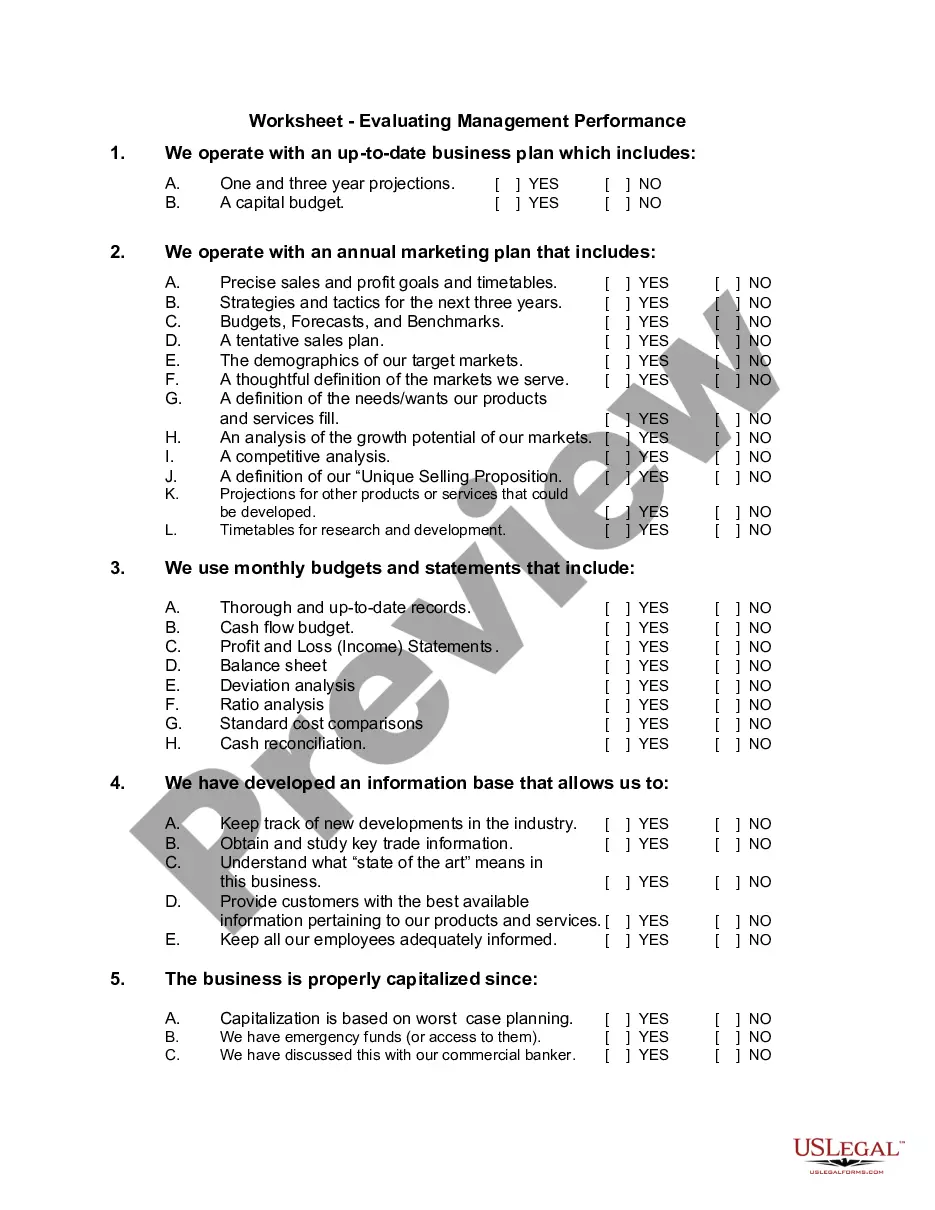
Mississippi Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status: A Comprehensive Guide Introduction: Determining self-employed contractor status in Mississippi is crucial for both employers and individuals engaged in independent contracting work. This detailed description aims to provide valuable insights, guidelines, and relevant keywords to understand the various aspects of Mississippi's self-employed contractor status. Key Terms and Definitions: 1. Self-employed contractor: An individual who operates as an independent contractor rather than an employee, offering services to clients or businesses on a contract basis. 2. Employee: An individual hired by an employer to work under their direction in exchange for wages or salary. Types of Mississippi Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status: 1. Mississippi Independent Contractor Law: The State of Mississippi recognizes the distinction between employees and independent contractors. Employers need to determine the employment status correctly to comply with state regulations and laws. 2. IRS Guidelines: While not specific to Mississippi, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides guidelines to help employers determine the classification of workers as independent contractors or employees. Compliance with these guidelines is essential for consistent classification across all states, including Mississippi. Factors for Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status: 1. Control: The level of control an employer exercises over the worker's tasks, including the instruction given, supervision, and evaluation. 2. Financial aspects: Consideration of whether the worker has a significant investment in their tools, provides their own materials, and bears the risk of profit or loss. 3. Nature of the relationship: Evaluating the permanency of the relationship, contractual agreements, and benefits associated with the engagement. 4. Skill and expertise: The worker's specialized skills, training, or knowledge required for performing the job. 5. Intent of the parties: The mutual understanding and intent of both the employer and the worker regarding their relationship. Benefits of Being Classified as a Self-Employed Contractor in Mississippi: 1. Flexibility: Independent contractors have the freedom to choose the projects they undertake, set their working hours, and work with multiple clients simultaneously. 2. Potential tax advantages: Contractors are eligible for various tax deductions, such as business expenses, office space, equipment, travel, and healthcare costs. 3. Diverse income sources: Self-employed contractors can diversify their income streams by working for multiple clients or pursuing different projects simultaneously. 4. Autonomy: Contractors have greater control over their work methods, providing an opportunity for creative expression and professional growth. Consequences of Misclassification: Misclassifying workers can lead to severe consequences, including: 1. Legal and financial penalties: Employers may face fines, back-payment of benefits, unpaid taxes, and litigation costs if they misclassify employees as independent contractors. 2. Loss of benefits: Misclassified workers may miss out on essential benefits, such as workers' compensation, unemployment insurance, healthcare coverage, and retirement plans. 3. Audit risk: Misclassification can trigger audits from governmental agencies like the Mississippi Department of Revenue or the IRS, leading to additional scrutiny and potential penalties. Conclusion: Determining self-employed contractor status in Mississippi requires careful consideration of various factors outlined by Mississippi Independent Contractor Law and the IRS guidelines. Accurate classification ensures compliance, prevents legal issues, and provides workers with the rights and benefits they are entitled to. Employers and individuals should understand the implications, seek legal advice if necessary, and maintain proper documentation to navigate the self-employed contractor landscape effectively.
Mississippi Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status
Description
How to fill out Mississippi Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status?
