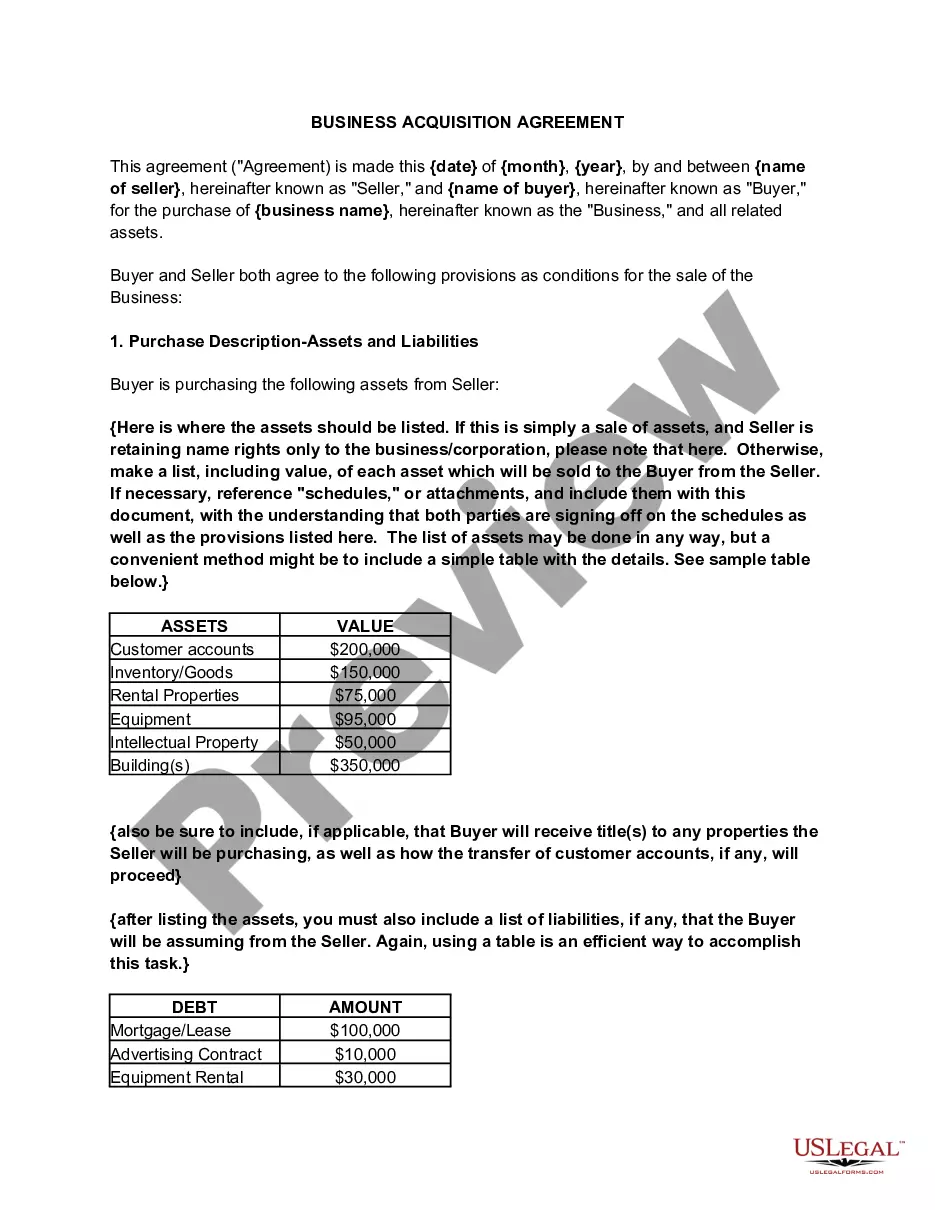
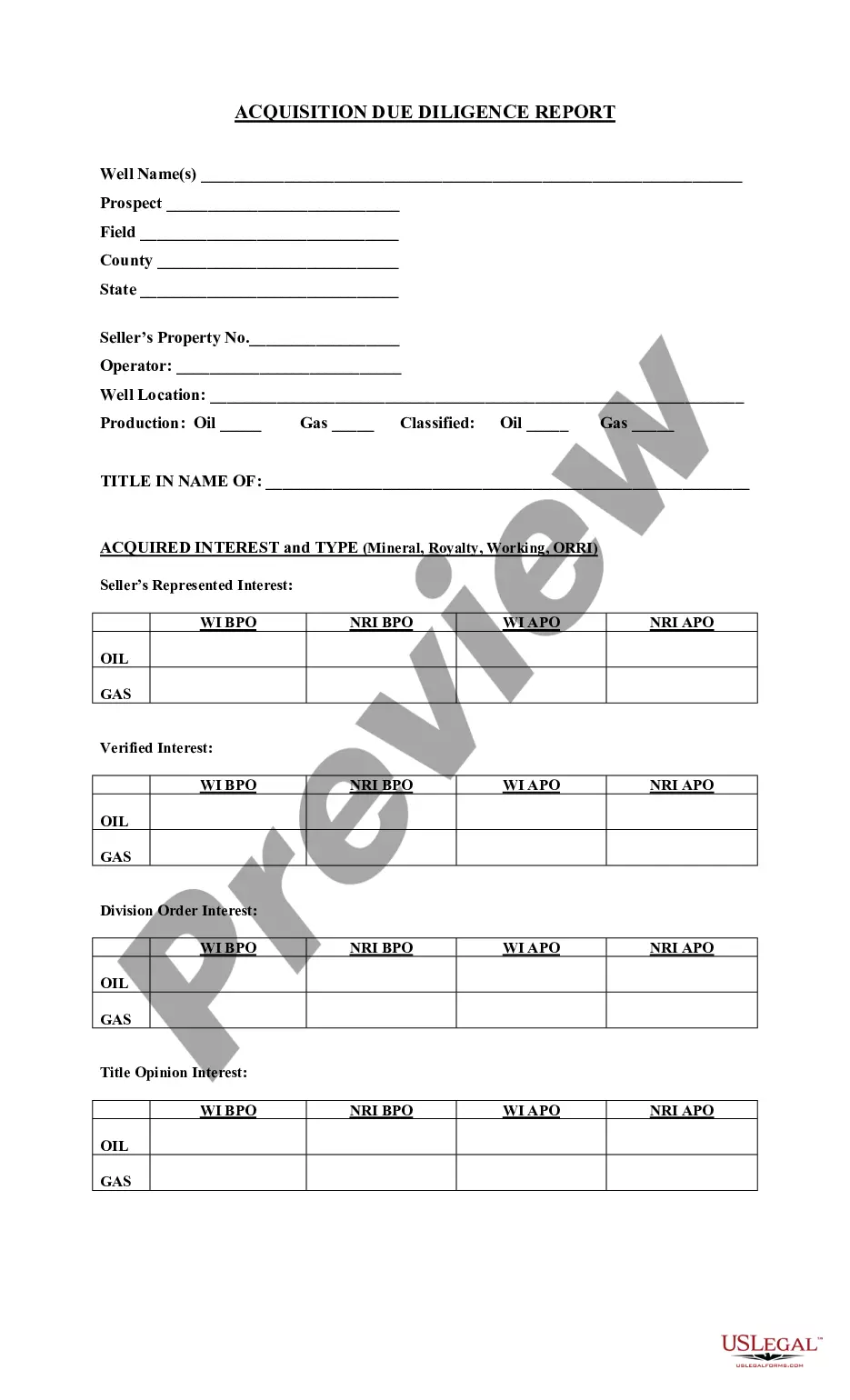
Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties, this form is is a outline of the acquisition representing the sellers and buyers in the sale of producing properties in the dealing with oil, gas or minerals.
Mississippi Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties
Description
How to fill out Outline Of The Acquisition Process Representing Sellers And Buyers In The Sale Of Producing Properties?
US Legal Forms - one of several most significant libraries of legitimate varieties in the USA - gives an array of legitimate papers layouts you may down load or print. Utilizing the website, you can find 1000s of varieties for company and person purposes, categorized by classes, suggests, or keywords.You can get the newest models of varieties just like the Mississippi Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties in seconds.
If you currently have a registration, log in and down load Mississippi Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties through the US Legal Forms catalogue. The Obtain button can look on every type you see. You have accessibility to all earlier saved varieties inside the My Forms tab of your accounts.
