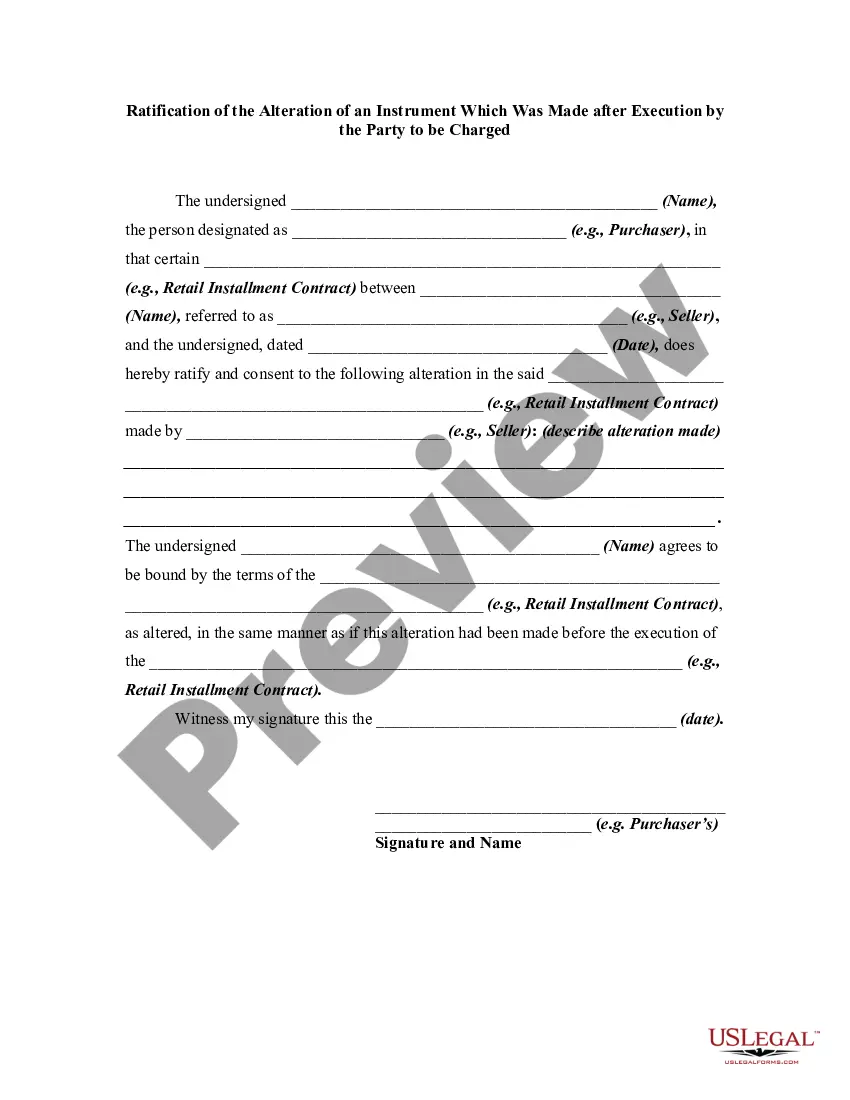
An alteration of a written instrument is a change in language of the instrument that is made by one of the parties to the instrument who is entitled to make the change. Any material alteration of a written instrument, after its execution, made by the owner or holder of the instrument, without the consent of the party to be charged, renders the instrument void as to the nonconsenting party. The party to be charged refers to that party or parties against whom enforcement of a contract or instrument is sought.
If a party consents to the alteration, the instrument will not be rendered invalid as to that party.
The Mississippi Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged refers to a legal process in the state of Mississippi where a party acknowledges and approves a modification or alteration made to a document after its initial execution. In legal terms, ratification in Mississippi generally means that the party who made the alteration seeks confirmation from the other party involved that they agree to the changes made to the document. This process is essential to ensure the validity and enforceability of the altered instrument. Keywords: Mississippi, ratification, alteration, instrument, execution, party to be charged. There are various types of Mississippi Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged, including: 1. Mississippi Ratification of Alteration in a Contract: This type of ratification specifically relates to modifications made to a contract after its original execution. It allows the parties involved to confirm their acceptance of the changes made, ensuring that the contract remains legally binding. 2. Mississippi Ratification of Alteration in a Deed: This form of ratification pertains to any changes made to a deed after its initial execution. It serves to establish the parties' consent to the alterations, thereby maintaining the integrity of the deed and ensuring its enforceability. 3. Mississippi Ratification of Alteration in a Will: In the context of wills, this ratification refers to any amendments or modifications made to a will document after it has been executed. The party to be charged verifies their acceptance of the alterations to guarantee that the revised will accurately reflect their intentions. 4. Mississippi Ratification of Alteration in a Promissory Note: This type of ratification involves changes made to a promissory note, such as modifications to loan terms, repayment schedules, or interest rates. The party to be charged ratifies the alterations to signify their agreement and consent to the updated terms of the note. Overall, Mississippi Ratification of the Alteration of an Instrument Which Was Made after Execution by the Party to be Charged ensures transparency, agreement, and legality in cases where modifications are made to written instruments after their initial execution.