If you need to complete, acquire, or print out authorized file themes, use US Legal Forms, the largest selection of authorized varieties, that can be found on the Internet. Use the site`s basic and handy research to get the documents you will need. Numerous themes for business and individual uses are categorized by classes and claims, or key phrases. Use US Legal Forms to get the Mississippi Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status with a few clicks.
If you are presently a US Legal Forms client, log in for your account and click on the Acquire switch to obtain the Mississippi Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status. You can even access varieties you previously saved in the My Forms tab of your account.
If you use US Legal Forms the very first time, follow the instructions below:
- Step 1. Make sure you have selected the shape for the proper town/nation.
- Step 2. Utilize the Preview solution to look over the form`s information. Do not overlook to learn the explanation.
- Step 3. If you are unhappy with the form, make use of the Research field near the top of the display screen to locate other types of your authorized form template.
- Step 4. Once you have discovered the shape you will need, click the Acquire now switch. Pick the pricing plan you prefer and include your credentials to sign up on an account.
- Step 5. Method the deal. You can use your Мisa or Ьastercard or PayPal account to complete the deal.
- Step 6. Choose the structure of your authorized form and acquire it on your own device.
- Step 7. Comprehensive, edit and print out or indicator the Mississippi Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status.
Every single authorized file template you acquire is the one you have permanently. You possess acces to every form you saved with your acccount. Go through the My Forms section and decide on a form to print out or acquire once more.
Be competitive and acquire, and print out the Mississippi Determining Self-Employed Contractor Status with US Legal Forms. There are thousands of expert and status-specific varieties you can utilize for your personal business or individual requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
The general rule is that an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done. If you are an independent contractor, then you are self-employed.
Self contracting means you are the one overseeing the project. You are in charge of everything including budgeting, getting permits, hiring the workers, getting inspections, and keeping everything organized and clean.
Simply put, being an independent contractor is one way to be self-employed. Being self-employed means that you earn money but don't work as an employee for someone else.
Becoming an independent contractor is one of the many ways to be classified as self-employed. By definition, an independent contractor provides work or services on a contractual basis, whereas, self-employment is simply the act of earning money without operating within an employee-employer relationship.
The IRS says that someone is self-employed if they meet one of these conditions: Someone who carries on a trade or business as a sole proprietor or independent contractor, A member of a partnership that carries on a trade or business, or. Someone who is otherwise in business for themselves, including part-time business
Four ways to verify your income as an independent contractorIncome-verification letter. The most reliable method for proving earnings for independent contractors is a letter from a current or former employer describing your working arrangement.Contracts and agreements.Invoices.Bank statements and Pay stubs.
Independent contractors are self-employed workers who provide services for an organisation under a contract for services. Independent contractors are not employees and are typically highly skilled, providing their clients with specialist skills or additional capacity on an as needed basis.
Simply put, being an independent contractor is one way to be self-employed. Being self-employed means that you earn money but don't work as an employee for someone else.
Self-employed people are those who own their own businesses and work for themselves. According to the IRS, you are self-employed if you act as a sole proprietor or independent contractor, or if you own an unincorporated business.