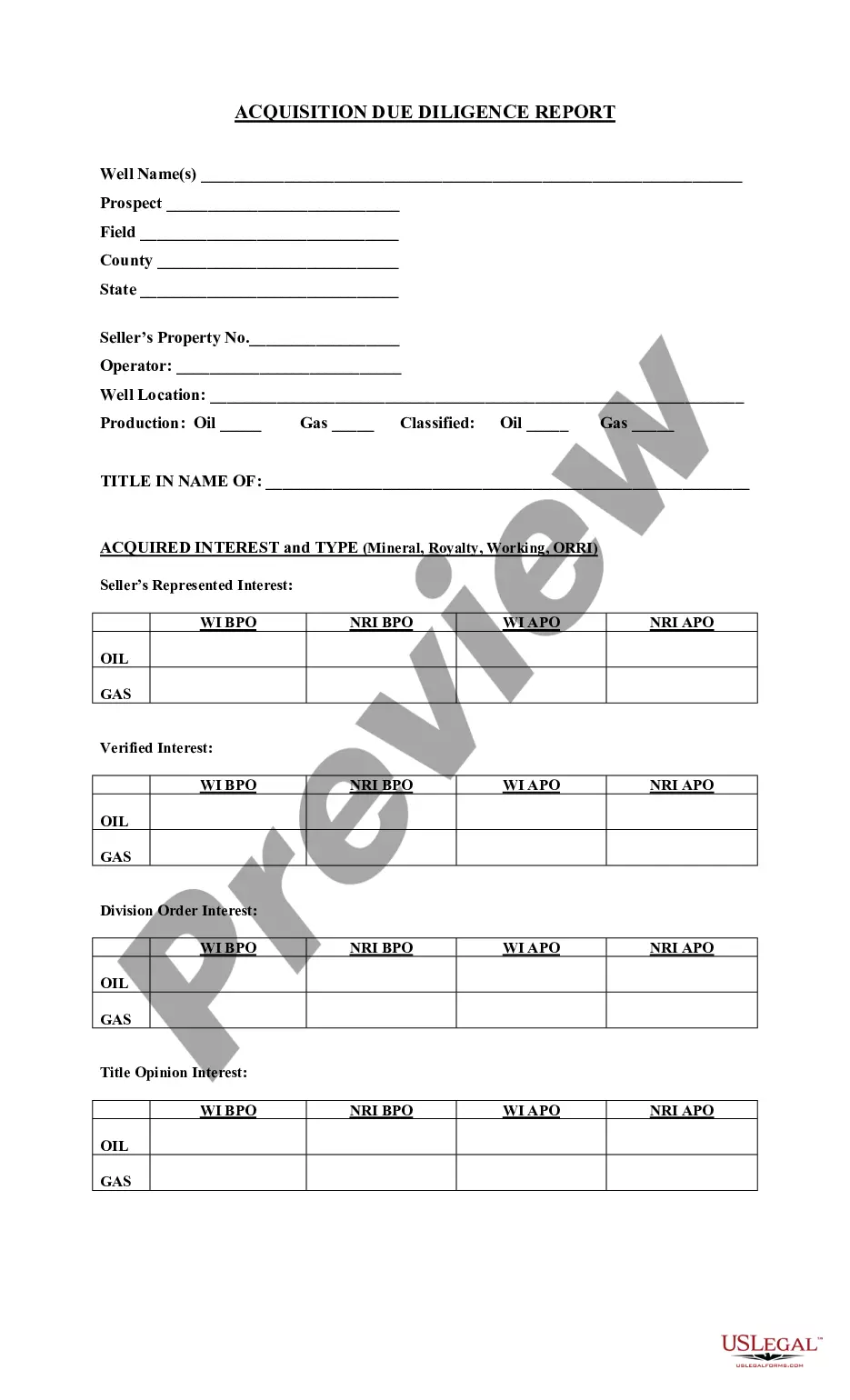
Missouri Confidentiality Agreement Addressed to Party Presenting Data and / or Information
Description
How to fill out Confidentiality Agreement Addressed To Party Presenting Data And / Or Information?
