Missouri Writ of Replevin or Repossession
Description
How to fill out Writ Of Replevin Or Repossession?
Choosing the right legal file format might be a battle. Of course, there are tons of layouts available on the net, but how do you find the legal develop you will need? Make use of the US Legal Forms web site. The assistance delivers thousands of layouts, including the Missouri Writ of Replevin or Repossession, which you can use for business and personal demands. All the kinds are inspected by specialists and fulfill state and federal demands.
In case you are currently signed up, log in to your bank account and click on the Download switch to get the Missouri Writ of Replevin or Repossession. Make use of your bank account to look with the legal kinds you possess bought previously. Proceed to the My Forms tab of your own bank account and get one more duplicate of the file you will need.
In case you are a fresh consumer of US Legal Forms, listed below are easy recommendations so that you can adhere to:
- Initial, make certain you have chosen the right develop for your personal town/county. You may look through the shape using the Review switch and look at the shape information to ensure it will be the right one for you.
- In the event the develop fails to fulfill your expectations, utilize the Seach field to get the correct develop.
- When you are certain that the shape is suitable, click the Get now switch to get the develop.
- Choose the costs program you want and enter in the necessary details. Design your bank account and purchase an order utilizing your PayPal bank account or credit card.
- Choose the file file format and obtain the legal file format to your device.
- Total, edit and print and sign the obtained Missouri Writ of Replevin or Repossession.
US Legal Forms will be the greatest local library of legal kinds that you can discover various file layouts. Make use of the company to obtain appropriately-created documents that adhere to condition demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
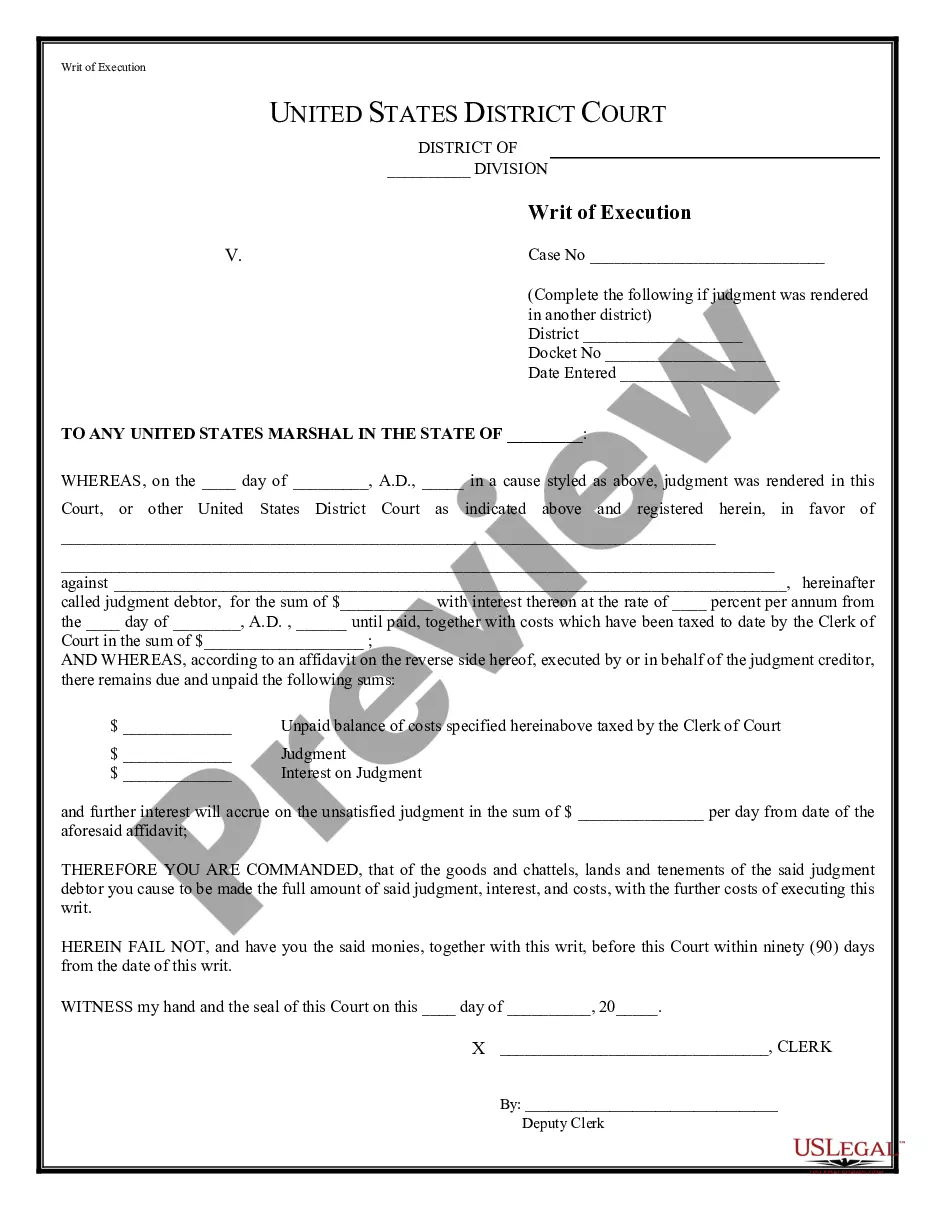
A writ of replevin is a prejudgment process ordering the seizure or attachment of alleged illegally taken or wrongfully withheld property to be held in the U.S. Marshal's custody or that of another designated official, under order and supervision of the court, until the court determines otherwise.
Replevin allows the plaintiff to gain possession of the personal property; the other causes of action only allow the plaintiff to recover damages, not possession of the property. Replevin also allows the plaintiff to obtain possession of the property at the beginning of a lawsuit.
Replevin, also known as "claim and delivery," is an action to recover personal property that was wrongfully taken or detained. Unlike other forms of legal recovery, replevin seeks the return of the actual thing itself, as opposed to monetary damages (the more commonly sought-after remedy).
Replevin (/r??pl?v?n/) or claim and delivery (sometimes called revendication) is a legal remedy, which enables a person to recover personal property taken wrongfully or unlawfully, and to obtain compensation for resulting losses.
If a court order has been issued against you, the landlord will then request a writ of execution of the eviction. Once the Court issues the writ of execution, the Sheriff's Department may move forward with the eviction. The Sheriff's Department will post a Notice of Eviction on the premises (property).
?The action of replevin may be maintained to recover any goods or chattels in which the plaintiff has a general or special property interest with a right to immediate possession and which are wrongfully detained from him in any manner, together with the damages for such wrongful detention.? Conn. Gen. Stat.
There is a procedure under Missouri law, however, whereby a judgment creditor can seek an extension of the ten years during which a judgment is active. To do so, the judgment creditor must file a motion to revive the judgment in the court which entered it.
(a) When and by Whom. A judgment may be revived by order of the court that entered it pursuant to a motion for revival filed by a judgment creditor within ten years after entry of the judgment, the last payment of record, or the last prior revival of the judgment.