Montana Writ of Execution
Description
How to fill out Writ Of Execution?
US Legal Forms - one of several most significant libraries of legal varieties in the USA - provides a variety of legal papers web templates you can down load or print. Making use of the website, you will get thousands of varieties for organization and individual uses, categorized by categories, states, or keywords.You will discover the most recent versions of varieties just like the Montana Writ of Execution within minutes.
If you already have a monthly subscription, log in and down load Montana Writ of Execution from your US Legal Forms local library. The Down load button can look on every kind you view. You have accessibility to all earlier downloaded varieties within the My Forms tab of your bank account.
If you would like use US Legal Forms for the first time, here are straightforward recommendations to help you get started out:
- Be sure you have picked out the right kind for the area/county. Go through the Review button to check the form`s articles. Browse the kind description to actually have chosen the right kind.
- When the kind does not satisfy your requirements, take advantage of the Look for industry towards the top of the display screen to obtain the one who does.
- In case you are satisfied with the shape, confirm your option by visiting the Get now button. Then, pick the prices plan you like and supply your qualifications to sign up on an bank account.
- Method the purchase. Utilize your credit card or PayPal bank account to accomplish the purchase.
- Pick the structure and down load the shape on your own gadget.
- Make adjustments. Fill out, modify and print and indicator the downloaded Montana Writ of Execution.
Every single format you put into your account lacks an expiry date and is also yours for a long time. So, if you want to down load or print another version, just check out the My Forms portion and then click around the kind you will need.
Gain access to the Montana Writ of Execution with US Legal Forms, by far the most extensive local library of legal papers web templates. Use thousands of expert and status-distinct web templates that fulfill your small business or individual needs and requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
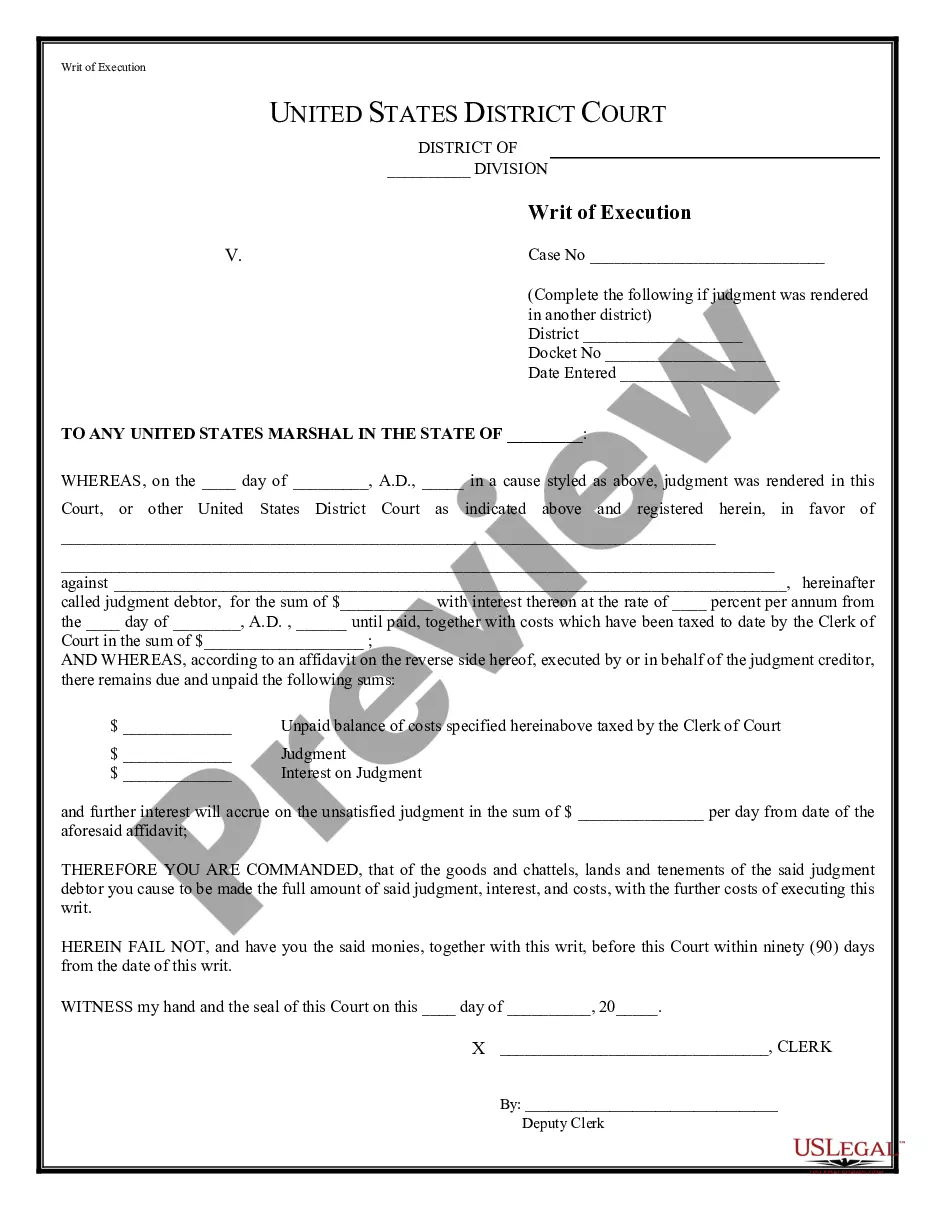
NOW, you, the Sheriff, Constable, or Levying Officer, are hereby required to make this sum due on the judgment, with interest, and costs, to satisfy the judgment out of the personal property of the Defendant not exempt from execution on the day on which the judgment was docketed in the county, or at any time hereafter, ...
Be sure to tell the Judge all of the important and relevant facts and to make any argument that helps to support your position. You should tell the Judge what law or laws your Response is based on.
NOW, you, the Sheriff, Constable, or Levying Officer, are hereby required to make this sum due on the judgment, with interest, and costs, to satisfy the judgment out of the personal property of the Defendant not exempt from execution on the day on which the judgment was docketed in the county, or at any time hereafter, ...
The judgment may be executed against a savings or checking account, personal property (not a necessity of life), wages, vehicles, or any other assets of the judgment debtor. Praecipe - The winning party may ask the sheriff or a process server to serve papers on the other party.
Montana Civil Statutes of Limitations Montana's time limits for filing a civil action generally range from two to three years. However, actions for collection on the value of a court judgment carry a ten-year limit.
(i) Responses to motions to dismiss, for judgment on the pleadings, or for summary judgment must be filed within 21 days after the motion was filed. (ii) Responses to all other motions must be filed within 14 days after the motion was filed.
The appellant may file a brief in reply to the brief of the appellee, and if the appellee has cross-appealed, the appellee may file a brief in reply to the response of the appellant to the issues presented by the cross-appeal. The reply brief must be confined to new matter raised in the brief of the appellee.
The appellant may serve and file a reply brief within 14 days after service of the brief of the appellee.
Writ of Execution: After being awarded a Judgment, you may file a written request for a Writ of Execution. A Writ can be used to garnish wages or execute against a checking or savings account. A Writ can only be served by the Sheriff's Office or a licensed levying officer.
There are three things you can try to do to deal with a judgement if you can't pay: Try to negotiate a voluntary payment plan with the creditor. File to have the judgment vacated. File bankruptcy to discharge the debt.