US Legal Forms - among the greatest libraries of lawful types in the States - offers a variety of lawful file layouts you may down load or print out. Making use of the website, you can find a huge number of types for organization and personal functions, sorted by types, says, or keywords and phrases.You can find the latest versions of types like the Missouri Confidentiality Agreement Addressed to Party Presenting Data and / or Information within minutes.
If you already have a membership, log in and down load Missouri Confidentiality Agreement Addressed to Party Presenting Data and / or Information from the US Legal Forms collection. The Down load switch can look on each and every form you look at. You gain access to all earlier acquired types in the My Forms tab of your own accounts.
If you would like use US Legal Forms initially, here are simple instructions to help you started off:
- Ensure you have selected the proper form for your personal town/state. Go through the Review switch to review the form`s content material. Read the form outline to ensure that you have selected the appropriate form.
- If the form does not suit your requirements, utilize the Lookup industry at the top of the screen to obtain the one which does.
- In case you are happy with the shape, confirm your choice by clicking on the Purchase now switch. Then, select the rates strategy you prefer and supply your qualifications to register on an accounts.
- Process the deal. Make use of charge card or PayPal accounts to finish the deal.
- Pick the format and down load the shape on the product.
- Make alterations. Load, change and print out and indicator the acquired Missouri Confidentiality Agreement Addressed to Party Presenting Data and / or Information.
Each format you put into your bank account lacks an expiration day and it is your own permanently. So, if you wish to down load or print out yet another copy, just go to the My Forms segment and then click around the form you will need.
Obtain access to the Missouri Confidentiality Agreement Addressed to Party Presenting Data and / or Information with US Legal Forms, one of the most comprehensive collection of lawful file layouts. Use a huge number of expert and condition-distinct layouts that fulfill your organization or personal requires and requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
The agreement will name the party or parties involved, the items subject to non-disclosure, the duration of the agreement and the obligations of the recipient(s) of confidential information.
Hear this out loud PauseUpon signing this agreement, [insert name of the receiving party] agrees not to use any sensitive, privileged, or confidential information disclosed to them by [insert your name or business name] for any purpose other than the intended use as would be relevant to the relationship entered into by the parties. Confidentiality Agreement | LGM Advisors lgmadvisors.com.au ? uploads ? 2016/11 lgmadvisors.com.au ? uploads ? 2016/11
A confidentiality agreement should include a clear definition of the confidential information, scope of the agreement, obligations of the receiving party, the duration of the contract, any exceptions to confidentiality, and the consequences of a breach of the contract.
Detailed five essential elements that every confidentiality agreement should include. 1) What information is considered confidential? ... 2) Exceptions to confidentiality. ... 3) Obligations/Requirements of signees. ... 4) Consequences of breaking the confidentiality agreement. ... 5) Length of the agreement.
Hear this out loud PauseOne way to indicate confidentiality and sensitivity is to use labels on the letter and the envelope, such as "Confidential", "Personal", "Private", or "Sensitive". These labels should be placed on the top or bottom of the letter, and on the front or back of the envelope. How to Write Confidential and Sensitive Letters with Enclosures linkedin.com ? advice ? how-do-you-indicat... linkedin.com ? advice ? how-do-you-indicat...
Hear this out loud PauseA confidentiality agreement should include a clear definition of the confidential information, scope of the agreement, obligations of the receiving party, the duration of the contract, any exceptions to confidentiality, and the consequences of a breach of the contract. How to Write a Confidentiality Agreement (+ Free Template) onboardmeetings.com ? blog ? confidentiali... onboardmeetings.com ? blog ? confidentiali...
Hear this out loud PauseThe agreement should identify the purpose to which the recipient can put the confidential information. All other uses of the confidential information should be prohibited. Sometimes a confidentiality agreement states that no rights are licensed by the confidentiality agreement. This is stating the obvious. What should a confidentiality agreement cover? business.qld.gov.au ? ip-kit ? browse-ip-topics business.qld.gov.au ? ip-kit ? browse-ip-topics
Contents Parties to the agreement. Identification of what information is confidential. Time frame of the agreement. Return of the information. Obligations of the recipient. Remedies for breaches of agreement. Other clauses.