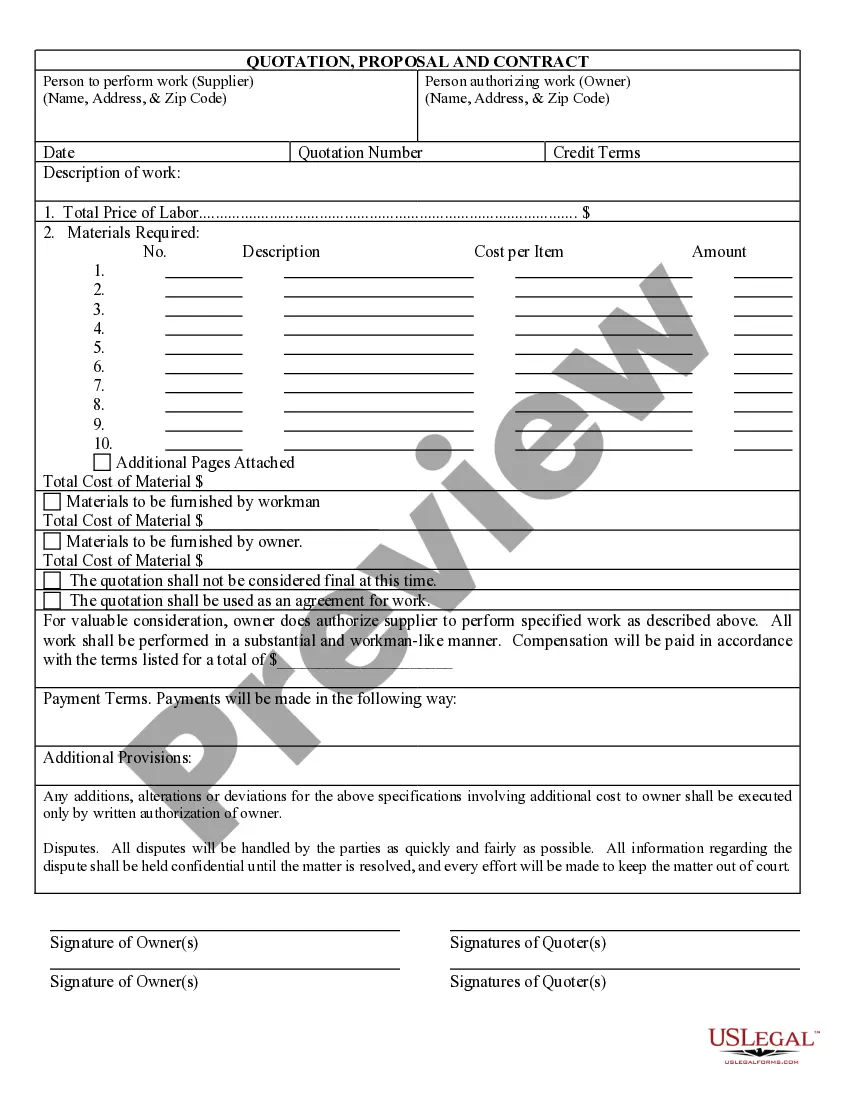
Missouri Arbitration Agreement - Future Dispute
Description
How to fill out Arbitration Agreement - Future Dispute?
It is feasible to spend hours online searching for the legal document template that fulfills the federal and state requirements you need.
US Legal Forms provides thousands of legal forms that are reviewed by experts.
You can retrieve or create the Missouri Arbitration Agreement - Future Dispute from the services.
If available, utilize the Review option to examine the document template as well.
- If you already possess a US Legal Forms account, you can Log In and click on the Download option.
- Subsequently, you can complete, modify, create, or sign the Missouri Arbitration Agreement - Future Dispute.
- Each legal document template you obtain is yours indefinitely.
- To get another copy of the downloaded form, navigate to the My documents tab and click on the appropriate option.
- If you are accessing the US Legal Forms website for the first time, follow the straightforward instructions below.
- First, ensure that you have chosen the correct document template for your region or area of interest.
- Review the form outline to confirm you have selected the correct form.
Form popularity
FAQ
In a nutshell, it can be concluded that claiming of arbitration clause after dispute varies according to situation. If the parties are not satisfied with the decision of mediation, conciliation or negotiation than they can opt for arbitration.
If an employee can show some substantial relationship between the fraud committed or the misrepresentation made by the employer and the arbitration agreement, a court will void the agreement.
Under the Armendariz standards, an arbitration agreement will not be enforced in California if it is both "procedurally unconscionable" and "substantively unconscionable." Any arbitration agreement required as a condition of employment (i.e., any mandatory arbitration agreement) is automatically considered procedurally
You Can Be Compelled to Arbitrate Based on an Agreement You Didn't Sign. As a general rule, parties cannot be forced to arbitrate a dispute unless they signed a clear and binding agreement to arbitrate.
Missouri Courts Uphold and Invalidate Arbitration Agreements. (2) Incorporation of the AAA rules in an arbitration agreement generally constitutes clear and unmistakable evidence of the parties' intention to arbitrate.
Under certain circumstances, a claimant's unreasonable delay can, in itself, lead to waiver of the right to arbitrate. While California courts have yet to provide a concrete deadline, an unreasonable delay of three years provides a sound basis to pursue waiver.
To enforce the right to arbitrate, the party must then file a motion to stay the lawsuit in favor of arbitration. If both parties to the agreement ignore the right to arbitrate, the right is waived.
What is Pre-Dispute Arbitration? Arbitration is a legal process in which a dispute is settled by one or more arbitrators who decide the outcome instead of a jury made up of members of the community. Pre-dispute arbitration means that the consumer must agree to arbitration before any dispute arises.
Yes, it is possible for arbitration clauses to apply to claims that predate the contract containing the arbitration clause at issue. Retroactive application of an arbitration clause depends on the language of the arbitration provision and applicable substantive law.