If you wish to use US Legal Forms the first time, listed below are easy instructions to help you get began:
- Make sure you have picked the right type for your personal city/area. Click the Review button to examine the form`s content material. Read the type information to ensure that you have selected the correct type.
- When the type does not satisfy your requirements, take advantage of the Research area near the top of the screen to get the one which does.
- If you are content with the shape, affirm your option by clicking on the Purchase now button. Then, choose the rates plan you want and supply your qualifications to register on an accounts.
- Approach the purchase. Make use of Visa or Mastercard or PayPal accounts to finish the purchase.
- Select the format and down load the shape on your own gadget.
- Make modifications. Complete, edit and print and indicator the saved Mississippi Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties.
Every single template you included in your money lacks an expiration day which is your own property for a long time. So, if you wish to down load or print an additional duplicate, just go to the My Forms portion and click on on the type you want.
Obtain access to the Mississippi Outline of the Acquisition Process Representing Sellers and Buyers in the Sale of Producing Properties with US Legal Forms, the most comprehensive catalogue of legitimate papers layouts. Use 1000s of skilled and state-particular layouts that satisfy your small business or person needs and requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
Your Cash Out will generally be deposited into your Bank Account within 1-2 business days after you request a Cash Out. Depending on your bank, you may be able to request a Cash Out with EarnIn's "Lightning Speed" service, which enables Cash Out funds to be deposited to your Bank Account much more quickly. Cash Out Terms | EarnIn earnin.com ? cash-out ? terms-of-service earnin.com ? cash-out ? terms-of-service
"Mississippi Real Estate Commission," or "Commission" means the agency of the State of Mississippi created by §73-35-1, et seq. To regulate the licensing of real estate brokers and salespersons and by §73-35-35 directed to regulate the sale of timeshare and condominium properties. MISSISSIPPI REAL ESTATE COMMISSION RULES AND ... Mississippi Secretary of State (.gov) ? ACProposed Mississippi Secretary of State (.gov) ? ACProposed PDF
§ 31-7-13. All agencies and governing authorities shall purchase their commodities and printing; contract for garbage collection or disposal; contract for solid waste collection or disposal: contract for sewage collection or disposal; contract for public construction; and contract for rentals as herein provided. Purchase Law Update - Mississippi Office of the State Auditor - | MS.GOV ms.gov ? downloads ? purchase_law_up... ms.gov ? downloads ? purchase_law_up...
Two to three percent Earnest Money The amount that is deposited is negotiable between the buyer and the seller. It is common for buyers to deposit two to three percent of the offer price. The amount of earnest money intended to be deposited is written in the offer. Real Estate Trust Accounts in Mississippi | Study.com study.com ? academy ? lesson ? real-estate-trust-a... study.com ? academy ? lesson ? real-estate-trust-a...
Earnest money deposits are usually 1% of the offer price, but amounts can vary from as low as $500 to as high as $5,000 ? depending on the house you want to buyer. Be prepared to have that earnest money check cashed within two days of your offer being accepted. Down Payment vs. Earnest Money | North Alabama Real Estate rebeccalowrey.com ? blog ? down-payment... rebeccalowrey.com ? blog ? down-payment...
Between 1% and 3% In most real estate markets, the average good faith deposit is between 1% and 3% of the property's purchase price. It can be as high as 10% for highly competitive homes with multiple interested buyers. Some sellers prefer to set fixed amounts to help filter out buyers that aren't serious. Earnest Money: What It Is & How Much Should You Pay | Chase chase.com ? understanding-earnest-money chase.com ? understanding-earnest-money
YES. Key components of property management (managing, renting and leasing) are considered real estate brokerage services under existing Mississippi real estate licensing laws. Mississippi Property Management Laws allpropertymanagement.com ? resources allpropertymanagement.com ? resources
How much earnest money to put down. A typical earnest money deposit is 1% to 3% of the purchase price. For new construction, the seller might ask for 10%. So, if you're looking to purchase a $250,000 home, you can expect to put down anywhere from $2,500 to $25,000 in earnest money. Earnest Money: How It Works and How Much You'll Need - Credible credible.com ? blog ? mortgages ? earnest-... credible.com ? blog ? mortgages ? earnest-...