Montana Property or Boundary Line Agreement
Description
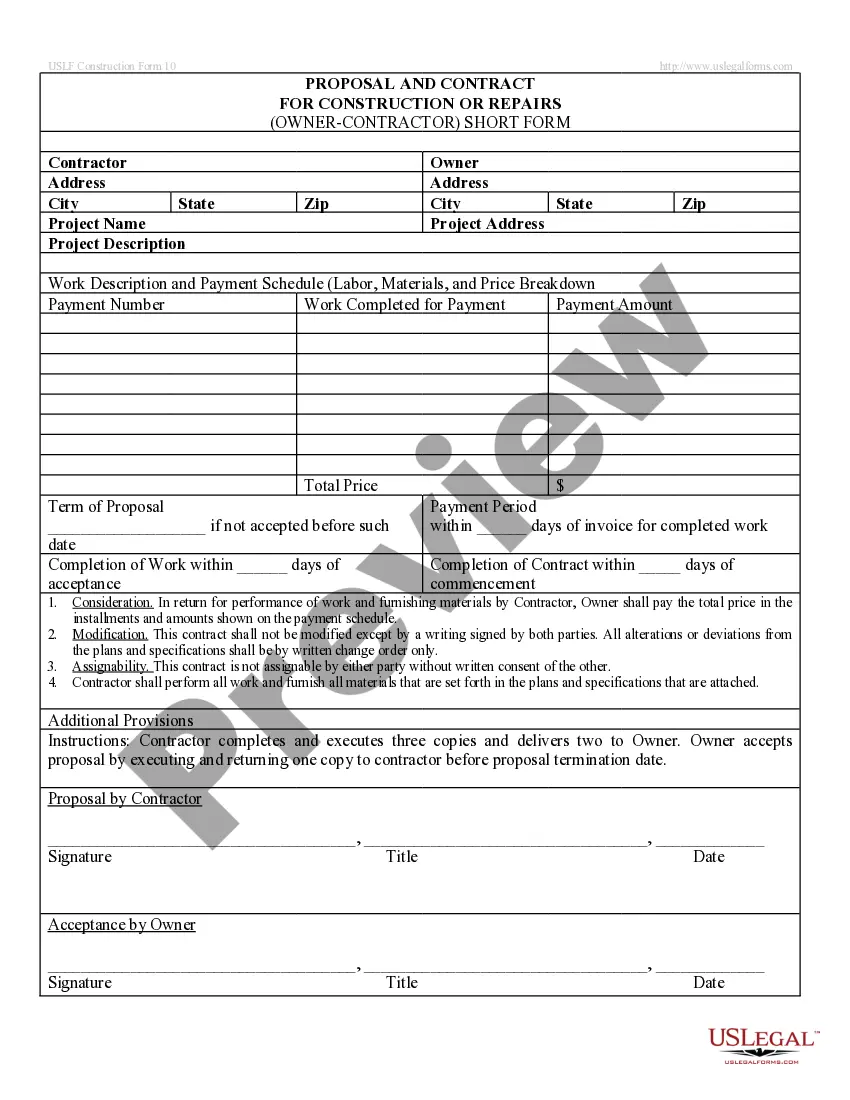
How to fill out Property Or Boundary Line Agreement?
If you wish to sum, obtain, or create verified document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the largest collection of legal forms, available online.
Leverage the site’s user-friendly search to locate the files you require. Various templates for commercial and personal purposes are categorized by types and states, or keywords.
Utilize US Legal Forms to find the Montana Property or Boundary Line Agreement within a few clicks.
Every legal document template you purchase belongs to you for a long time. You can access every form you downloaded in your account. Visit the My documents section and choose a form to print or download again.
Be proactive and download, and print the Montana Property or Boundary Line Agreement with US Legal Forms. There are numerous professional and state-specific forms you can utilize for your business or personal needs.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms user, Log In to your account and click the Download button to obtain the Montana Property or Boundary Line Agreement.
- You can also access forms you previously downloaded in the My documents section of your account.
- If using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow the instructions below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have selected the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Use the Preview option to review the contents of the form. Don’t forget to check the details.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, use the Search field at the top of the screen to find other versions of the legal form format.
- Step 4. Once you have found the form you need, click the Download now button. Choose the payment plan you prefer and enter your details to register for an account.
- Step 5. Proceed with the payment. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
- Step 6. Choose the format of the legal form and download it to your device.
- Step 7. Complete, modify, and print or sign the Montana Property or Boundary Line Agreement.
Form popularity
FAQ
Surveyors use a variety of tools to identify property boundaries, including GPS devices, total stations, and measuring tapes. These tools enable them to take precise measurements and establish the true limits of your property. In addition to this, they reference plat maps and legal descriptions to ensure accuracy. This thorough process is essential for creating a valid boundary line agreement for your Montana property.
Yes, you can use your phone to find property lines with the help of reliable mapping apps that include boundary features. Many apps provide access to satellite imagery and property line overlays. However, keep in mind that while these tools are useful, they may not always offer the precision of a professional surveyor. For accurate boundary line agreements in Montana, it is advisable to consult with an expert.
You can look up property boundaries by accessing your local county’s property records or land office websites. These resources often provide maps, surveys, and ownership details for all properties in your area. Additionally, using platforms like US Legal Forms can simplify the process of obtaining the necessary boundary line agreement documentation for your Montana property.
Surveying property boundaries involves several steps, beginning with researching legal documents concerning your property. The surveyor then uses tools like GPS and theodolites to measure and establish clear property lines. After completing the measurements, they compile a detailed report that outlines the findings. This process is crucial to creating a precise boundary line agreement for your Montana property.
To conduct a boundary survey, a surveyor identifies and marks the exact boundaries of your property using specialized tools. They start by researching public records and any existing property descriptions. After that, they will visit the site to measure distances and angles accurately. This information helps ensure that you have a clear understanding of your Montana property or boundary line agreement.
A cease and desist letter is a formal document that instructs an individual or entity to stop an action that infringes upon your property rights, like encroachment. This letter serves as an official warning and can play a critical role in resolving property disputes before they escalate. Understanding how to issue such a letter can be crucial in maintaining clarity in your Montana Property or Boundary Line Agreement.
Generally, homeowners insurance does not cover legal disputes arising from property line disagreements. Such disputes often require legal intervention and solutions that insurance policies typically exclude. Establishing a clear Montana Property or Boundary Line Agreement upfront can help prevent these costly disputes from arising.
Homeowners insurance typically does not cover easements, as these are rights granted to others for specific uses of your property. If issues arise concerning easements and property use, it’s wise to consult your policy details. Understanding the implications of easements on your Montana Property and any associated agreements can protect your interests.
To resolve a property line dispute with your neighbor, first review your property surveys and any existing agreements. Open communication can often lead to an amicable resolution, so consider discussing the issue directly with them. If necessary, formalizing your understanding with a Montana Property or Boundary Line Agreement can provide clarity and prevent future disagreements.
Yes, property deeds are considered public records in Montana and can be accessed through county clerk and recorder offices. This accessibility allows you to verify property ownership and related legal agreements. Ensuring you have accurate documentation, especially regarding your Montana Property or Boundary Line Agreement, can prevent disputes and clarify ownership.