Mississippi Balance Sheet Deposits
Description
How to fill out Balance Sheet Deposits?
Finding the appropriate legal document template can be quite challenging. Of course, there are numerous formats available online, but how can you locate the legal form you require.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. The service offers thousands of formats, including the Mississippi Balance Sheet Deposits, which can be utilized for both business and personal purposes.
All of the documents are verified by experts and comply with state and federal requirements.
Once you confirm that the document is right, click the Buy now button to obtain the form. Select the pricing plan you prefer and enter the required information. Create your account and complete your order using your PayPal account or credit card. Choose the file format and download the legal document template to your device. Complete, edit, print, and sign the received Mississippi Balance Sheet Deposits. US Legal Forms is the largest collection of legal documents where you can find numerous document templates. Take advantage of the service to obtain professionally created paperwork that meets state requirements.
- If you are already signed up, Log Into your account and click on the Download button to retrieve the Mississippi Balance Sheet Deposits.
- Use your account to browse the legal documents you have previously obtained.
- Visit the My documents section of your account to get another copy of the documents you require.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are simple steps to follow.
- First, ensure that you have chosen the correct form for your city/state. You can view the document using the Preview button and read the description to confirm it is suitable for you.
- If the document does not meet your needs, use the Search field to find the appropriate form.
Form popularity
FAQ
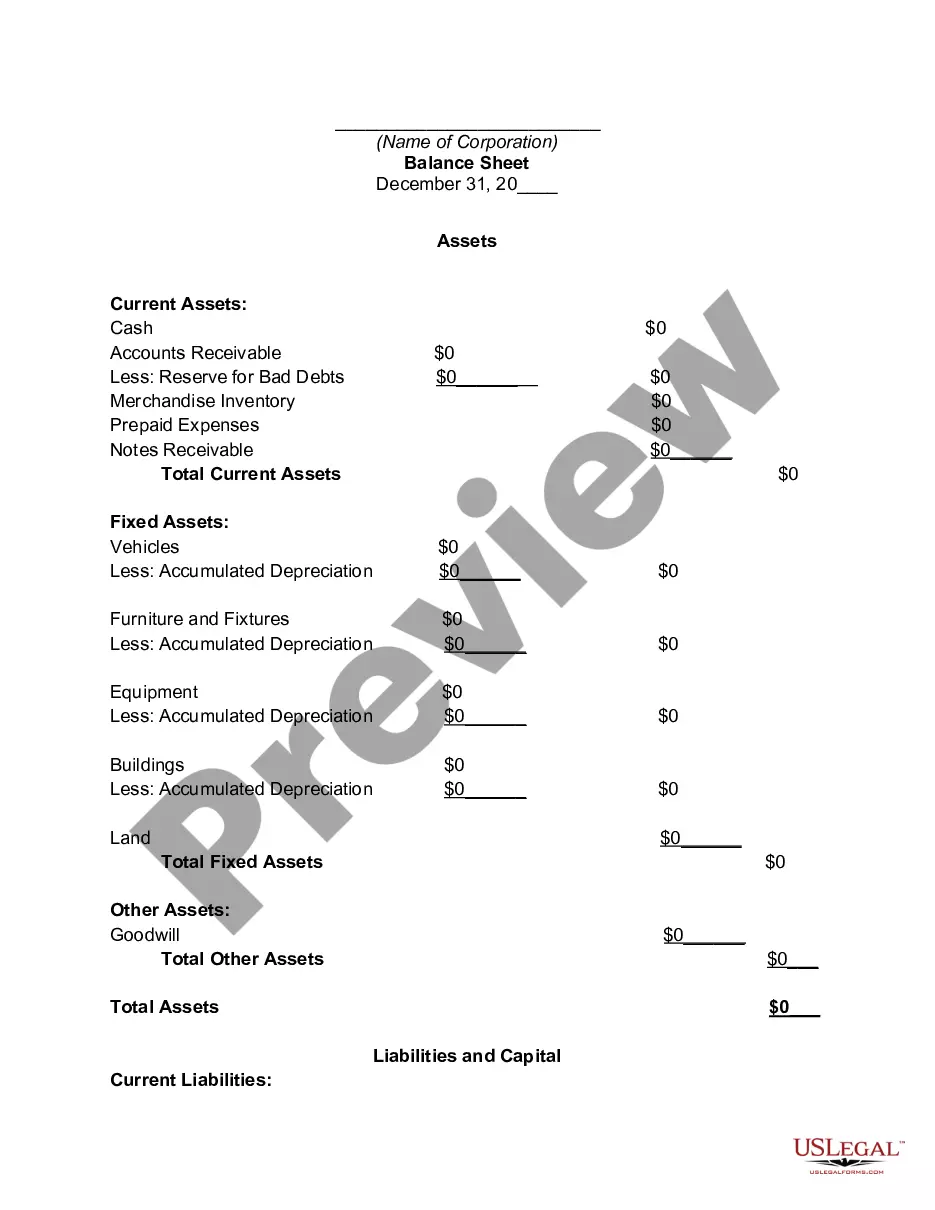
Deposits is a current liability account in the general ledger, in which is stored the amount of funds paid by customers in advance of a product or service delivery. These funds are essentially down payments.
