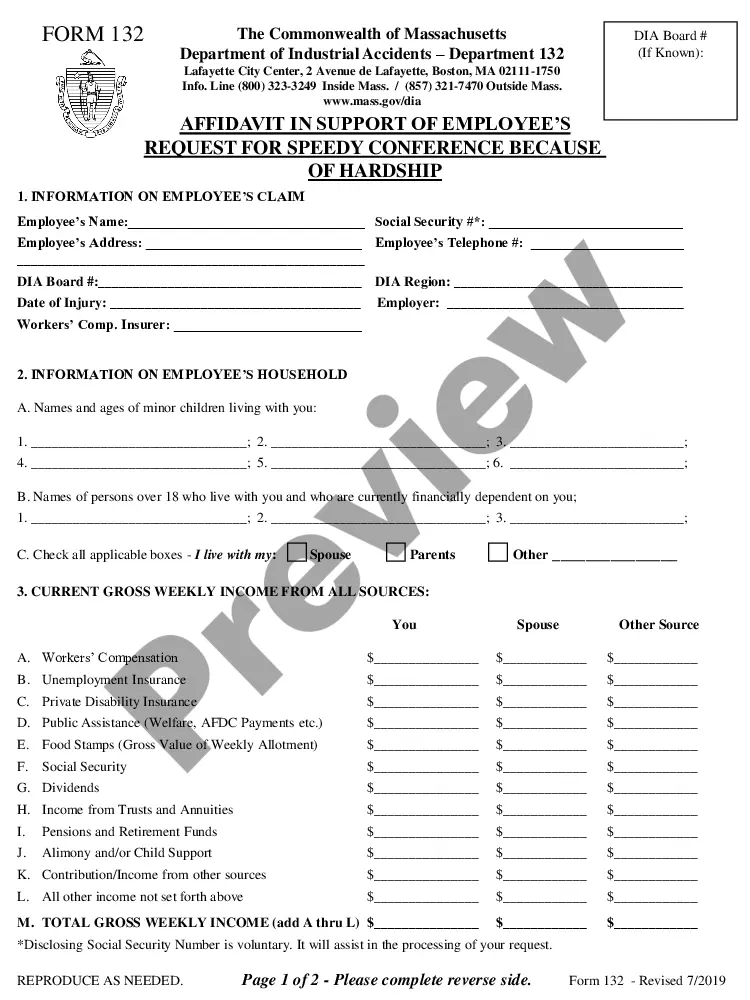
This office lease form contains a contractual right in the transfer clause for the landlord to withhold its consent for specific situations not usually prohibited under the reasonableness standard. The tenant shall neither assign the lease nor sublet all or a portion of the demised premises without the landlord's prior written consent. This form outlines the specific situation where the landlord may withhold such consent.
Keywords: Montana Transfer Clause, contractual right, landlord, withhold consent, types Title: Understanding the Montana Transfer Clause: A Powerful Tool for Landlords Introduction: The Montana Transfer Clause, containing a contractual right for the landlord to withhold consent, is a crucial provision in lease agreements. This clause empowers landlords in Montana to regulate and control the transfer of a tenant's leasehold interest. By understanding the implications of this clause, both landlords and tenants can navigate lease agreements more effectively. In this article, we delve into the details of the Montana Transfer Clause, its significance, and various types that exist. 1. Definition of the Montana Transfer Clause: The Montana Transfer Clause, also known as a transfer consent provision, outlines a landlord's right to withhold consent when a tenant seeks to transfer their leasehold interest. It provides a process through which landlords can maintain control over who assumes responsibility for the lease agreement. 2. The Significance of the Montana Transfer Clause: By incorporating a Transfer Clause in their lease agreement, landlords ensure that they retain control over the quality and suitability of the new tenant taking over the lease. This clause safeguards the landlord's interests, protects the property, and helps maintain a harmonious community within a commercial or residential space. 3. Types of Montana Transfer Clauses: a. Absolute Consent Clause: Under an Absolute Consent Clause, the landlord has the unrestricted ability to withhold consent without providing any valid reason. These clauses grant the landlord significant discretionary power but should be used judiciously and in adherence to local laws. b. Reasonable Consent Clause: Alternatively, in a Reasonable Consent Clause, landlords must provide reasonable justification for withholding consent. This type of clause provides more protection to the tenant, preventing landlords from unreasonably denying a transfer request. c. Permitted Transfers Clause: A Permitted Transfers Clause outlines specific circumstances or conditions under which consent will be granted automatically. It allows the tenant to transfer their leasehold interest without seeking explicit permission from the landlord, thereby expediting the process. 4. Compliance with Montana Law: While Montana allows landlords to include a Transfer Clause in lease agreements, it is vital to ensure compliance with state-specific laws and regulations. Landlords should familiarize themselves with applicable statutes to avoid potential legal disputes. Conclusion: The Montana Transfer Clause with a contractual right for the landlord to withhold consent is a crucial provision within lease agreements. By understanding its implications and the different types available, both landlords and tenants can shape agreements that protect their interests. Landlords should exercise their rights judiciously, considering both the welfare of the property and the reasonable requests of tenants.
Keywords: Montana Transfer Clause, contractual right, landlord, withhold consent, types Title: Understanding the Montana Transfer Clause: A Powerful Tool for Landlords Introduction: The Montana Transfer Clause, containing a contractual right for the landlord to withhold consent, is a crucial provision in lease agreements. This clause empowers landlords in Montana to regulate and control the transfer of a tenant's leasehold interest. By understanding the implications of this clause, both landlords and tenants can navigate lease agreements more effectively. In this article, we delve into the details of the Montana Transfer Clause, its significance, and various types that exist. 1. Definition of the Montana Transfer Clause: The Montana Transfer Clause, also known as a transfer consent provision, outlines a landlord's right to withhold consent when a tenant seeks to transfer their leasehold interest. It provides a process through which landlords can maintain control over who assumes responsibility for the lease agreement. 2. The Significance of the Montana Transfer Clause: By incorporating a Transfer Clause in their lease agreement, landlords ensure that they retain control over the quality and suitability of the new tenant taking over the lease. This clause safeguards the landlord's interests, protects the property, and helps maintain a harmonious community within a commercial or residential space. 3. Types of Montana Transfer Clauses: a. Absolute Consent Clause: Under an Absolute Consent Clause, the landlord has the unrestricted ability to withhold consent without providing any valid reason. These clauses grant the landlord significant discretionary power but should be used judiciously and in adherence to local laws. b. Reasonable Consent Clause: Alternatively, in a Reasonable Consent Clause, landlords must provide reasonable justification for withholding consent. This type of clause provides more protection to the tenant, preventing landlords from unreasonably denying a transfer request. c. Permitted Transfers Clause: A Permitted Transfers Clause outlines specific circumstances or conditions under which consent will be granted automatically. It allows the tenant to transfer their leasehold interest without seeking explicit permission from the landlord, thereby expediting the process. 4. Compliance with Montana Law: While Montana allows landlords to include a Transfer Clause in lease agreements, it is vital to ensure compliance with state-specific laws and regulations. Landlords should familiarize themselves with applicable statutes to avoid potential legal disputes. Conclusion: The Montana Transfer Clause with a contractual right for the landlord to withhold consent is a crucial provision within lease agreements. By understanding its implications and the different types available, both landlords and tenants can shape agreements that protect their interests. Landlords should exercise their rights judiciously, considering both the welfare of the property and the reasonable requests of tenants.