North Carolina Ratification
Description
How to fill out Ratification?
Are you currently in a position the place you will need files for either enterprise or person functions almost every day time? There are tons of lawful file themes accessible on the Internet, but getting ones you can trust isn`t effortless. US Legal Forms delivers a large number of kind themes, much like the North Carolina Ratification, that happen to be created to fulfill state and federal demands.
When you are presently informed about US Legal Forms website and have an account, basically log in. After that, you are able to download the North Carolina Ratification template.
Unless you provide an accounts and would like to begin to use US Legal Forms, adopt these measures:
- Find the kind you require and ensure it is for that proper area/region.
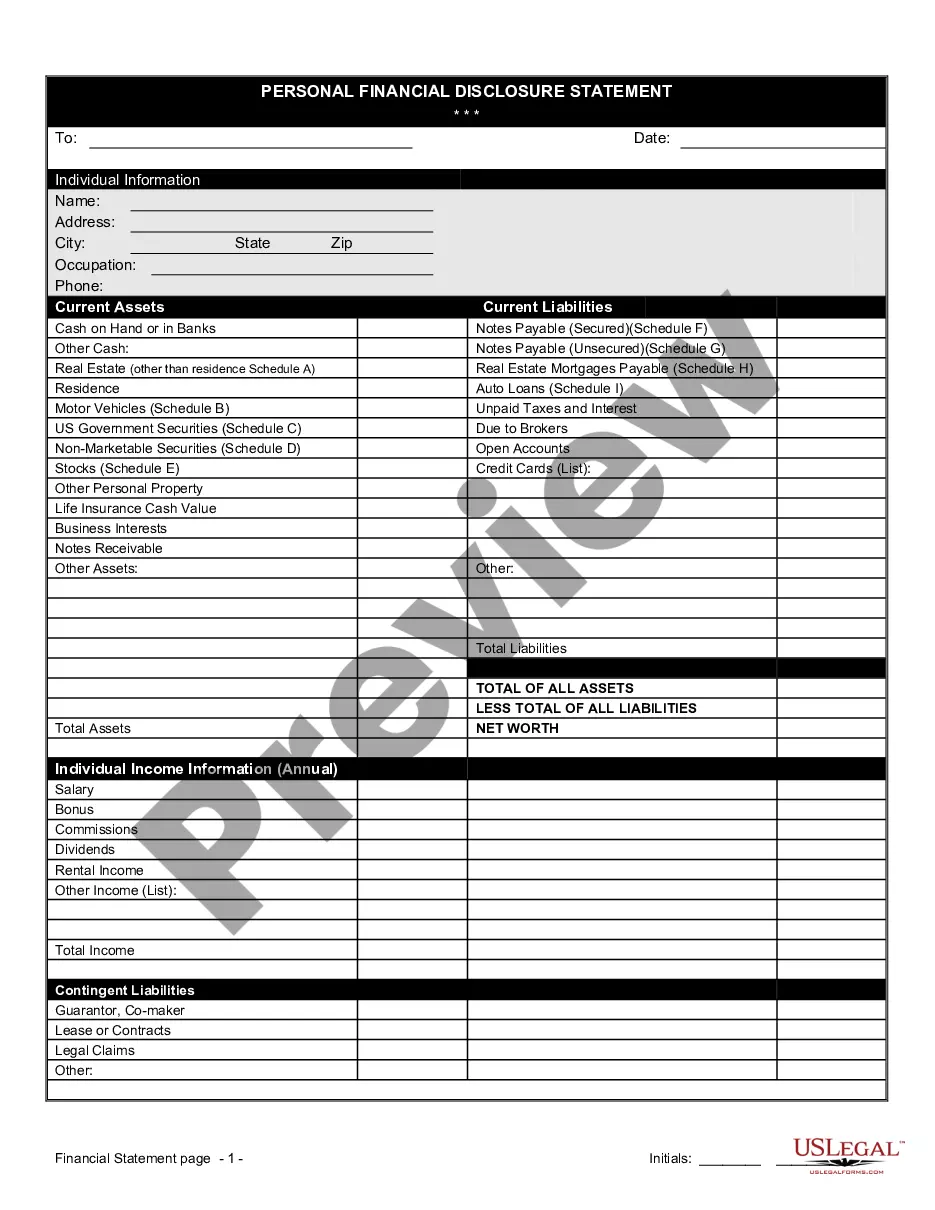
- Use the Preview key to examine the form.
- Read the information to ensure that you have selected the right kind.
- In the event the kind isn`t what you`re searching for, take advantage of the Look for area to find the kind that suits you and demands.
- Once you obtain the proper kind, just click Purchase now.
- Pick the prices program you desire, submit the specified details to make your bank account, and buy the order using your PayPal or credit card.
- Decide on a hassle-free document file format and download your copy.
Get every one of the file themes you have bought in the My Forms menus. You may get a extra copy of North Carolina Ratification at any time, if required. Just click on the needed kind to download or print the file template.
Use US Legal Forms, by far the most comprehensive variety of lawful types, to save lots of some time and steer clear of faults. The support delivers professionally manufactured lawful file themes that can be used for an array of functions. Create an account on US Legal Forms and commence generating your way of life easier.
Form popularity
FAQ
One of the major reasons for North Carolina not ratifying the Constitution was its lack of a Bill of Rights. The delegates, however, proposed a series of amendments to personal liberties and urged the new federal Congress to adopt measures to incorporate a bill of rights into the Constitution.
On June 21, New Hampshire became the ninth state to ratify the new Constitution, making its adoption official. Preceding New Hampshire were Delaware, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Georgia, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Maryland, and South Carolina.
North Carolina: November 21, 1789.
Enrolled Edition The final version of a bill, which has passed both chambers, and is reprinted in preparation for the signatures of the President of the Senate and the Speaker of the House. After these confirmatory signatures, the enrolled bill goes to the Governor.
Some states included proposed amendments as part of their state's ratifications, and the primary reason North Carolina didn't initially ratify the Constitution was because it lacked protections for individual liberties and freedoms.
21, 1789. On this day in 1789, North Carolina ratified the U.S. Constitution to become the 12th state in the Union.
A proposal of a new or revised Constitution or an amendment or amendments to this Constitution may be initiated by the General Assembly, but only if three-fifths of all the members of each house shall adopt an act submitting the proposal to the qualified voters of the State for their ratification or rejection.
On September 25, 1789, the first Congress of the United States adopted 12 amendments to the U.S. Constitution?the Bill of Rights?and sent them to the states for ratification. Ten of these amendments were ratified in 1791. In November 1789, North Carolina became the 12th state to ratify the U.S. Constitution.