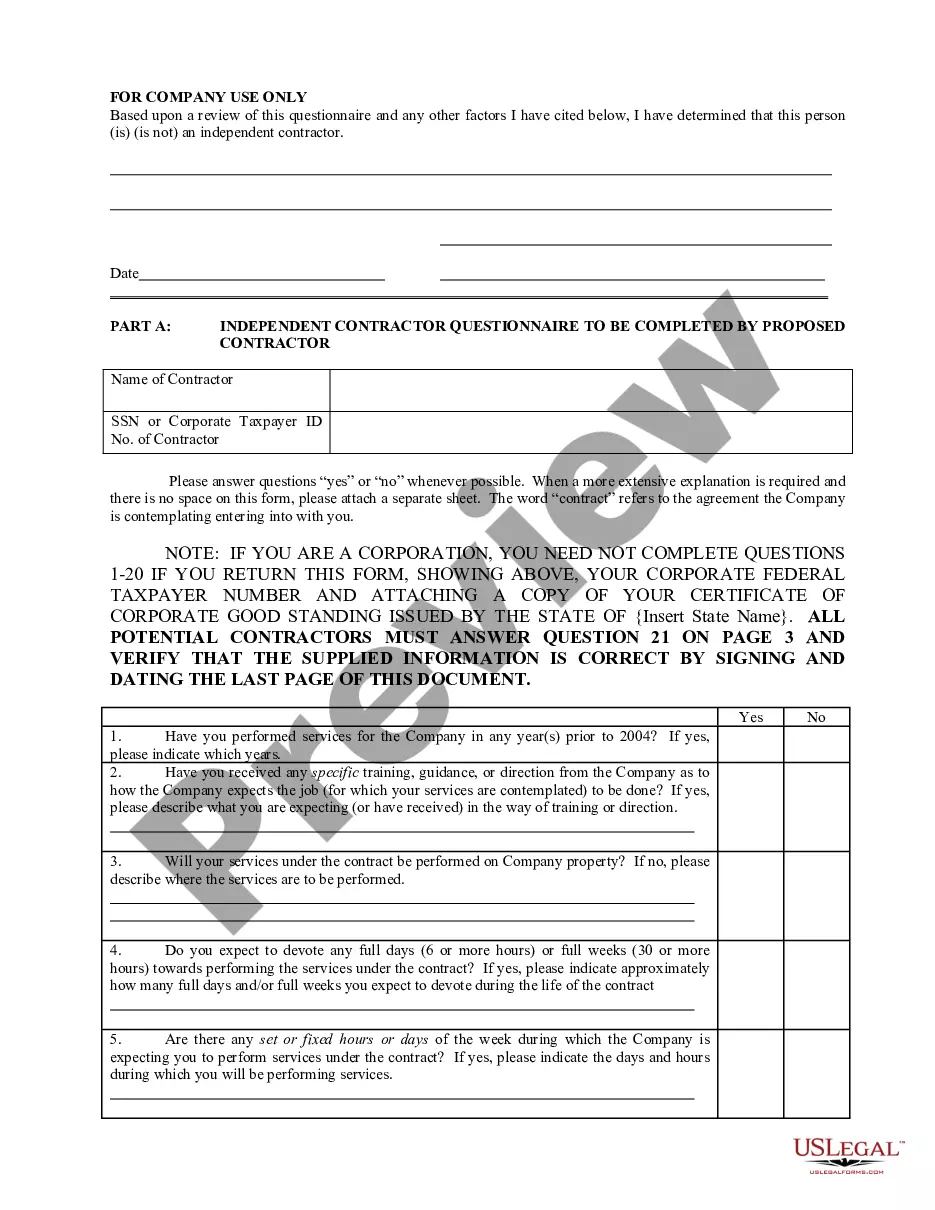
Minnesota Determining Self-Employed Independent Contractor Status
Description
How to fill out Determining Self-Employed Independent Contractor Status?
Finding the appropriate official document format can be a challenge. Of course, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how do you locate the official form you require? Utilize the US Legal Forms website.
The platform provides a vast array of templates, including the Minnesota Determining Self-Employed Independent Contractor Status, which is suitable for both business and personal purposes. All forms are reviewed by experts and comply with federal and state regulations.
If you are already registered, Log In to your account and hit the Obtain button to download the Minnesota Determining Self-Employed Independent Contractor Status. Use your account to explore the legal forms you have previously purchased. Visit the My documents section of your account to download an additional copy of the document you require.
US Legal Forms is the largest collection of legal forms where you can find a multitude of document templates. Utilize the service to download professionally crafted documents that meet state requirements.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct form for your area/county. You can view the form using the Preview button and review the form summary to confirm it is suitable for you.
- If the form does not meet your requirements, use the Search field to find the appropriate form.
- Once you are confident that the form is appropriate, click the Get now button to obtain the form.
- Select the pricing plan you prefer and input the necessary information. Create your account and complete your purchase using your PayPal account or credit card.
- Choose the file format and download the official document to your device.
- Complete, modify, print, and sign the downloaded Minnesota Determining Self-Employed Independent Contractor Status.
Form popularity
FAQ
Independent contractors are self-employed workers who provide services for an organisation under a contract for services. Independent contractors are not employees and are typically highly skilled, providing their clients with specialist skills or additional capacity on an as needed basis.
The basic test for determining whether a worker is an independent contractor or an employee is whether the principal has the right to control the manner and means by which the work is performed.
Paying yourself as an independent contractor Independent contractor pay allows your business the opportunity to stay on budget for projects rather than hire via a third party. As an independent contractor, you will need to pay self-employment taxes on your wages. You will file a W-9 with the LLC.
Four ways to verify your income as an independent contractorIncome-verification letter. The most reliable method for proving earnings for independent contractors is a letter from a current or former employer describing your working arrangement.Contracts and agreements.Invoices.Bank statements and Pay stubs.
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
To set yourself up as a self-employed taxpayer with the IRS, you simply start paying estimated taxes (on Form 1040-ES, Estimated Tax for Individuals) and file Schedule C, Profit or Loss From Business, and Schedule SE, Self-Employment Tax, with your Form 1040 tax return each April.
Becoming an independent contractor is one of the many ways to be classified as self-employed. By definition, an independent contractor provides work or services on a contractual basis, whereas, self-employment is simply the act of earning money without operating within an employee-employer relationship.
How to demonstrate that you are an independent worker on your resumeMention that time when you had to work on a project on your own.Talk about projects that required extra accountability.Describe times when you had to manage several projects all at once.More items...
What Is an Independent Contractor? An independent contractor is a self-employed person or entity contracted to perform work foror provide services toanother entity as a nonemployee. As a result, independent contractors must pay their own Social Security and Medicare taxes.