North Carolina Hospital National Patient Safety Goals
Description
How to fill out Hospital National Patient Safety Goals?
Selecting the appropriate legal document format can be challenging.
Indeed, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how can you acquire the specific legal document you require.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website.
If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are basic instructions for you to follow: First, ensure you have chosen the correct type for your area/region. You can preview the form using the Preview button and read the form details to confirm it is suitable for you. If the form does not meet your needs, use the Search field to find the appropriate form. Once you are confident that the form will suffice, click on the Acquire now button to obtain the form. Select the pricing plan you desire and enter the required information. Create your account and complete the order using your PayPal account or credit card. Choose the file format and download the legal document to your device. Complete, modify, print, and sign the acquired North Carolina Hospital National Patient Safety Goals. US Legal Forms is the largest collection of legal documents where you can find various file templates. Use the service to download professionally crafted documents that comply with state regulations.
- The platform provides thousands of templates, such as the North Carolina Hospital National Patient Safety Goals, suitable for both business and personal purposes.
- All forms are reviewed by professionals and comply with state and federal regulations.
- If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click on the Download button to locate the North Carolina Hospital National Patient Safety Goals.
- Use your account to browse the legal documents you have previously purchased.
- Navigate to the My documents section of your account and obtain an additional copy of the file you need.
Form popularity
FAQ
The initiative recommends that care providers make sure that all drugs are labeled clearly. The Hospital National Patient Safety Goals also call for increased caution when treating individuals with different diagnosis. An example of this would be for someone who requires medication to thin their blood.
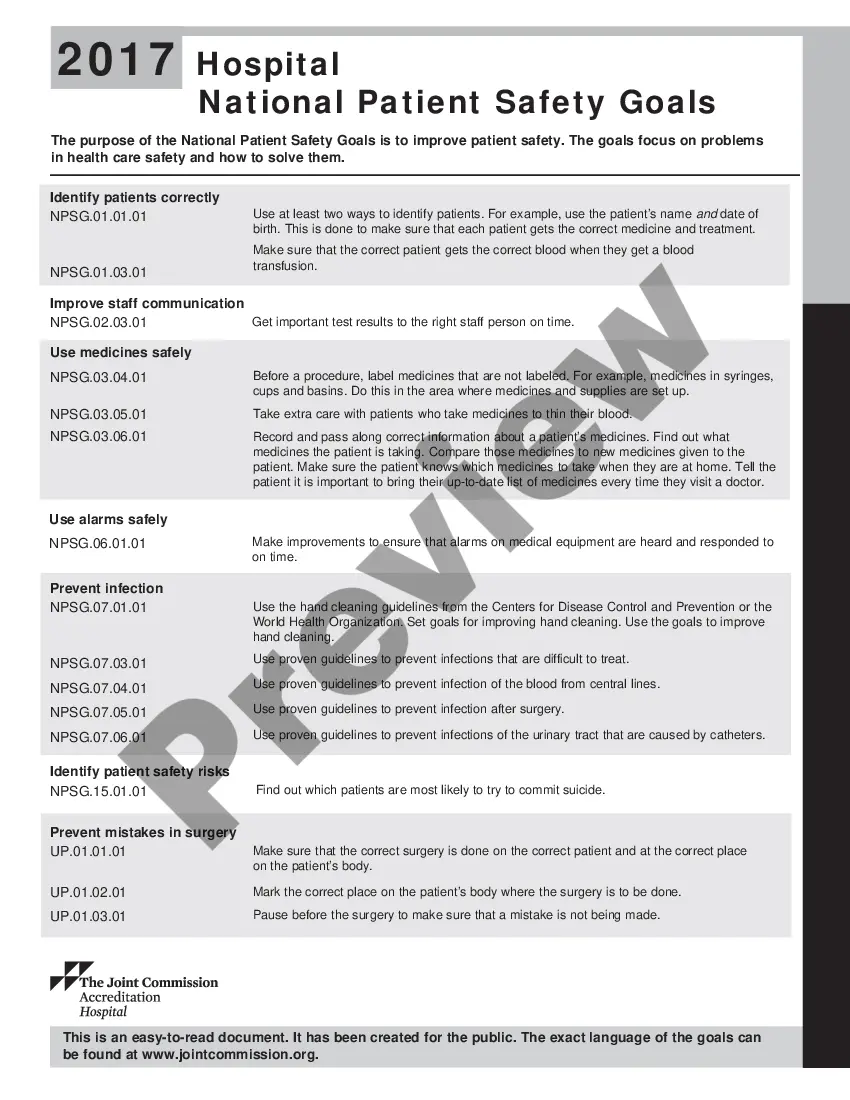
20172021 versionsGoal 1: Identify patients correctly.Goal 2: Improve effective communication.Goal 3: Improve the safety of high-alert medications.Goal 4: Ensure safe surgery.Goal 5: Reduce the risk of health care-associated infections.Goal 6: Reduce the risk of patient harm resulting from falls.
What Are the 7 National Patient Safety Goals for Hospitals in 2021?Identify patients correctly.Improve staff communication.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.Prevent infection.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...
2022 Joint Commission National Patient Safety Goals1 Identify Patients Correctly.2 Improve Staff Communication.3 Use Medicines Safely.4 Use Alarms Safely.5 Prevent Infection.6 Surgery Verification.04-Jan-2022
The idea is, over time, to have all those numbered goals migrate into standards.Goal 1: Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification.Goal 2: Improve Communication.Goal 3: Improve the Safety of Using Medications.Goal 6: Reduce the Harm Associated with Clinical Alarm Systems.More items...
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.Use medicines safely.Use alarms safely.