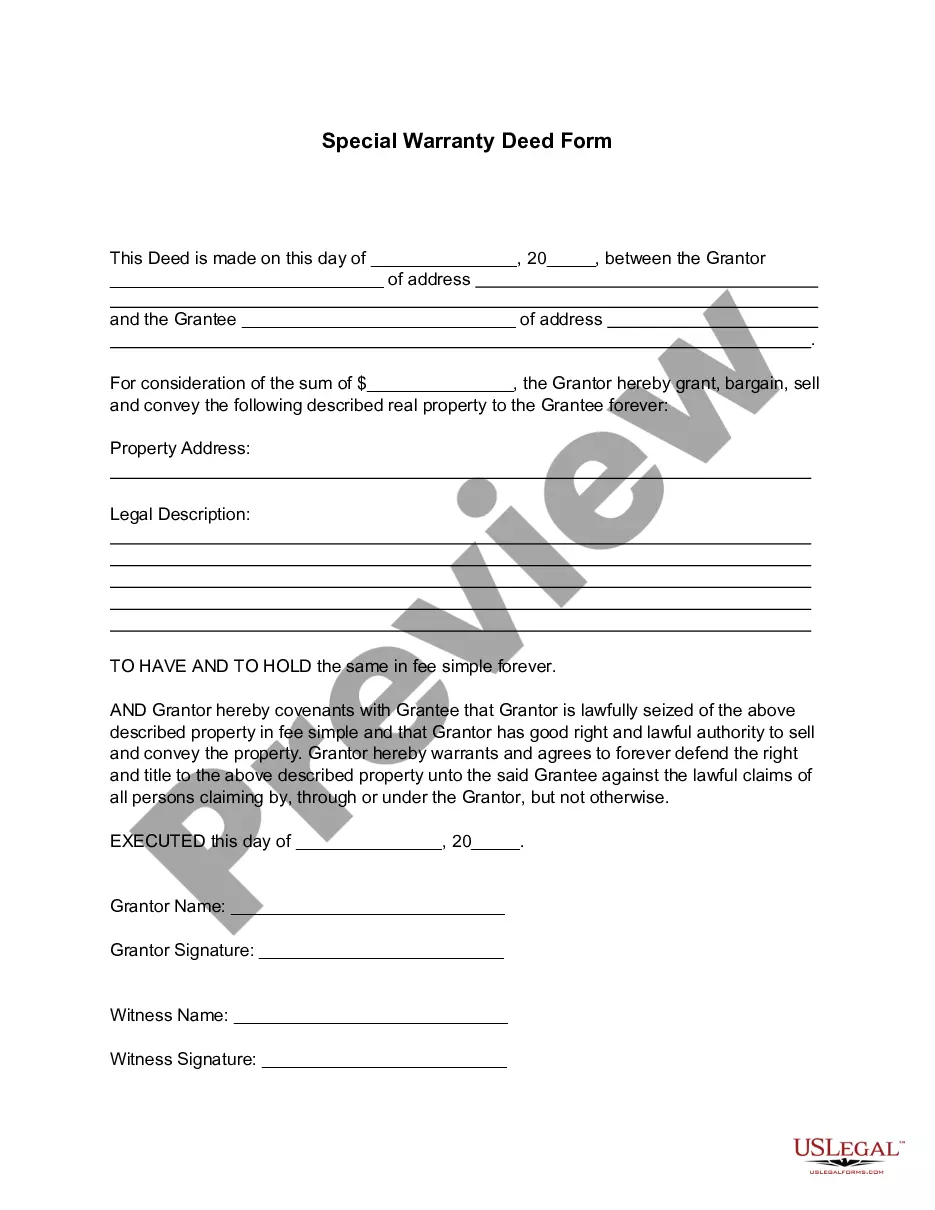
Minnesota Noise Ordinance
Description
How to fill out Noise Ordinance?
You are able to devote several hours on the Internet trying to find the authorized papers format that suits the state and federal demands you need. US Legal Forms provides 1000s of authorized types which are reviewed by experts. You can actually download or print the Minnesota Noise Ordinance from our services.
If you have a US Legal Forms profile, you can log in and then click the Download key. Following that, you can complete, modify, print, or signal the Minnesota Noise Ordinance. Each authorized papers format you purchase is yours eternally. To have an additional duplicate associated with a bought develop, go to the My Forms tab and then click the corresponding key.
Should you use the US Legal Forms site for the first time, stick to the simple instructions listed below:
- First, be sure that you have chosen the right papers format for your county/town of your choosing. See the develop outline to make sure you have picked the correct develop. If readily available, utilize the Review key to appear with the papers format too.
- If you would like discover an additional variation of your develop, utilize the Lookup discipline to find the format that meets your needs and demands.
- When you have discovered the format you desire, just click Get now to move forward.
- Choose the rates plan you desire, type your qualifications, and sign up for your account on US Legal Forms.
- Comprehensive the deal. You may use your credit card or PayPal profile to cover the authorized develop.
- Choose the formatting of your papers and download it to the system.
- Make modifications to the papers if needed. You are able to complete, modify and signal and print Minnesota Noise Ordinance.
Download and print 1000s of papers templates utilizing the US Legal Forms website, which provides the biggest collection of authorized types. Use professional and state-distinct templates to handle your organization or person needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
There is not a limit on maximum noise. The statutory limits for a residential location are L10 = 65 dBA and L50 = 60 dBA during the daytime ( a.m ? p.m.) and L10 = 55 dBA and L50 = 50 dBA during the nighttime ( p.m. ? a.m.) (Minn. State Noise Pollution Control Rules 7030.0040).
Measuring sound transmission 30 dB has little sound-control effectiveness. 35 dB allows normal conversation to be heard through the wall. 40 dB allows loud conversation to be heard through the wall. 50 dB will prevent loud conversation from being heard through the wall.
50dBA is incredibly noisy for a fan. I also like to keep my fans to below or near 20dBA if possible. The incredibly noisy Fulltech fan you link to does 175 m3/h, which is quite a bit more, but even slowing it down to something equivalent will not net you anything bearable.
Tips for using sound to fall asleep Try to keep your white noise volume to 50 decibels or lower. Set a timer if you can. Too much noise consistently while you sleep may be disruptive to your sleep quality and hearing abilities.
Sound is measured in decibels (dB). A whisper is about 30 dB, normal conversation is about 60 dB, and a motorcycle engine running is about 95 dB. Noise above 70 dB over a prolonged period of time may start to damage your hearing. Loud noise above 120 dB can cause immediate harm to your ears.
50 dB is as loud as a quiet conversation, a quiet suburb, a quiet office, or a quiet refrigerator. Notice the use of the word 'quiet' when describing this noise level?
Generally, exposure to sound levels above 85 dB is considered damaging to human hearing. That is why this is the most common maximum value allowed in industrial environments. For residential environments, the accepted decibel level is lower. Any noise exceeding 70 dB is considered disturbing.
What to do Everyone calls the property owner when a party disturbs neighbors. Invite tenants or owner to a meeting or mediation session. Contact your Crime Prevention Specialist.
Sounds at or below 70 dB are considered safe for our hearing. That's the sound of a normal conversation between two people. Sounds above 70 dB will damage hearing over time. Like the Richter scale for measuring earthquakes, the decibel scale is logarithmic.
30 dB: Whispering nearby. 40 dB: Quiet library sounds. 50 dB: Refrigerator.