Cash and cash equivalents under the current assets section of a balance sheet represent the amount of money the company has in the bank, whether in the form of cash, savings bonds, certificates of deposit, or money invested in money market funds.
How to Prepare Financial StatementsStep 1: Verify Receipt of Supplier Invoices.Step 2: Verify Issuance of Customer Invoices.Step 3: Accrue Unpaid Wages.Step 4: Calculate Depreciation.Step 5: Value Inventory.Step 6: Reconcile Bank Accounts.Step 7: Post Account Balances.Step 8: Review Accounts.More items...?
How to Fill Out a Personal Financial StatementComplete the identifying information at the top of the personal financial statement.List each asset in the section provided.List each liability in the section provided.Calculate the net worth by subtracting the total liabilities from the total assets.More items...
The deposit itself is a liability owed by the bank to the depositor. Bank deposits refer to this liability rather than to the actual funds that have been deposited. When someone opens a bank account and makes a cash deposit, he surrenders the legal title to the cash, and it becomes an asset of the bank.
Total liabilities: Add up the total amount of your liabilities. Net worth: Subtract your total liabilities from your total assets to determine your net worth. Total: Add your Total Liabilities and your Net Worth. This value should be equal to your total assets.
Cash and cash equivalents under the current assets section of a balance sheet represent the amount of money the company has in the bank, whether in the form of cash, savings bonds, certificates of deposit, or money invested in money market funds. It tells you how much money is available to the business immediately.
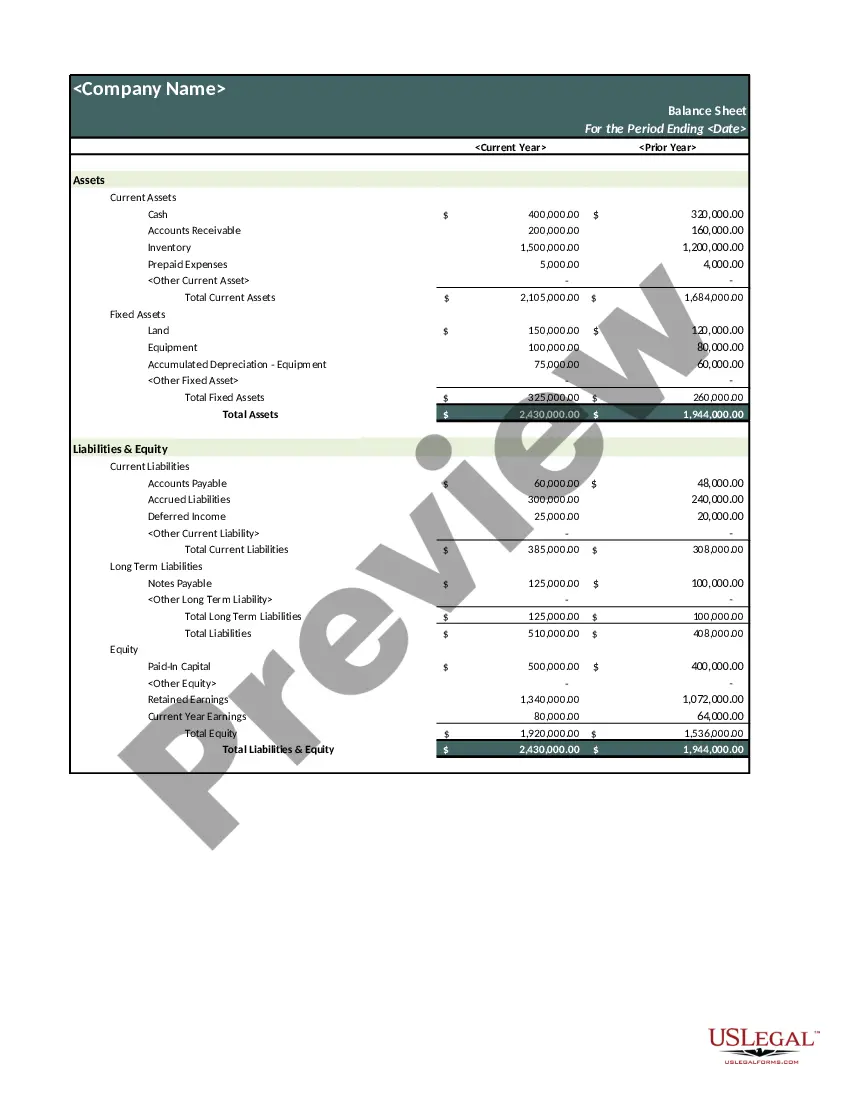
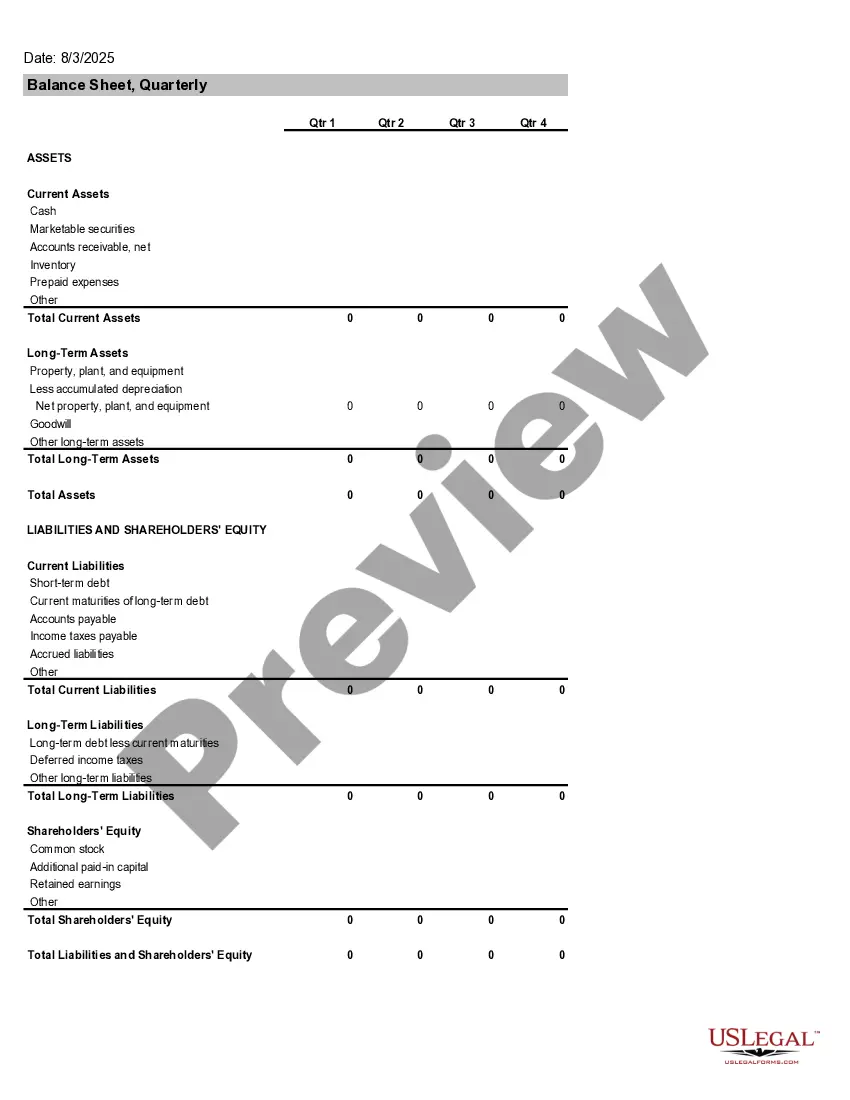
How to make a balance sheetStep 1: Pick the balance sheet date.Step 2: List all of your assets.Step 3: Add up all of your assets.Step 4: Determine current liabilities.Step 5: Calculate long-term liabilities.Step 6: Add up liabilities.Step 7: Calculate owner's equity.Step 8: Add up liabilities and owners' equity.
How to Make a Financial Statement for Small BusinessBalance Sheet.Income Sheet.Statement of Cash Flow.Step 1: Make A Sales Forecast.Step 2: Create A Budget for Your Expenses.Step 3: Develop Cash Flow Statement.Step 4: Project Net Profit.Step 5: Deal with Your Assets and Liabilities.More items...?
How to Prepare a Basic Balance SheetDetermine the Reporting Date and Period.Identify Your Assets.Identify Your Liabilities.Calculate Shareholders' Equity.Add Total Liabilities to Total Shareholders' Equity and Compare to Assets.