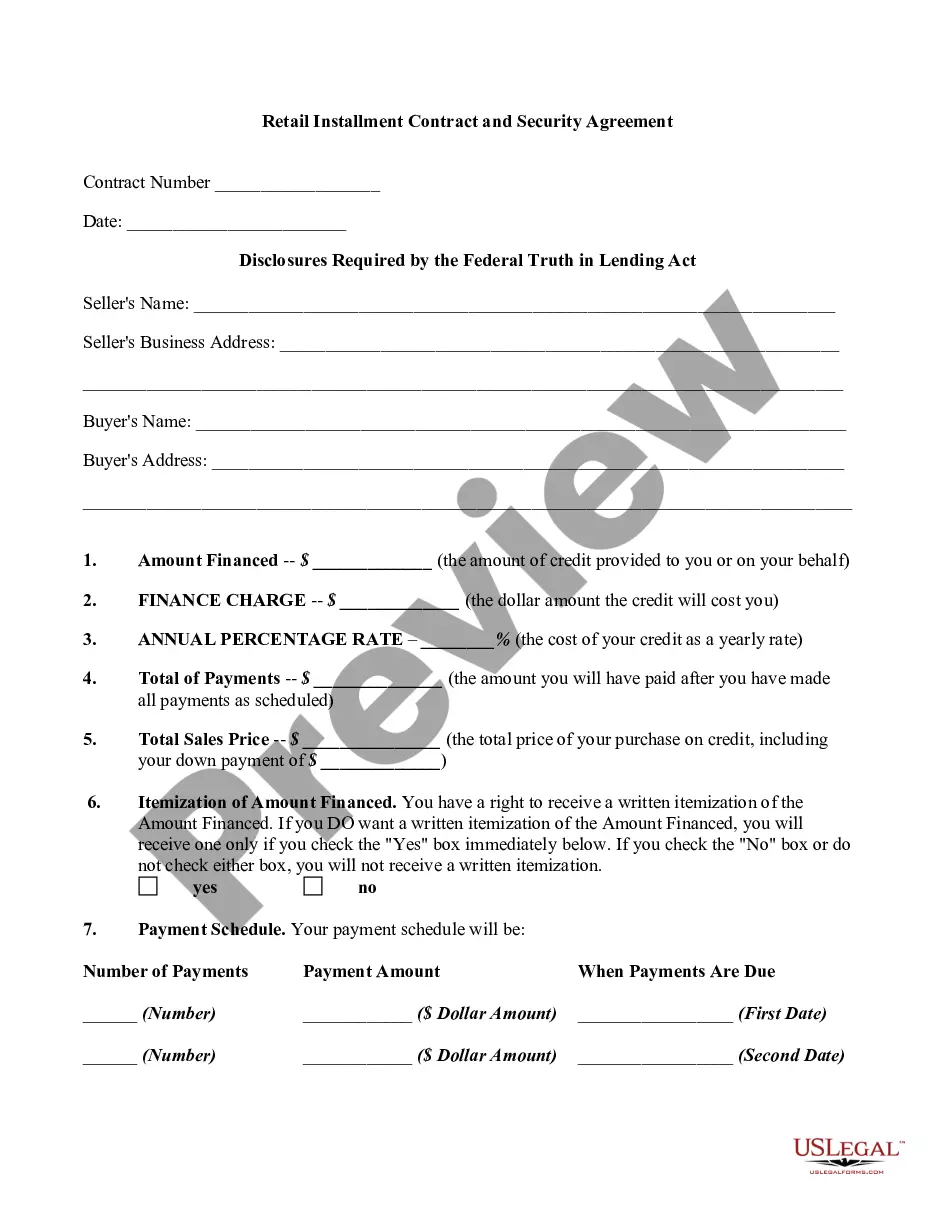
A secured transaction is created when a buyer or borrower (debtor) grants a seller or lender (creditor or secured party) a security interest in personal property (collateral). A security interest allows a creditor to repossess and sell the collateral if a debtor fails to pay a secured debt.
A secured transaction involves a sale on credit or lending money where a creditor is unwilling to accept the promise of a debtor to pay an obligation without some sort of collateral. The creditor requires the debtor to secure the obligation with collateral so that if the debtor does not pay as promised, the creditor can take the collateral, sell it, and apply the proceeds against the unpaid obligation of the debtor. A security interest is an interest in personal property or fixtures that secures payment or performance of an obligation. The property that is subject to the security interest is called the collateral. The party holding the security interest is called the secured party.