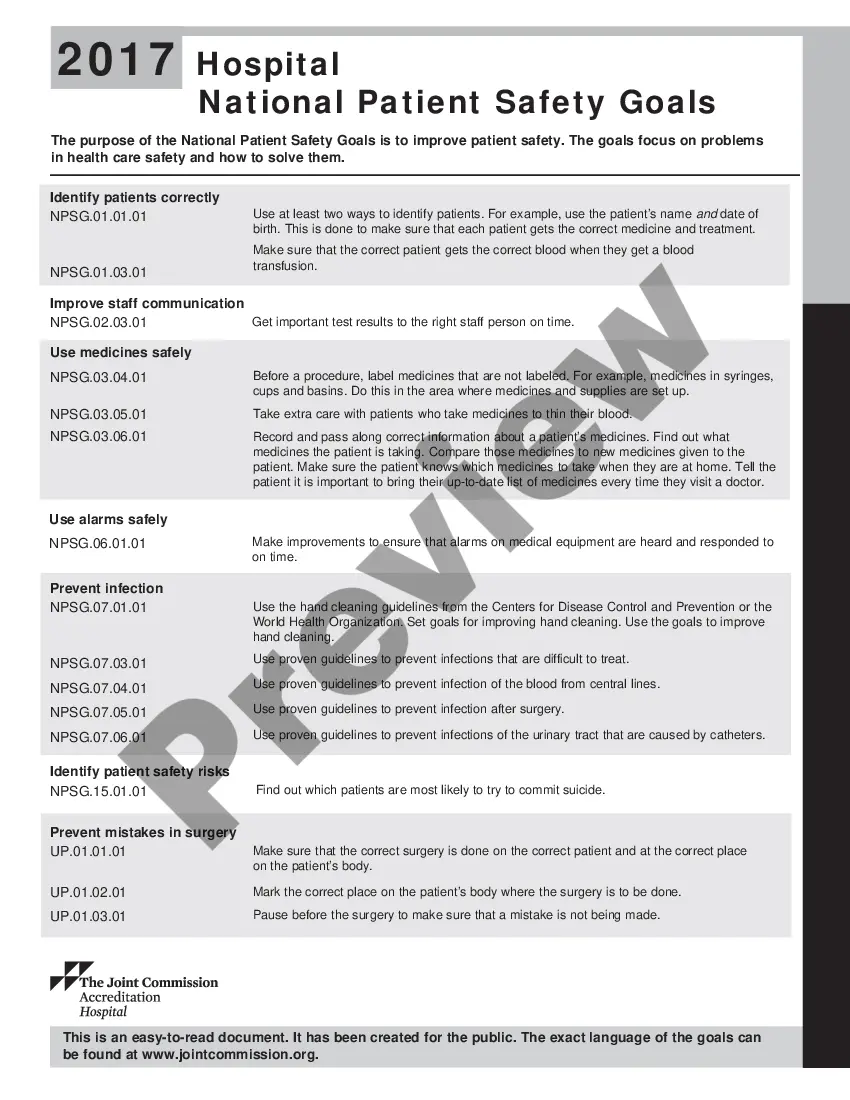
Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals are a set of guidelines outlined by the state of Montana to ensure the safety and well-being of patients in hospitals. These goals aim to address common patient safety issues and promote the delivery of high-quality healthcare services. By adhering to these goals, hospitals in Montana can enhance patient outcomes and minimize risks. One of the main objectives of Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals is to prevent and reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections (His). Hospitals are required to implement best practices and protocols to prevent infections such as central line-associated bloodstream infections (Class) and surgical site infections (Skis). This includes proper hand hygiene, sterilization of equipment, and appropriate use of antibiotics. Another important goal is to improve medication safety. Hospitals must focus on preventing medication errors, such as administering the wrong medication or incorrect dosages. They should implement processes to ensure accurate prescribing, dispensing, and administration of medications. This may involve using computerized physician order entry (CPE) systems, barcode scanning, and medication reconciliation. Fall prevention is another key aspect of Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. Hospitals must take measures to identify patients at risk of falling and implement interventions to minimize falls. This may involve regular patient assessments, providing assistance devices (e.g., grab bars, non-slip mats), educating staff and patients about fall prevention, and closely monitoring high-risk patients. Additionally, the goals emphasize the need for proper hand hygiene compliance. Hospitals are encouraged to educate staff on the importance of hand hygiene, promote regular handwashing or sanitizing, and monitor compliance rates. This helps prevent the transmission of infections and improve overall patient safety. Furthermore, Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals aim to enhance patient identification and prevent errors in patient identification. It is vital for hospitals to implement effective systems to accurately identify patients, such as using two patient identifiers (e.g., name and date of birth) before administering any treatment or medication. This helps prevent miscommunication and ensures that patients receive the correct care. In summary, Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals encompass various aspects of patient safety, including infection prevention, medication safety, fall prevention, hand hygiene compliance, and patient identification. By adhering to these goals, hospitals in Montana can provide optimal care while minimizing the risks and improving patient outcomes.
Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
If you want to full, acquire, or produce lawful papers themes, use US Legal Forms, the largest assortment of lawful types, that can be found on the Internet. Use the site`s easy and practical lookup to discover the papers you need. Different themes for organization and specific uses are categorized by classes and claims, or key phrases. Use US Legal Forms to discover the Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals with a number of clicks.
In case you are currently a US Legal Forms client, log in to the profile and click on the Obtain option to have the Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. You can also entry types you formerly acquired within the My Forms tab of your own profile.
Should you use US Legal Forms the very first time, follow the instructions below:
- Step 1. Be sure you have chosen the form for that right metropolis/region.
- Step 2. Make use of the Preview choice to look through the form`s information. Do not neglect to read the description.
- Step 3. In case you are not satisfied with the type, use the Search discipline at the top of the monitor to find other variations in the lawful type template.
- Step 4. Upon having identified the form you need, select the Acquire now option. Choose the pricing strategy you choose and add your qualifications to sign up to have an profile.
- Step 5. Approach the transaction. You can utilize your bank card or PayPal profile to finish the transaction.
- Step 6. Choose the formatting in the lawful type and acquire it on your system.
- Step 7. Full, revise and produce or signal the Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals.
Each lawful papers template you acquire is your own property eternally. You possess acces to every single type you acquired in your acccount. Select the My Forms portion and choose a type to produce or acquire once again.
Compete and acquire, and produce the Montana Hospital National Patient Safety Goals with US Legal Forms. There are millions of professional and status-particular types you may use for the organization or specific needs.