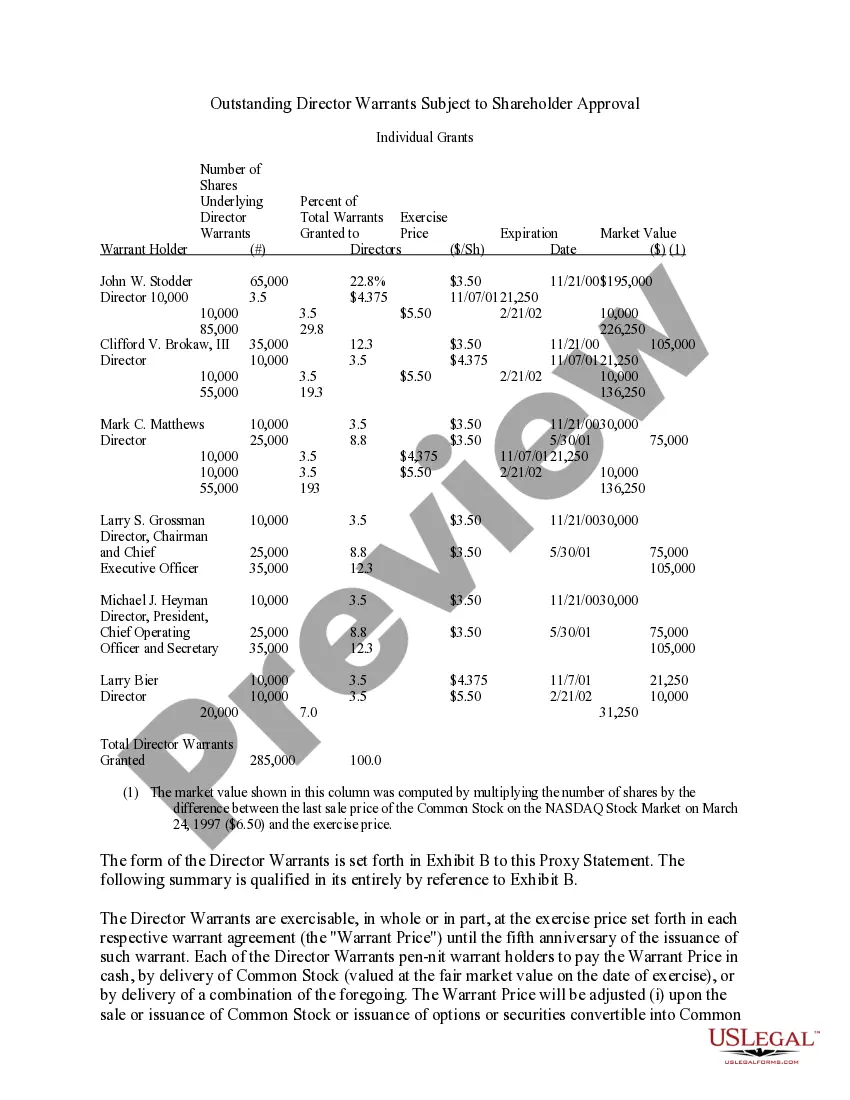
Montana Approval of Director Warrants: Explained in Detail Montana Approval of Director Warrants refers to the process and procedures related to granting authorization for director warrants within the state of Montana. Director warrants are financial instruments allowing directors within a corporation to purchase additional shares at a specified price within a certain time frame. These warrants are often used as an incentive and a form of compensation for directors. In Montana, the approval of director warrants involves several key steps to ensure compliance and fairness. First and foremost, the company's bylaws and articles of incorporation must allow for the issuance of director warrants. These documents outline the rules and regulations concerning the authorization and use of such warrants. The approval process begins with the company's board of directors initiating the decision to grant director warrants. The board must determine the number of warrants to be issued, the strike price (the price at which the director can purchase the shares), and the expiration date or duration of the warrant. Once the board has made these determinations, they must seek approval from the shareholders. Shareholders are typically presented with a detailed proposal outlining the terms of the director warrants, including the number of warrants, the strike price, and the expiry date. Shareholders must then vote to approve or reject the proposal during a designated meeting or through written consent. Montana's corporate laws require a majority vote from the shareholders to approve director warrants. However, different types of director warrants may have varying requirements. For example, if the warrants are classified as nonqualified stock options, their approval might necessitate compliance with additional provisions outlined by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Tax-qualified director warrants, on the other hand, may require adherence to specific criteria set forth by Montana tax authorities, ensuring compliance with state tax regulations. Furthermore, Montana has its own regulations regarding the disclosure and reporting requirements surrounding the approval of director warrants. Companies must provide comprehensive details of the approved warrants in their annual reports, including information on the number of warrants granted, names of the directors receiving them, strike prices, and expiration dates. In summary, Montana Approval of Director Warrants involves the process of obtaining authorization from the board of directors and shareholders to issue director warrants. This process must comply with relevant state laws, the corporation's governing documents, and potentially additional regulations imposed by external bodies such as the IRS or state tax authorities. By adhering to these regulations, companies maintain transparency and ensure compliance, ultimately benefiting both directors and shareholders.
Montana Approval of director warrants
Description
How to fill out Montana Approval Of Director Warrants?
US Legal Forms - one of the most significant libraries of legitimate kinds in the United States - gives a wide array of legitimate papers templates you can obtain or print. While using site, you can find 1000s of kinds for company and person uses, categorized by groups, says, or search phrases.You can find the most up-to-date variations of kinds like the Montana Approval of director warrants within minutes.
If you currently have a registration, log in and obtain Montana Approval of director warrants from your US Legal Forms catalogue. The Acquire option will appear on each develop you see. You gain access to all previously downloaded kinds inside the My Forms tab of your own profile.
If you wish to use US Legal Forms the very first time, listed below are straightforward directions to help you get started off:
- Be sure to have picked out the right develop to your town/region. Click the Preview option to analyze the form`s articles. Browse the develop outline to ensure that you have selected the proper develop.
- In the event the develop doesn`t suit your requirements, make use of the Search discipline at the top of the display screen to get the one that does.
- Should you be happy with the shape, affirm your selection by clicking on the Buy now option. Then, pick the pricing prepare you prefer and offer your credentials to sign up on an profile.
- Method the financial transaction. Make use of your Visa or Mastercard or PayPal profile to accomplish the financial transaction.
- Pick the structure and obtain the shape on your device.
- Make adjustments. Fill out, revise and print and indicator the downloaded Montana Approval of director warrants.
Every single format you included with your money lacks an expiry day which is your own forever. So, if you want to obtain or print an additional version, just check out the My Forms portion and then click on the develop you need.
Obtain access to the Montana Approval of director warrants with US Legal Forms, by far the most comprehensive catalogue of legitimate papers templates. Use 1000s of expert and condition-specific templates that meet your small business or person requires and requirements.